- BBC Online
-
BBC Online 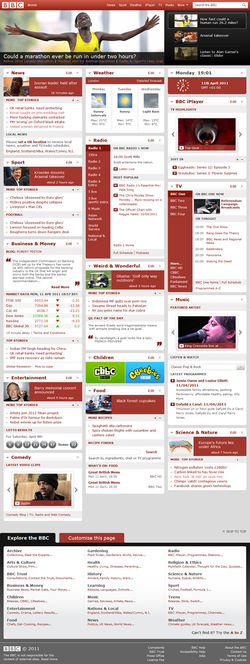
URL bbc.co.uk Commercial? No Type of site Portal Registration 1994 Owner BBC Created by BBC Launched 1997 Alexa rank  41 (November 2011[update])[1]
41 (November 2011[update])[1]Current status Active BBC Online is the brand name and home for the BBC's UK online service. It is a large network of websites including such high profile sites as BBC News and Sport, the on-demand video and radio services co-branded BBC iPlayer, the pre-school site Cbeebies, and learning services such as Bitesize. The BBC has had an online presence supporting its TV and radio programmes and web-only initiatives since 1994 but did not launch officially until December 1997, following government approval to fund it by TV licence fee revenue as a service in its own right. Throughout its short history, the online plans of the BBC have been subject to various public consultations and government reviews illustrating concerns from commercial rivals that its large presence and public funding distorts the UK market.
The website has gone through several branding changes since it was launched. Originally named BBC Online, it was then rebranded as BBCi (which itself was the brand name for interactive TV services) before being named bbc.co.uk. It was then branded BBC Online again in 2008.[2] The Web-based service of the BBC is one of the world's largest and most visited websites (thirty-ninth most visited according to Alexa in April 2011).[3] As of 2007, it contained over two million pages.
On 26 February 2010 The Times claimed that Mark Thompson, Director General of the BBC, proposed that the BBC's web output should be cut by 50%, with online staff numbers and budgets reduced by 25% in a bid to scale back BBC operations and allow commercial rivals more room.[4] On 2 March 2010, the BBC reported that it will cut its website spending by 25% and close BBC 6 Music and Asian Network.[5][6] On 24 January 2011, the confirmed cuts of 25% were announced leaving a £34 million shortfall. This resulted in the closure of several sites such as BBC Switch, BBC Blast, 6-0-6 and the announcement of plans to sell on the Douglas Adams created site h2g2.[7]
Contents
History
BBC Networking Club
The service's original home was www.bbcnc.org.uk (the "nc" standing for "networking club") launched on 11 May 1994 as a paid subscription service. For a joining fee of £25 and a monthly subscription of £12, members of the club were given access to an early type of social networking site featuring a bulletin board for sharing information and real-time conversation, along with a dialup internet connection service.[8]
Within 12 months, the BBC offered "auntie" on-line discussion groups; web pages for select web-related programs and BBC departments; free web pages for associate members; and an internet connection service www.bbc.co.uk [9] was introduced in 1996 though the old address also remained active for some time afterwards.
BBC Online
The BBC Director General John Birt sought government approval to direct licence fee revenue into the service, describing planned BBC internet services as the “third medium” joining the BBC's existing TV and Radio networks, achieving a change in the BBC Charter. This led to the official launch of BBC Online at the www.bbc.co.uk address in December 1997.
For a time, www.bbc.co.uk was used for the organisation's corporate and educational site, while entertainment-based content appeared on www.beeb.com. The two sites were merged in 1998 to become BBC Online,[10] at www.bbc.co.uk. By December 1998, the BBC Homepage was being described as "your gateway to 200 sites and 25,000 pages" [11]
In 1999, the BBC bought the www.bbc.com domain name for $375,000, previously owned by Boston Business Computing,[12] but the price of this purchase was not revealed until 6 years later.[13] As of 2005, www.bbcnc.org.uk no longer exists. The beeb.com address now redirects to the BBC Shop website run by BBC Worldwide, at www.bbcshop.com.
BBCi
In 2001 BBC Online was rebranded as BBCi. The BBCi name was conceived as an umbrella brand for all the BBC's digital interactive services across web, digital teletext, interactive TV and on mobile platforms.[14][15] The use of letter "i" prefixes and suffixes to denote information technology or interactivity was very much in vogue at this time, according to the BBC, the "i" in BBCi stood for "interactivity" as well as "innovation".[16]
As part of the rebrand, BBC website pages all displayed a standard navigation bar across the top of the screen, offering a category-based navigation: Categories, TV, Radio, Communicate, Where I Live, A-Z Index and a search.[17] The navbar was designed to offer a similar navigation system to the i-bar on BBCi interactive television.
bbc.co.uk and the return of BBC Online
After three years of consistent use across different platforms, the BBC began to drop the BBCi brand gradually; on 6 May 2004, the BBC website was renamed bbc.co.uk, after the main URL used to access the site.[18] Interactive TV services continued under the BBCi brand until it was dropped completely in 2008. The BBC's online video player, the iPlayer has, however, retained an i-prefix in its branding.
On 14 December 2007, a beta version of a new bbc.co.uk homepage was launched, with the ability to customise the page by adding, removing and rearranging different categories, such as 'News', 'Weather' and 'Entertainment'. The widget-based design was inspired by sites such as Facebook and iGoogle, and allowed the BBC to add new content to the homepage without cluttering it and still retaining personal choice.[19] The new homepage also had a simple searchbox taskbar with the clock design used in the 1970s on the BBC's television service. The homepage also featured a box containing featured content of the website, located on the right hand side of the main page. The new BBC homepage left beta stage on Wednesday, 27 February 2008 to serve as the new BBC Homepage under the same URL as the previous version did. This very different look was disorientating at first, but easier to understand later on.
On 30 January 2010, a new webpage design became available as a beta version,[20] that by May 2010, replaced the old homepage with the, now current, one. This new homepage expanded on the modules idea and the customisation theme. The website allowed certain themes that interested the viewer to be tracked, via a new module. It also included a new 'Media Zone' where featured content could be displayed, with this new featured box being located across the entire top of the webpage, below the header. The Media Zone was also changed so that the content changed by running the mouse over the tabs. The header was again changed to include the headings of the major sections of the website, these being: Home, News, Sport, Weather, iPlayer, TV, Radio and more, spread out evenly across the header. This new header was included across the entire website. Despite the cosmetic appearance of the relaunch, the new website was actually relaunched using a completely different operating system, allowing the site's four differnt international versions to be changed and altered easier. It also brought their website layouts and operations closer to that of the main website.
Following the launch of the new BBC News Website, which altered the header bar on that site, in October 2010, the new style of header was launched across the whole website, starting off with some of the larger, not obvious, sites, such as Doctor Who, first before relaunching all of the sites, including the homepage with the new look. This new style of header included the headings as before, but with the search box redesigned and aligned right, as with the links which are significantly smaller. Other links, such as BBC id login and mobile versions of the website also appear on the header, just to the right of the smaller BBC logo.
On 21 September 2011, a new BBC Homepage went into beta testing that was drastically different from those before it. The new homepgae was based on feedback that stated that the current page was too narrow in focus and not distinctive enough, with the homepage not displaying the full extend of the BBC Online site and that some didn't realise it was the homepage. As a result, they launched a new version that featured as a centrepeice a revolving carousel of content on the BBC Online website, with filters beneath to restrict it to, and to show more of entertainment, lifestyle, knowledge and news and sports topics. At the top of the page, a new header has been inserted giving the date, the time through the use of the vintage BBC clock, as well as weather prospects for the next three days through the use of the traditional weather symbols. Below the carousel, boxes contain links to the most popular video material, web articles and pages on the site, as well as TV and Radio listings alongside an A-Z list of the BBC's top level domains.[21]
Content
The websites include news from the BBC News Online, a sports section, music, science, technology and entertainment pages, amongst other things. As might be expected, the website has a British orientation, although the home page, news section and sports section each provide different content between UK and "International" visitors. There are also separate pages for Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland written by the BBC Nations and individual county pages containing local news and programme schedules.
The website focuses around the primary top level domains of News, Sport, Weather, iPlayer, TV and Radio. These are easily accessible from the taskbar running across the top of all current BBC Online pages. However other top level domains are also in existence: some are available from a drop down list on the taskbar including CBBC, CBeebies, Comedy, Food, Health, History, Learning, Music, Science and Nature, while other top level domains are only available through the A-Z index on the BBC website. These include Archive, Arts & Culture, Ethics, Gardening, Parenting, Religion and Travel news. However there are many more top level domains - some 400 in March 2010[22] however this number has decreased as top level domains now frequently link to a lower domain name - that link to websites for individual services or programmes.
In February 2001, BBC Online incorporated Douglas Adams' previously independent h2g2 project into its group of web sites, and eventually replaced all its existing message boards, which used an archaic system called Howerd, with the DNA software derived from that project. The site's now archived Collective magazine also used the DNA software along with numerous other sites created after the BBC's acquisition of h2g2.
The website has extensive technical information available about its operation. The BBC also makes some of the content on bbc.co.uk and the BBC News Website available in XML format on its developer network backstage.bbc.co.uk. Also, through participation in the Creative Archive Licence group, bbc.co.uk allows legal downloads of selected material via the Internet.
Further, you can also solve quizzes, especially designed to improve your comprehension and understanding of the English language.[23]
Children's
The BBC runs a comprehensive children's website sub-site. It includes information on all of CBBC's shows along with several sub-sites covering art, sport, news, and other current events. Its message boards are especially popular with children who use them to communicate with each other about all of CBBC's output among other salient topics for kids like bullying, books, and personal problems. The "Your Life" [24] page was especially geared to helping young people sort through their difficulties. "Your Life" featured agony uncle "Ask Aaron," a professional psychotherapist who provided regular answers to children's questions across the message boards. The "Your Life" page and its boards are now closed, and the agony uncle has moved on to Radio One's Sunday Surgery as their mental health expert.
The BBC also runs a message board for young people named onion street.
There is integration between television output and website content with aspects of children's programming have followup information on their websites. [http;//www.bbc.co.uk/cbeebies/childern site
BBC Blast
BBC Blast was the BBC's network for creative teenagers. It provided access to mentors both online and at free events and workshops across the UK. The website specifically catered for 13 to 19 year olds but the BBC Blast project also ran a variety of work experience schemes for young adults between the ages of 18 to 25. Blast was running from 2002 until 2011. It included a forum where participants could upload videos, audio tracks and images and comment on each others work. In the past the BBC Blast tour featured workshops and talks with stars from a variety of backgrounds, including rapper Akala, director and actor Noel Clarke, BBC Radio 1Xtra DJs Ace and Vis, singer-songwriter Jay Sean, rapper Chipmunk, Panjabi Hit Squad and Yngve & The Innocent.
Blast worked with a number of partners to put on events and give content a chance to be promoted at a higher level. These partners included the Victoria and Albert Museum, RSC, National Portrait Gallery, National Theatre, Zoo Nation, and the British Film Institute.
On 24 January 2011, the BBC announced the closure of BBC Blast as part of a 25% cut to the BBC Online budget, resulting in a £34 million shortfall.[7]
Programmes
BBC Programmes is a service of BBC Online which provides a page for every television and radio programme broadcast by the BBC in the United Kingdom. It was launched in October 2007 and gives each programme a eight digit alphanumeric identifier which is used to provide a permanent URL.[25][26] It currently only holds data from the launch date plus a selection of high profile programmes (notably Natural History programmes and Radio 4 programmes), but Jana Bennett, Director of BBC Vision, said in June 2008 that the BBC will eventually add a page for each programme it has broadcast over its history to the service.[27]
BBC Programmes is available as HTML and RDF/XML and JSON.
The BBC Programme Catalogue is an internal archive of the BBC back catalogue which was briefly available online to the public in beta.
Streaming media
A service, called BBC iPlayer, was launched in December 2007, which allows users to download both radio and TV content for up to seven days after broadcast. The television version allows users to either stream programmes or to download them using peer-to-peer and DRM technology.
Initially streams were generally broadcast in the RealAudio and RealVideo formats controlled by RealNetworks and the BBC drew criticism with some for using those closed formats which, at the time, could only be played using RealPlayer. In response to such criticisms, the BBC negotiated a deal with RealNetworks a 'cut-down' version of RealPlayer which did not contain as much advertising and marketing.
Windows Media has also been adopted and since Autumn 2006, a Windows Media stream of all national BBC radio stations has been available.
More recently, the BBC has been experimenting with MP3 downloads and podcasting facilities for an increasing number of radio shows, with a high level of success[citation needed]; a less publicised trial of Ogg Vorbis streams for certain programmes was less successful, and has now been discontinued.
During major events, the BBC often features liveblogs which publish the most recent text and image posts from BBC corespondents; particularly-significant political events may pair live blogs with live video streams or recorded video loops relevant to the event.
Tracking cookies and privacy policy
BBC Online uses several third-party companies to log information from users, by means of cookies. The BBC lists the companies it uses in its privacy policy:[28]
Users that block certain of these tracking domains will find certain parts of the BBC's websites inaccessible[citation needed].
Funding
The BBC's site was initially entirely free from advertising, this was due to the BBC's funding, derived primarily from compulsory television licence fees from UK viewers. BBC Worldwide who exploit BBC brands commercially have had several attempts at launching services online including Beeb.com in the late 1990s.
In 2006, the BBC began making controversial plans to raise revenue by including advertising on the international version of BBC News Online accessed from outside the United Kingdom.[29] BBC Online is currently freely available worldwide (via various URLs including bbc.com/news) but planned video services and a lower than expected licence fee settlement paid for by UK residents only led to the BBC introducing banner advertisements to the site from November 2007.[30] The BBC Trust approved the plans for introducing advertisements which also involved creating bbc.com as a part of BBC Worldwide.[31] Sir Michael Lyons, Chairman of the Trust, confirmed the BBC would not charge for online news following News International's planned introduction of charges for online content.[32]
Prior to this there had been criticism from some, as web users outside the UK could use the services (including the entire BBC radio services) without having to pay for them.[33] In addition, where rights to sporting events (such as certain football or cricket matches) do not include international online coverage, users from outside the UK are blocked from listening to commentaries.
On 24 January 2011, it was announced that the BBC was to cut its online budget by 25% or £34 million. To cope with this, many BBC websites would be closed including BBC Switch, BBC Blast, 6-0-6, BBC raw, Video Nation, and planned to sell the Douglas Adams created website h2g2, as well as the automation of many programme websites and radio websites.[7]
Graf report
In early 2004, the site was made the focus of a government review, launched by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport, led by Philip Graf. Sections of the UK internet industry had argued that the BBC site offered things that were available in the commercial sector, creating unnecessary competition.
The review was published in July 2004 and it was recommended that the BBC "prioritise news, current affairs, education and information which is of value to the citizen." In response the BBC also shut down a small number of sections of the site, including the Soaps section.
In November 2004, the Governors of the BBC announced a newer, much more tightly drawn remit for bbc.co.uk as part of their response to the review. They also announced, as Graf had recommended, a new approach towards external providers which will see bbc.co.uk aiming to spend at least 25% of its eligible budget on content and services through independent commissions by the end of 2006/07.
The implementation of the Graf report has seen the popular message boards in the BBC Sport section shut down, as the BBC tries to promote its 606 brand, but these changes have proved unpopular as the interface has proven unusable and large numbers of content providers have abandoned the BBC site[citation needed].
Cult TV
From 1999 to 2005, the BBC ran a popular sub-site called Cult TV. This sub-site had news, star interviews, trivia, and other content popular with fans of the cult TV shows they covered. Examples of covered TV shows include The X-Files, Doctor Who, Buffy the Vampire Slayer, Farscape and The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy.
On 15 July 2005, the BBC announced that the site was closing as of the end of the month, although the Doctor Who section would be unaffected as the series was an ongoing BBC concern. The announcement explained that this was "part of the restructuring of the BBC's online activities". It was promised that some of the content would be moved to new places on bbc.co.uk, although as of March 2008 it is currently still all online at the no-longer-updated Cult site. In recent years, some of the content covered in the Cult section was included in the BBC's Archive section, such as content and information on the 25th Anniversary of Children's BBC.
Vulnerabilities in the system
In March 2007, a vulnerability was exposed in the BBC's "Most Emailed" and "Most Read" news sections.[34]
See also
Notes
- ^ "Bbc.co.uk Site Info". Alexa Internet. http://www.alexa.com/siteinfo/bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 2011-11-02.
- ^ "BBC launches PSB partnerships" (Press release). BBC Press Office. 11 December 2008. http://www.bbc.co.uk/pressoffice/pressreleases/stories/2008/12_december/11/partnership1.shtml. Retrieved 13 December 2008.
- ^ Alexa Top 500 Sites Alexa
- ^ "BBC signals an end to era of expansion" 26 February 2010 Retrieved 2010-02-26
- ^ "BBC Proposes Deep Cuts in Web Site" 2 March 2010 Retrieved 2010-03-02
- ^ "BBC 6 Music and Asian Network face axe in shake-up" 2 March 2010 Retrieved 2010-03-02
- ^ a b c "BBC News – BBC to cut online budget by 25%". BBC Online. 24 January 2011. http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/entertainment-arts-12265173. Retrieved 24 January 2011.
- ^ "The BBC is launching an on-line service...". The Sunday Times. 17 April 1994. http://www.bbc.co.uk/blogs/bbcinternet/2007/12/the_www_inforainforest_1.html. Quoted in Connor, Alan (25 December 2007). "The WWW Info-Rainforest". BBC Internet Blog. BBC. http://www.bbc.co.uk/blogs/bbcinternet/2007/12/the_www_inforainforest_1.html. Retrieved 2 October 2008.
- ^ British Broadcasting Corporation BBC
- ^ BBC Online – Homepage BBC
- ^ BBC Online – Help/newcomers section BBC
- ^ Boston Business Computing – OpenVMS Migration Solutions Boston Business Computing
- ^ BBC blew $375k on bbc.com The Register
- ^ "BBCi heralds new interactive era". BBC News. 7 November 2001. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/entertainment/1643259.stm. Retrieved 2 October 2008.
- ^ "What is BBCi?". BBC. 15 December 2002. Archived from the original on 15 December 2001. http://web.archive.org/web/20011215000308/http://www.bbc.co.uk/home/whatisbbci/. Retrieved 2 October 2008.
- ^ Gibson, Owen (12 November 2001). "A fresh i for BBC". London: The Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/media/2001/nov/12/mondaymediasection.bbc1. Retrieved 2 October 2008.
- ^ "What is BBCi? – On the web". BBC. 15 December 2002. Archived from the original on 15 December 2001. http://web.archive.org/web/20011215101431/http://www.bbc.co.uk/home/whatisbbci/on_web.shtml. Retrieved 2 October 2008.
- ^ "BBC website gets new look and new name: bbc.co.uk". BBC Press Office. 4 May 2004. http://www.bbc.co.uk/pressoffice/pressreleases/stories/2004/05_may/04/bbc_co_uk.shtml. Retrieved 30 September 2008.
- ^ A Lick of Paint for the BBC Homepage, bbc.co.uk, 13 December 2007
- ^ [1], id.bbc.co.uk, 30 January 2010
- ^ Thornett, James. "Redisigning the BBC Online Homepage". BBC Internet Blog. http://www.bbc.co.uk/blogs/bbcinternet/2011/09/bbc_online_homepage_beta_producer.html. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ Huggers, Erik. "BBC Online's top level directories". BBC Internet Blog. BBC Internet Blog. http://www.bbc.co.uk/blogs/bbcinternet/2010/03/bbc_onlines_top_level_director.html. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ http://www.bbc.co.uk/worldservice/learningenglish/quizzes/index.shtml
- ^ CBBC Your Life BBC
- ^ Walpole, Sophie (5 November 2007). "A Page For Every Programme". BBC Internet Blog. BBC. http://www.bbc.co.uk/blogs/bbcinternet/2007/11/a_page_for_every_programme_1.html. Retrieved 9 January 2010.
- ^ Scott, Tom (18 October 2007). "Ladies and gentlemen I give you BBC Programmes". derivadow.com. http://derivadow.com/2007/10/18/programme-support/. Retrieved 9 January 2010.
- ^ West, Dave (11 June 2008). "BBC to expand web programmes database". Digital Spy. http://www.digitalspy.co.uk/broadcasting/news/a99319/bbc-to-expand-web-programmes-database.html. Retrieved 9 January 2010.
- ^ BBC 2008. BBC – Homepage – Privacy and Cookies Policy. Retrieved 7 July 2008
- ^ BBC urged to resist website ads BBC News Online. 16 February 2007
- ^ BBC's global website to carry adsBBC News Online. 18 October 2007
- ^ BBC Trust approval for BBC to implement its 'bbc.com' proposals BBC Trust. 18 October 2007
- ^ BBC Trust dampens Worldwide's plans for global domination Nick Clark. The Independent. 25 November 2009
- ^ Q&A: Adverts on BBC website Torin Douglas. BBC News Online. 21 February 2007
- ^ Statistics Hacking – Exploiting Vulnerabilities in News Websites PDF, Amrinder Arora, International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, Vol.7 No.3, March 2007
References
- Latest on plans for bbc.co.uk including archive
- Summary of results of Graf Review
- BBC's response to Graf review
- Press release concerning radio podcasting and download trials
- Press release announcing extended trial of iMP
- BBC Politics 97 Site – look at an old BBC web page that is still active since 1997
- Backstage
- BBC Home Archive
- Creative Archive
- BBC Commissioning
- Engineering Data
External links
Categories:- BBC New Media
- British websites
- Broadcasting websites
- Internet properties established in 1994
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




