- Gestational age
-
This article is about gestational age in humans. For information on gestational age in non-human animals, see gestation.
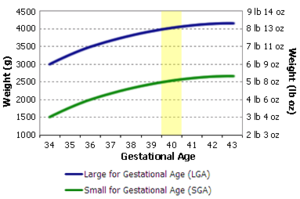
Birth weight and gestational age Classifications - Large for gestational age: Weight is above the 90th percentile at gestational age
- Macrosomia: Weight is above a defined limit at any gestational age
- Appropriate for gestational age: Normal birth weight
- Small for gestational age: Weight is below the 10th percentile at gestational age
- Low birth weight: Weight is below a defined limit at any gestational age
Gestational age relates to the age of an embryo or fetus (or newborn infant). There is some ambiguity in how it is defined:[1]
- In embryology, gestational age is the time elapsed since conception. This interval is also termed fertilisation age.
- In human obstetrics in many countries, gestational age is defined as the time elapsed since 14 days prior to conception. This is approximately the duration since the woman's last menstrual period (LMP) began. There is also a further distinction between the calendar gestational age described here, and the developmental gestational age determined by comparing an embryo or fetus to the average age of others that were at the same stage of development.
Unless the exact date of conception is known, counting from LMP has been the common method of computing gestational age.[2] It involves the assumption that conception in humans typically occurs a consistent period (14 days) from the onset of the LMP. Although this "LMP method" of calculating gestational age is convenient, other methods are in use or have been proposed.[3]
Contents
Methods
Some countries count gestational age from fertilization instead of LMP.[4] This method of counting is also known as fertilization age, embryonic age, conceptional age or (intrauterine) developmental (IUD)[5] age. This method is more prevalent in descriptions of prenatal development of the embryo or fetus. The LMP gestational age is usually greater by about two weeks.[3] Also, pregnancy often is defined as beginning with implantation, which happens about three weeks after the LMP (see the beginning of pregnancy controversy).[3]
Accuracy
Calculations of gestational age from LMP are sometimes incorrect due to normal variation from the average ovulation date. The gestational age of an individual infant can be more accurately estimated from:
- The mother's knowledge of the date of sexual intercourse.
- The mother's knowledge of fertility signs related to ovulation. The needed observations are normally made by mothers who use fertility awareness methods to get pregnant.
- Examination of the newborn infant. In the twentieth century, doctors (especially pediatricians) were trained to recognize the physical changes occurring to the fetus in the latter half of pregnancy so that a maturational age could be estimated.
- An obstetric ultrasound ("dating scan", in the UK routinely offered around 12 weeks) during the pregnancy, whereby sizes of certain fetal body parts are measured.
The fertilization age of children conceived by in vitro fertilization is known to the hour.
Uses
Using the LMP method, a full-term human pregnancy is considered to be 40 weeks (280 days), though pregnancy lengths between 38 and 42 weeks are considered normal. A fetus born prior to the 37th week of gestation is considered to be preterm. A preterm baby is likely to be premature and consequently faces increased risk of morbidity and mortality. An estimated due date is given by Naegele's rule.
 Stages in prenatal development, with weeks and months numbered from last menstruation.
Stages in prenatal development, with weeks and months numbered from last menstruation.
The events of prenatal development usually occur at specific gestational ages. The gestational timing of a toxin exposure or infection can be used to predict the potential consequences to the fetus.
In classifying infant deaths and stillbirths
For most of the 20th Century, official definitions of a live birth and infant death in the Soviet Union and Russia differed from common international standards, such as those established by the World Health Organization in the latter part of the century.[6] Babies who were less than 28 weeks of gestational age, or weighed less than 1000 grams, or less than 35 cm in length – even if they showed some sign of life (breathing, heartbeat, voluntary muscle movement) – were classified as "live fetuses" rather than "live births." Only if such newborns survived seven days (168 hours) were they then classified as live births. If, however, they died within that interval, they were classified as stillbirths. If they survived that interval but died within the first 365 days they were classified as infant deaths.
It has been estimated that because of these special rules relying on gestational age as one criterion, the reported infant mortality rates in Russia and the Soviet Union were some 22 to 25 percent lower than they would have been had the WHO standard been applied.[7]
It has been reported that Belgium and France have a practice of counting newborns of less than 26 weeks of gestational age that die shortly after birth as stillbirths.[8]
Postnatal use
Gestational age (as well as fertilization age) is sometimes used postnatally (after birth) to estimate various risk factors. For example, it is a better predictor than postnatal age for risk of intraventricular hemorrhage in preterms treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.[9]
See also
References
- ^ Stedman's Online Medical Dictionary, 27th Edition
- ^ John Goldenring, ed (November 2004). "MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia: Gestational age". A.D.A.M., Inc.. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/002367.htm. Retrieved 2007-01-28. (distinguishing between "calendar gestational age" and "developmental gestational age").
- ^ a b c Engle W, American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus and Newborn (2004). "Age terminology during the perinatal period". Pediatrics 114 (5): 1362–4. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-1915. PMID 15520122. http://aappolicy.aappublications.org/cgi/content/full/pediatrics;114/5/1362. Retrieved 2007-01-28.
- ^ Rahman, Anika; Laura Katzive and Stanley K. Henshaw (June 1998). "A Global Review of Laws on Induced Abortion, 1985-1997". International Family Planning Perspectives 24 (2): 56–64 (see p.59). doi:10.2307/2991926. JSTOR 2991926. http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/2405698.pdf. Retrieved 2008-12-02.
- ^ Wagner F, Erdösová B, Kylarová D (December 2004). "Degradation phase of apoptosis during the early stages of human metanephros development". Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 148 (2): 255–6. PMID 15744391.
- ^ Barbara A. Anderson and Brian D. Silver, “Infant Mortality in the Soviet Union: Regional Differences and Measurement Issues,” Population and Development Review 12 (December 1986): 705-738; Barbara A. Anderson and Brian D. Silver, "“The Geodemography of Infant Mortality in the Soviet Union, 1950-1990,” in G. J. Demko, Z. Zaionchkovskaya, S. Pontius, and G. Ioffe, Eds., Population Under Duress: The Geodemography of Post-Soviet Russia (Boulder: Westview, 1999): 73-103.
- ^ Anderson and Silver, "Infant Mortality in the Soviet Union," cited earlier.
- ^ Bernadine Healy, "Behind the Baby Count," U.S. News & World Report, September 24, 2006. For a general discussion of the problems associated with using gestational age as a criterion for viability, see Gabriel Duc, "The Crucial Role of Definition in Perinatal Epidemiology," Sozial- und Präventivmedizin/Social and Preventive Medicine 40, No. 6 (November 1995): 357-360.
- ^ Alan H. Jobe, MD, PhD. Post-conceptional age and IVH in ECMO patients. RadiologySource Volume 145, Issue 2, Page A2 (August 2004). PII: S0022-3476(04)00583-9. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.07.010.
Pregnancy and childbirth Planning Conception Testing Prenatal AnatomyProceduresChildbirth PreparationRolesDeliveryPostpartum Obstetric history Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.