- Intestinal gland
-
Intestinal gland 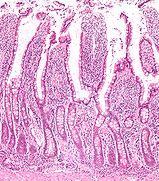
Micrograph of the small intestine mucosa showing the crypts of Lieberkühn - bottom 1/3 of image. H&E stain. Latin glandulae intestinales Gray's subject #248 1174 In histology, an intestinal crypt (also crypt of Lieberkühn and intestinal gland) is a gland found in the epithelial lining of the small intestine and colon. The crypts secrete various enzymes, including sucrase and maltase, along with enteropeptidase.
Also, new epithelium is formed here, which is important because the cells at this site are continuously worn away by the passing food. The basal (further from the intestinal lumen) portion of the crypt contains multipotent stem cells. During each mitosis, one of the two daughter cells remains in the crypt as a stem cell, while the other differentiates and migrates up the side of the crypt and eventually into the villus. Goblet cells are among the cells produced in this fashion. Many genes have been shown to be important for the differentiation of intestinal stem cells.[clarification needed]
Loss of proliferation control in the crypts is thought to lead to colorectal cancer.
Contents
Pathologic changes
 Micrograph showing intestinal crypt branching, a histopathological finding of chronic colitides. H&E stain.
Micrograph showing intestinal crypt branching, a histopathological finding of chronic colitides. H&E stain.
Pathologic processes that lead to chronic, i.e. on-going, intestinal crypt destruction are associated with branching of the crypts.
Causes of crypt branching include:
- inflammatory bowel disease (e.g. ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease),
- persistent infectious colitides, and
- ischemic colitis.
Crypt inflammation is known as cryptitis and characterized by the presence of neutrophils between the enterocytes. A severe cryptitis may lead to a crypt abscess.
Eponym
The eponymous term (crypts of Lieberkühn) is named after the 18th-century German anatomist Johann Nathanael Lieberkühn.
See also
Additional images
External links
- Illustration at trinity.edu
- Illustration at kumc.edu
- Illustration at uokhsc.edu
- synd/2651 at Who Named It?
- intestinal+glands at eMedicine Dictionary
Categories:- Digestive system
- Digestive system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


