- Geography of Germany
-
Coordinates: 51°00′N 10°00′E / 51.00°N 10.00°E
 The location of Germany
The location of Germany
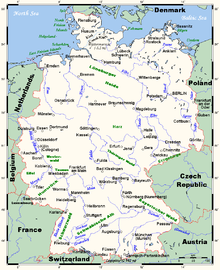
Germany is a country in Central Europe, stretching from the Alps, across the North European Plain to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Germany has the second largest population in Europe (after the European part of Russia) and is seventh largest in area. The territory of Germany covers 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 349,223 km2 (134,836 sq mi) of land and 7,798 km2 (3,011 sq mi) of water. Elevation ranges from the mountains of the Alps (highest point: the Zugspitze at 2,962 metres (9,718 ft) in the south to the shores of the North Sea (Nordsee) in the northwest and the Baltic Sea (Ostsee) in the northeast. Between lie the forested uplands of central Germany and the low-lying lands of northern Germany (lowest point: Neuendorf-Sachsenbande at 3.54 metres (11.6 ft) below sea level), traversed by some of Europe's major rivers such as the Rhine, Danube and Elbe.[1] Because of its central location, Germany shares borders with nine European countries, second only to Russia: Denmark in the north, Poland and the Czech Republic in the east, Austria and Switzerland in the south, France in the southwest and Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands in the west. German Unity Day is celebrated on October 3 every year.
The current, post-1990 territory of the Federal Republic of Germany is 30.3% bigger than the Cold-War era West Germany and 23.8% and 33.9% smaller than the former territories of Weimar and Imperial Germany, respectively.
Contents
Terrain
The northern third of the country lies in the North European Plain, with flat terrain crossed by northward-flowing watercourses (Elbe, Ems, Weser, Oder). Wetlands and marshy conditions are found close to the Dutch border and along the Frisian coast. Sandy Mecklenburg in the northeast has many glacier-formed lakes dating to the last glacial period.
Moving south, central Germany features rough and somewhat patternless hilly and mountainous countryside, some of it formed by ancient volcanic activity. The Rhine valley cuts through the western part of this region. The central uplands continue east and north as far as the Saale and merge with the Ore Mountains on the border with the Czech Republic. Upland regions include the Eifel, Hunsrück but Palatine Forest west of the Rhine, the Taunus hills north of Frankfurt, the Vogelsberg massif, the Rhön, and the Thüringer Wald. South of Berlin, the east-central part of the country is more like the low northern areas, with sandy soil and river wetlands such as the Spreewald region.
Southern Germany's landforms are defined by various linear hill and mountain ranges like the two adjacent ranges of the Swabian and Franconian Alb (reaching approximately from the source of the Danube in the southwest of Baden-Württemberg, south of Stuttgart, across Swabia into Central Franconia and to the valley of the river Main) and the Bavarian Forest along the border between Bavaria and the Czech Republic. The Alps on the southern border are the highest mountains, but relatively little Alpine terrain lies within Germany (in southeastern Swabia and Upper Bavaria) compared to Switzerland and Austria. The Black Forest, on the southwestern border with France, separates the Rhine from the headwaters of the Danube on its eastern slopes.
Climate
See also: Climate of Germany
Germany's climate is temperate and marine, with cool, cloudy, wet winters and summers and in the south occasional warm föhn wind. The greater part of Germany lies in the cool/temperate climatic zone in which humid westerly winds predominate. In the northwest and the north the climate is extremely oceanic and rain falls all the year round. Winters there are relatively mild and summers comparatively cool. In the east the climate shows clear continental features; winters can be very cold for long periods, and summers can become very warm. Here too, long dry periods are often recorded. In the centre and the south there is a transitional climate which may be predominantly oceanic or continental, according to the general weather situation. Winters are mild and summers tend to be cool, though maximum temperatures can exceed 30 °C (86 °F) for several days in a row during heat waves. The warmest regions of Germany can be found in the south-west (see rhine rift, German Wine Route and Palatinate). Here summers can be hot with a high number of days exceeding 30 °C (86 °F). Sometimes minimum temperatures don't drop under 20 °C (68 °F), which is relatively rare in other regions.[2][3]
Land use
Germany covers a total of 357,021 km², of which 4,750 km² is irrigated land and 7,798 km² is covered by water, the largest lakes being Lake Constance (total area of 536 km², with 62% of the shore being German; international borders are not defined on the lake itself), Müritz (117 km²) and Chiemsee (80 km²). The majority of Germany is covered by either arable land (33%) or forestry and woodland (31%). Only 15% is covered by permanent pastures.
Germany has a total of 2,389 km of coastline, and borders totalling 3,621 km (clockwise from north: Denmark 68 km, Poland 456 km, Czech Republic 646 km, Austria 784 km, Switzerland 334 km, France 451 km, Luxembourg 138 km, Belgium 167 km, Netherlands 577 km). The German-Austrian border crosses itself near Jungholz. The border with Belgium includes 5 German exclaves because the Vennbahn railway is on Belgian territory crossing in and out of Germany.Caves
Throughout the Karst rocks many caves were formed especially in the valley of the Hönne. The biggest culture cave of Europe is located in Balve.
Rivers
The main rivers in Germany are:
- the Rhine (Rhein in German) with a German part of 865 km (main tributaries including the Neckar, the Main and the Moselle (Mosel));
- the Elbe with a German part of 727 km (also drains into the North Sea); and,
- the Danube (Donau) with a German part of 687 km.
Further important rivers include the Isar in the southeast, the Main in central Germany, the Neckar in the southwest, and the Weser in the North. See also the list of rivers in Germany.
Maritime claims
- Continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
- Exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi). The exact EEZ is due to conventions with neighbouring states.
- Territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Natural resources
- Iron ore, coal, potash, timber, lignite, uranium, copper, natural gas, salt, nickel, arable land, water
Environment
- Current issues
- Emissions from coal-burning utilities and industries contribute to air pollution; acid rain, resulting from sulphur dioxide emissions, is damaging forests; pollution in the Baltic Sea from raw sewage and industrial effluents from rivers in eastern Germany; hazardous waste disposal; government (under Chancellor Schröder, SPD) announced intent to end the use of nuclear power for producing electricity; government working to meet EU commitment to identify nature preservation areas in line with the EU's Flora, Fauna, and Habitat directive. Germany's last glacier is disappearing. [1]
- International agreements
- Party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
- Signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants
- Natural hazards
- Flooding through rivers after heavy rainfall, such as during the 2002 European floods, or Storm surge, such as the North Sea flood of 1962 or the historic floods of 1634 and 1362 that changed the coastline of what is now the west coast of Schleswig-Holstein.
Extreme points
Latitude and longitude
This is a list of the extreme points of Germany, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- northernmost point: List, Sylt, Schleswig-Holstein 55°03′N 8°24′E / 55.05°N 8.4°E
- southernmost point: Haldenwanger Eck, Oberstdorf, Bavaria 47°16′12.39″N 10°10′41.95″E / 47.2701083°N 10.1783194°E
- westernmost point: Isenbruch, Selfkant, North Rhine-Westphalia 51°1′N 5°53′E / 51.017°N 5.883°E
- easternmost point: Deschka, Neißeaue, Saxony 51°16′N 15°2′E / 51.267°N 15.033°E
The northernmost point in mainland Germany lies near Aventoft, Schleswig-Holstein at 54°54′N 8°49′E / 54.9°N 8.817°E
The extreme points of the German Confederation are mentioned in the first stanza of Das Lied der Deutschen, of which the third stanza is today the national anthem of Germany. They were accurate when the song was penned in 1841, but are no longer accurate today. The limits mentioned are the following rivers:
- Meuse River which crosses France, Belgium and the Netherlands and formed the border of the Duchy of Limburg, then part of the German Confederation and today the Dutch Province of Limburg.
- Memel, which runs through Belarus and Lithuania but previously formed part of the border of East Prussia
- Adige (Etsch), beginning in South Tyrol (then part of the Austria-Hungarian Empire) which was transferred from the Habsburg Empire to Italy after World War I
- Belt which is a part of the Baltic Sea between Germany and Denmark.
Elevation
- lowest point: Wilstermarsch at Neuendorf-Sachsenbande (near Itzehoe) 3.53 m below sea level 53°57′48″N 9°19′05″E / 53.96333°N 9.31806°E
- highest point: Zugspitze (in the Bavarian Alps, on the Austrian border) 2,962 m 47°25′N 10°59′E / 47.417°N 10.983°E
See also
- Geography of Europe
- List of administrative divisions of Germany
- National parks (Germany)
References
- ^ Germany CIA Factbook. November 14, 2006. Retrieved November 29, 2006.
- ^ German Climate Handbuch Deutschland. Retrieved November 30, 2006.
- ^ German Climate and Weather World Travels. Retrieved November 30, 2006.
Geography of Europe Sovereign
statesAlbania · Andorra · Armenia · Austria · Azerbaijan · Belarus · Belgium · Bosnia and Herzegovina · Bulgaria · Croatia · Cyprus · Czech Republic · Denmark · Estonia · Finland · France · Georgia · Germany · Greece · Hungary · Iceland · Ireland · Italy · Kazakhstan · Latvia · Liechtenstein · Lithuania · Luxembourg · Macedonia · Malta · Moldova · Monaco · Montenegro · Netherlands · Norway · Poland · Portugal · Romania · Russia · San Marino · Serbia · Slovakia · Slovenia · Spain · Sweden · Switzerland · Turkey · Ukraine · United Kingdom (England • Northern Ireland • Scotland • Wales) · Vatican City
States with limited
recognitionDependencies
and other territoriesÅland · Faroe Islands · Gibraltar · Guernsey · Jan Mayen · Jersey · Isle of Man · Svalbard
Other entities Climate of Europe Sovereign
statesAlbania · Andorra · Armenia · Austria · Azerbaijan · Belarus · Belgium · Bosnia and Herzegovina · Bulgaria · Croatia · Cyprus · Czech Republic · Denmark · Estonia · Finland · France · Georgia · Germany · Greece · Hungary · Iceland · Ireland · Italy · Kazakhstan · Latvia · Liechtenstein · Lithuania · Luxembourg · Macedonia · Malta · Moldova · Monaco · Montenegro · Netherlands · Norway · Poland · Portugal · Romania · Russia · San Marino · Serbia · Slovakia · Slovenia · Spain · Sweden · Switzerland · Turkey · Ukraine · United Kingdom (England • Northern Ireland • Scotland • Wales) · Vatican City
States with limited
recognitionAbkhazia · Kosovo · Nagorno-Karabakh · Northern Cyprus · South Ossetia · Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territoriesOther entities European Union · Sovereign Military Order of MaltaThe Danube Countries 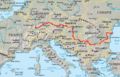
Cities Ulm · Ingolstadt · Regensburg · Passau · Linz · Vienna · Bratislava · Győr · Budapest · Dunaújváros · Novi Sad · Belgrade · Pančevo · Smederevo · Drobeta-Turnu Severin · Vidin · Giurgiu · Rousse · Brăila · Galaţi · Izmail · TulceaTributaries Islands Ada Kaleh (currently submerged) · Balta Ialomiţei · Belene Island · Csepel Island · Donauinsel · Great Brăila Island · Great War Island · Island of Vukovar · Island of Šarengrad · Kozloduy Island · Margaret Island · Ostrovul Ciocăneşti · Ostrovul Mare, Islaz · Ostrvo (Kostolac) · Vardim Island · Žitný ostrovList of crossings Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.