- Climate of Svalbard
-
The climate of Svalbard is principally a result of its latitude, which is between 74° and 81° north. Average July temperatures range from 4 to 6 °C (39.2 to 42.8 °F), and in January temperatures are normally between −12 and −16 °C (10.4 and 3.2 °F).[1] The North Atlantic Current moderates Svalbard's temperatures, particularly during winter, giving it up to 20 °C (36 °F) higher winter temperature than similar latitudes in continental Russia and Canada. This keeps the surrounding waters open and navigable most of the year. The interior fjord areas and valleys, sheltered by the mountains, have less temperature differences than the coast, giving about 2 °C (3.6 °F) lower summer temperatures and 3 °C (5.4 °F) higher winter temperatures. On the south of Spitsbergen, the temperature is slightly higher than further north and west. During winter, the temperature difference between south and north is typically 5 °C (9 °F), while only about 3 °C (5.4 °F) in summer. Bear Island has average temperatures even higher than the rest of the archipelago.[2]
The archipelago is the meeting place for cold polar air from the north and mild, wet sea air from the south, creating low pressure and changing weather and fast winds, particularly in winter; in January, a strong breeze is registered 17% of the time at Isfjord Radio, but only 1% of the time in July. In summer, particularly away from land, fog is common, with visibility under 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) registered 20% of the time in July and 1% of the time in January, at Hopen and Bear Island.[3] Precipitation is frequent, but falls in small quantities, typically less than 400 millimetres (15.7 in) in Western Spitsbergen. More rain falls in the uninhabited east side, where there can be more than 1,000 millimetres (39.4 in).[3]
Contents
Longyearbyen
Climate data for Longyearbyen Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) −13
(8.6)−13
(8.6)−13
(8.6)−9
(15.8)−3
(26.6)3.0
(37.4)7.0
(44.6)6.0
(42.8)1.0
(33.8)−4
(24.8)−8
(17.6)−11
(12.2)−4.75
(23.45)Average low °C (°F) −20
(−4.0)−21
(−5.8)−20
(−4.0)−16
(3.2)−7
(19.4)−1
(30.2)3.0
(37.4)2.0
(35.6)−3
(26.6)−9
(15.8)−14
(6.8)−18
(−0.4)−10.33
(13.40)Precipitation mm (inches) 22.0
(0.866)28.0
(1.102)29.0
(1.142)16.0
(0.63)13.0
(0.512)18.0
(0.709)24.0
(0.945)30.0
(1.181)25.0
(0.984)19.0
(0.748)22.0
(0.866)25.0
(0.984)271
(10.67)Source: Climate and daylight in Svalbard (Longyearbyen)[4] Historical data
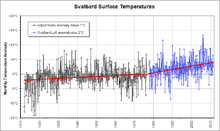
Because of its history of human occupation, Svalbard has one of the longest high-latitude meteorological records on earth. Computer models of global climate have long predicted enhanced greenhouse warming at such latitudes, so the Svalbard record is of particular interest.[5] It shows approximately 6 °C (10.8 °F) increase in 100 years; with 4 °C (7.2 °F) increase in the last 30 years.
References
- ^ "Temperaturnormaler for Spitsbergen i perioden 1961 - 1990" (in Norwegian). Norwegian Meteorological Institute. http://retro.met.no/observasjoner/svalbard/normaler_for_kommune_2111.html?kommuner. Retrieved 24 March 2010.
- ^ Torkilsen (1984): 98–99
- ^ a b Torkilsen (1984): 101
- ^ "Climate and daylight in Svalbard (Longyearbyen)". NordicVisitor. http://svalbard.nordicvisitor.com/travel-guide/climate-and-daylight/. Retrieved May 2011.
- ^ [http://www.realclimate.org/index.php?p=309 RealClimate]
Bibliography
- Torkildsen, Torbjørn et. al. (1984) (in Norwegian). Svalbard: vårt nordligste Norge. Oslo: Forlaget Det Beste. ISBN 82-7010-167-2.
Climate of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities - European Union
- Sovereign Military Order of Malta
Svalbard General Politics Settlements Former settlements Bölscheøya · Grumant · Kobbefjorden · Lægerneset · Pyramiden · Smeerenburg · Virgohamna · Ytre NorskøyaEnvironment Islands Barentsøya · Bjørnøya · Edgeøya · Hopen · Kong Karls Land · Kvitøya · Nordaustlandet · Prins Karls Forland · Sjuøyane · Spitsbergen · Tusenøyane · WilhelmøyaNational parks Forlandet National Park · Indre Wijdefjorden · Nordenskiöld Land · Nordre Isfjorden Land · Northwest Spitsbergen · Sassen – Bünsow Land · Sør-SpitsbergenCompanies Research Arctic Yellow River Station · Norwegian Polar Institute · Polish Polar Station · Seed Vault · Undersea Cable · University Centre · Himadri StationTransport Categories:- Climate of Norway
- Environment of Svalbard
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.