- Möngke Khan
-
Möngke Khan Khagan of the Mongol Empire
(Supreme Khan of the Mongols)
King of Kings
Emperor of China
Reign July 1, 1251 – August 11, 1259
(8 years, 41 days)Coronation July 1, 1251 Titles Khan, Khagan
Temple name: Yuan Xianzong (元宪宗)
Posthumous name: Emperor Huansu (桓肃皇帝)Born 10 January 1209 Died 11 August 1259 (aged 50–51) Place of death Fishing Town, Chongqing Buried Burkhan Khaldun, Khentii province Predecessor Güyük Khan Successor Kublai Khan Royal House Borjigin
Mongolian: БоржигинFather Tolui Mother Sorghaghtani Beki Möngke Khan (Mongolian: Мөнх хаан), born Möngke, (January 10, 1209 – August 11, 1259 ), was the fourth Great Khan of the Mongol Empire from July 1, 1251 – August 11, 1259. He was the first Great Khan from the Toluid line. Under Möngke, the Mongols conquered Iraq and Syria as well as the kingdom of Nanzhao and the area of present-day Vietnam.[1] He made significant reforms to improve the administration of the Empire.
Contents
Early life
Möngke was born on January 10, 1209 as the eldest son of Genghis Khan's teen-aged son Tolui and Sorghaghtani. Teb Tengri Khokhcuu, the powerful shaman, saw in the stars a great future for the child and bestowed on him the name Mongke, "eternal" in the Mongolian language. His uncle Ogedei's childless queen Angqui raised him at her ordo (nomadic palace).[2] Ogedei instructed Persian scholar Idi-dan Muhammed to teach writing to Mongke.
On his way back home after the conquest of Khwarizmian Empire, Genghis Khan performed the ceremony on his grandsons Mongke and Kublai after their first hunting in 1224 near the Ili River.[3] Mongke was eleven years old, and with his brother, Kublai, killed a rabbit and an antelope. Their grandfather smeared fat from killed animals onto their middle fingers following the Mongol tradition.
In 1230, Mongke went to war for the first time, following the Great Khan Ogedei and his father Tolui into battle against the Jin Dynasty. Tolui died in 1232 and Ogedei appointed Sorghaghtani head of the Toluid appanage. Following the Mongol custom, Mongke inherited at least one of his father's wives, Oghul-Khoimish of the Oirat clan. Mongke deeply loved her and gave special favor to her elder daughter, Shirin.[4]
Ogedei dispatched him along with his relatives to attack the Kipchaks, Russians and Bulgars in the west in 1235. When the most formidable Kipchak chief, Bachman, fled to an island in the Volga delta. Mongke crossed the river and captured Bachman. When he ordered Bachman to bend on knees, Bachman refused, and, hence, he was executed by Mongke's brother Bujek. Mongke also engaged in hand to hand combat in the sieges of Russian cities. While his cousins, Shiban and Büri, went to Crimea, Mongke and Khadan, a son of Ogedei, were ordered to reduce the tribes in Caucasus.[6] The Mongols captured the Alani capital Maghas and massacred its inhabitants. Many chiefs of the Alans and Circassians surrendered to Mongke. After the conquest of Europe, Mongke would bring them back to Mongolia. He also participated in the conquest of Kiev in 1240. Mongke was apparently taken by the splendor of Kiev and offered the city surrender, but his envoys were killed.[7] After Batu's army joined Mongke's soldiers, they sacked the city. And he also fought with Batu at the Battle of Mohi. In the summer of 1241, before the premature end of the campaign, Möngke returned home after his uncle Ogedei recalled him in winter 1240-41. However, Ogedei died.
In 1246, Temuge Odchigen, Genghis Khan's sole remaining brother, unsuccessfully tried to seize the throne without confirmation by a kurultai. The new Khagan Guyuk entrusted the delicate task of trying Odchigin to Mongke and Orda Khan, the eldest brother of Batu. Guyuk eventually died in route to west in 1248 and Batu and Mongke emerged as main contenders.
The Toluid revolution
 Möngke qaγan in traditional Mongolian script
Möngke qaγan in traditional Mongolian script
Following his mother Sorghaghtani's advice, Mongke went to the Golden Horde to meet Batu who was afflicted with the gout. Batu decided to support his election and called a kurultai at Ala Qamaq. The leader of the families of Genghis Khan's brothers, and several important generals, came to the kurultai. Guyuk's sons Naqu and Khoja attended briefly but then left. Despite vehement objections from Bala, Oghul Qaimish's scribe, the kurultai approved Mongke. Given its limited attendance and location, this kurultai was of questionable validity. Batu sent Mongke under the protection of his brothers, Berke and Tuqa-temur, and his son Sartaq to assemble a formal kurultai at Kodoe Aral in Mongolia. When Sorghaghtani and Berke organized a second kurultai on the 1st of July, 1251, the assembled throng proclaimed Mongke the Great Khan of the Mongol Empire, and a few of the Ogedeid and Chagatayid princes, such as his cousin Kadan and the deposed khan Khara Hulegu, acknowledged the decision.
Shortly thereafter, Oghul's son Khoja and Ogedei's favorite grandson Shiremun came to "pay homage" to Mongke as the new ruler, but they brought the entire army of the Ogedei faction with them. Mongke's the Kankali falconer, Kheshig, discovered the preparations for the attack and told his lord. At the end of the investigation under his father's loyal servant Menggesar noyan, he found his relatives guilty but at first wanted to give them mercy as written in the Great Yassa. Mongke's officials opposed it and then he began to punish his relatives. The trials took place on all parts of the empire from Mongolia and China in the east to Afghanistan and Iraq in the west. Mongke and Batu's brother Berke therefore arranged to have Oghul accused of using black magic against Mongke. After she was arrested and questioned by Sorghaghtani, Oghul Qaimish was sewn up into a sack, and tossed into a river and drowned (which was the traditional Mongol punishment for using black magic). Estimates of the deaths of aristocrats, officials and Mongol commanders include Eljigidei, Yesu Mongke, Büri and Shiremun and range from 77-300. Most of the princes of Genghisid blood involved in the plot, however, were given some form of exile. The anti-Mongke plot of an Uyghur scribe, Bala, and the Idiqut Salindi (the monarch of the Uyghurs) was discovered and they were publicly executed. Mongke also eliminated the Ogedeid and Chagataid families’ estates and shared the western part of the empire with his ally Batu Khan. After the bloody purge, Mongke ordered a general amnesty for prisoners and captives. Soon, Mongke's mother Sorghaghtani died in 1252.
After his accession to the throne in 1251, Mongke announced that he would follow his ancestors but he do not imitate other countries' ways.[8] To increase his legitimacy, in 1252 he retroactively awarded his father the title of Great Khan (Ikh Khagan). And Möngke's friendliness with Batu ensured the unity of the empire.
Mongol Imperialism
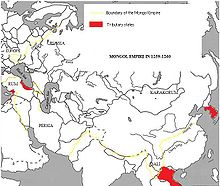
The Mongol Empire during the reign of Mongke Khan (r.1251-59)
Mongke drafted his own decrees and kept close watch on their revision. Mongke forbade practices of extravagant costs of the Borjigin and non-Borjigid nobles. He also limited gifts to the princes, converting them into regular salaries and made the merchants subject to taxes. Mongke limited notorious abuses and sent imperial investigators to supervise the business of the merchants who were sponsored by the Mongols. He prohibited them from using the imperial relay stations, yam (route) and paizas (tablet that gave the bearer authority to demand goods and services from civilian populations). With Guyuk dead, many local officials no longer wanted to pay off the paper drafts used by Guyuk. Mongke recognized that if he did not meet the financial obligations of Guyuk, it would make merchants reluctant to continue business with the Mongols. Mongke paid out all drafts drawn by high rank Mongol elites to these merchants. Ata Malik Juvaini stated, "And from what book of history has it been read or heard...that a king paid the debt of another king?" in his book. The generals and princes (including his son), who allowed their troops to plunder civilians without authorization, were repeatedly punished by Mongke Khan.[9] He used North Chinese, Muslim and Uyghur officials. The Khagan's chief judge (jarughachi) was the Jait-Jalayir official Menggeser while the chief sribe was the Kerait Bulghai who was a Christian. 9 of the 16 chief provincial officials of Mongke Khan were certainly Muslims. He reappointed Guyuk's three officials: Mahmud Yalavach in China, Masud Beg in Turkestan, and Arghun Agha of the Oirat in Persia. Mongke separated the position of the great judge at court from that of chief scribe.
 The legend citing "Struck by the Georgian King David in the name of his overlord Möngke, by the power of Heaven" in Persian. (Dated 1253)
The legend citing "Struck by the Georgian King David in the name of his overlord Möngke, by the power of Heaven" in Persian. (Dated 1253)
In 1253, Mongke established the Department of Monetary affairs to control the issuance of paper money in order to eliminate the overissue of the currency by Mongol and non-Mongol nobles since the reign of Great Khan Ogedei.[10] His authority established united measure based on sukhe or silver ingot, however, the Mongols allowed their foreign subjects to mint coins in the denominations and use weight they traditionally used.[11] During the reigns of Ogedei, Guyuk and Mongke, Mongol coinage increased with gold and silver coinage in Central Asia and copper and silver coins in Caucasus, Iran and Bolghar.[12]
In 1252-1259, Möngke conducted a census of the Mongol Empire including Iran, Afghanistan, Georgia, Armenia, Russia, Central Asia and North China. While that of China was completed in 1252, Novgorod in the far northwest was not counted until winter 1258-59. There was an uprising in Novgorod against Mongol rule in 1257, but Alexander Nevsky forced the city to submit to Mongol census and taxation. The new census counted not only households but also the number of men aged 15–60 and the number of fields, livestock, vineyards, and orchards. Within the civilian register craftsmen were listed separately while in the military registers auxiliary and regular households were distinguished. Clergy of the approved religions were separated and not counted. When the new register was completed, one copy was sent to Karakorum and one copy kept for the local administration.[13] Mongke tried to create a fixed poll-tax collected by imperial agents, which could forward to the needy units. Initially, the maximum rate was fixed at 10-11 gold dinars in the Middle East and 6-7 taels of silver in China. But protests from the landlord classes reduced this relatively low rate to 6-7 dinars and taels. Mongke's some officials raised the top rate on the wealthy of 500 dinars. Although, the reform of the taxation did not lighten the tax burden, it made the payments more predictable.[14] Even so, the census and the regressive taxation it facilitated sparked popular riots and resistance in the western districts. In 1259, the Georgian King David Narin revolted, unsuccessfully, against the Mongols and, then, fled to Kutaisi, from whence he reigned over western Georgia (Imereti) as a de facto separate ruler. In 1261, he gave shelter to David VII Ulu, who in his turn had attempted to end the Mongol dominance. However, David Ulu made peace with the Mongols and returned to Tbilisi in 1262. Mongke and Batu's official, Arghun, harshly punished the Georgian and Armenian nobles, plundering their cities and executing their prominent leaders.[15] He divided the Georgians into 6 tumens. Meanwhile, Baiju crushed the rebellion of the Seljuk Sultan Kaykaus II near Ankara in 1256 and reestablished Mongol authority over Eastern Turkey. By that time the Kashmiris had revolted, and Mongke appointed his generals, Sali and Takudar, to replace the court and a Buddhist master, Otochi, as darugachi to Kashmir. However, the Kashmiri king killed Otochi at Srinagar. Sali invaded again, killing the king, and put down the rebellion, after which the country remained subject to the Mongol Empire for many years.[16]
Religious policy
Statue of Mongke Khan in Mongolia
Mongke confirmed Guyuk's appointment of Haiyun as chief of all the Buddhists in the Mongol Empire in 1251. In 1253 Namo from Kashmir was made chief of all the Buddhist monks in the Empire. During the conquest of Tibet in 1252-53, all Buddhist clergy were exempted from taxation. The Tibetan Karma Pakshi received Mongke's patronage. Mongke had been so impressed by the aged Taoist monk Qiu Chuji who met his grandfather Genghis Khan in Afghanistan. Mongke made Li Zhichang chief of the Taoists. However, the Taoists had exploited their wealth and status by seizing Buddhist temples. Mongke demanded that the Taoists cease their denigration of Buddhism. Mongke ordered Kublai to end the clerical strife between the Taoists and Buddhists in his territory. Kublai called a conference of Taoist and Buddhist leaders in early 1258. At the conference, the Taoist claim was officially declared refuted and Kublai forcibly converted their 237 temples to Buddhism and destroyed all copies of the fraudulent texts.[17]
Despite his conquests of the Abbasid Caliphate and the Ismailis, Mongke favored Muslim perceptions. He and Hulegu made the Shiite community at Najaf autonomous tax-exempt ecclesiastical polity. Like his predecessors, he exempted clerics, monks, churches, mosques, monasteries and doctors from taxation.
Hethum I (seated) in the Mongol court of Karakorum, "receiving the homage of the Mongols".[18] "Histoire des Tartars", Hayton of Corycus, 1307.
During Mongke's reign, the French king Louis IX sent William Rubruck as a diplomat seeking an alliance with the Mongols against the Muslims. By that time Mongke's khatun Oghul-Khoimish was already dead. After making the French envoy wait for many months, Mongke officially received William Rubruck on May 24, 1254. Rubruck informed him that he had come to spread the word of Jesus Christ. Then he stayed to help the Christians in Karakorum and attended debates among rival religions organized by the Mongols. Mongke Khan summoned William Rubruck to send him back home in 1255. He told Rubruck:
"We Mongols believe in one God, by Whom we live and die". He then continued "Just as God gave different fingers to the hand so has He given different ways to men. To you God has given the Scriptures and you Christians do not observe them". He explained God had given the Mongols their shamans. Mongke offered Louis IX his cooperation but warned all Christians that "If, when you hear and understand the decree of the eternal God, you are unwilling to pay attention and believe it...and in this confidence you bring an army against us-we know what we can do".[19]
Ambassadors from the Latin Empire and the Empire of Nicaea came to the Mongol court to negotiate terms with Mongke Khan as well. From 1252 on King Hethum I of Lesser Armenia began his journey to Mongolia. He brought many sumptuous presents, and met with Mongke at Karakorum.[20] He had an audience with Mongke on September 13, 1254, advised the Khagan on Christian matters in Western Asia, and obtained from Mongke Khan documents guaranteeing the inviolability of his person and his kingdom. Hethum asked the Khagan and his officials to convert into Christianity. In reply, Mongke explained that he really wished his subjects to truly worship Messiah but he could not force the Mongols and other civilians to change their religion. Mongke also informed him that he was preparing to mount an attack on Baghdad and that he would remit Jerusalem to the Christians if they collaborated with him.[21] Hethum strongly encouraged other Crusaders to follow his example and submit to Mongol overlordship, but persuaded only his son-in-law Bohemond VI, ruler of the Principality of Antioch and County of Tripoli, who offered his own submission sometime in the 1250s.[22] The armies of the Kingdom of Cilician Armenia and Bohemond VI would assist Mongke's army in the West soon.
The Mongol shamans played an important role in the court and sometimes influenced the war preparation.
Period of conquests
As Khagan, Möngke seemed to take the legacy of world conquest he had inherited much more seriously than did Güyük. His conquests were all directed to East Asia and the Middle east.
 Audience with Möngke Khagan. Tarikh-i Jahangushay-i Juvaini
Audience with Möngke Khagan. Tarikh-i Jahangushay-i Juvaini
Conquest of the Goryeo Dynasty
Main article: Mongol invasions of KoreaIn his first plans of the Mongol conquests, Mongke chose Korea and Dali Kingdom in Yunnan in 1252.
Mongke sent envoys to the Goryeo, announcing his coronation in October 1251. He also demanded the King Gojong to summon before him in person and move his headquarter from Ganghwa Island to the mainland of Korea. But the Goryeo court refused to send the king because the old king was unable to go so far. Mongke dispatched his envoys with specific tasks again. The envoys were well-received by the Goryeo officials but they criticized the Goryeo officials that their king did not follow his overlord Mongke's orders.[23] Mongke ordered the prince Yeku to command the army against Korea. However, a Korean in the court of Mongke convinced them to begin their campaign in July 1253. Yeku, along with Amuqan, demanded the Goryeo court to surrender. The court refused but did not resist the Mongols and gathered the peasentry into the mountain fortresses and islands. Working together with the Goryeo commanders who had joined the Mongols, Jalairtai Qorchi ravaged Korea. When one of Yeku's envoys arrived, Gojong personally met him at his new palace. The king Gojong sent his stepson as hostage to Mongolia. The Mongols agreed to cease fire in January 1254.
However, Mongke realized that the hostage was not the blood prince of the Goryeo Dynasty. So Mongke blamed the Goryeo court for deceiving him. Mongke's commander Jalairtai devastated much of the Goryeo and took 206,800 captives in 1254.[24] Famine and despair forced peasants to surrender to the Mongols. They established a chiliarchy office at Yonghung with local officials. Ordering defectors to build ships, the Mongols began attacking the coastal islands from 1255 on.[25] In the Liaodong Peninsula, the Mongols formed Korean defectors into a colony of eventually 5,000 households.
In 1258 the king and the Choe clan retainer Kim Jun staged a counter-coup, assassinated the head of the Choe family and sued for peace. When the Goryeo court sent the future king Wonjong of Goryeo as hostage to the Mongol court and promised to return to Gaegyeong, the Mongols withdrew from Korea.
Yunnan, Vietnam and Tibet
Main articles: Mongol invasion of China, Mongol invasion of Vietnam, and Mongol-Tibetan relations in the 13th and 14th centuriesMöngke concerned himself more with the war in China, outflanking the Song Dynasty through the conquest of Yunnan in 1254 and an invasion of Indochina, which allowed the Mongols to invade from north, west, and south.
Mongke Khan dispatched Kublai to the Dali Kingdom in 1253. The ruling faimly, Gao, resisted and murdered Mongol envoys. The Mongols divided their forces into three. One wing rode eastward into the Sichuan basin. The second column under Uryankhadai took a difficult way into the mountains of western Sichuan.[26] Kublai himself headed south over the grasslands, meeting up with the first column. While Uryankhadai galloping in along the lakeside from the north, Kublai took the capital city of Dali and spared the residents despite the slaying of his ambassadors. The Mongols appointed King Duan Xingzhi as local ruler and stationed a pacification commissioner there.[27] After Kublai's departure, unrest broke out among the Black jang. By 1256, Uryankhadai, the son of Subutai had completely pacified Yunnan. After subjugating the Dali, Kublai sent one column under Uriyankhadai to south. Uriyankhadai sent envoys to ask the Vietnamese a route to attack Southern Song Dynasty. But the Tran Vietnamese imprisoned Mongol envoys.[28] This action led Uriyankhadai and his son Aju to invade Vietnam with 3,000 Mongols and 10,000 Yi tribesmen.[28] In 1257, a Mongol column under Uriyankhadai, the son of Subutai, invaded Vietnam (then known as Đại Việt or Great Land of the Viet people), routing the Vietnamese militants and sacking the capital at Thanh Long (renamed Hanoi in 1831). He executed its inhabitants for the murder of the envoys. After staying in Thang Long for a while, the Mongols fell ills due to unfamiliar climate. Realizing that it was time to drive the Mongols out, the Vietnamese launched a counter attack and won the decisive battle of Dong Bo Dau. In order to sooth the Mongol and prevent further war, the Tran accepted Mongol overlorship[29] Uriyankhadai withdrew when the Tran Emperor accepted Mongol overlordship.[30] The Vietnamese king Trần Thái Tông paid tribute to Uriyankhadi who had quickly evacuated Vietnam to escape malaria. The Trần Dynasty accepted terms of the vassalage and sent tributes to the administration of Mongke.[31]
In order to strengthen his control over Tibet, Mongke made Qoridai commander of the Mongol and Han troops in Tufan in 1251. In 1252-53 Qoridai invaded Tibet, reaching as far as Damxung. The Central Tibetian monasteries submitted to the Mongols and the Mongol princes divided between them as their appanages.
Conflicts with the Delhi Sultanate
Main article: Mongol invasions of IndiaIn 1252-3 Sali Noyan of the Tatar clan was sent to the Indian borderlands at the head of fresh troops, and was given authority over the Qaraunas. Sali himself was subordinate to Mongke's brother Hulegu. Due to the internal conflicts of the Delhi Sultanate, the Mamluk Sultan Nasir ud din Mahmud's brother, Jalal al-Din Masud, fled into Mongol territory in 1248. When Mongke was crowned as Khagan, Jalal al-Din Masud attended the ceremony and asked help from Mongke. Mongke ordered Sali to assist him to recover his ancestral realm.[32] Sali made successive attacks on Multan and Lahore. Sham al-Din Muhammad Kart, the client malik of Herat, accompanied the Mongols. Jalal al-Din was installed as client ruler of Lahore, Kujah and Sodra. In 1254 the Delhi official Kushlu Khan offered his submission to Mongke Khan and accepted a Mongol darugachi. When he failed to take Delhi, Kushlu turned to Hulegu. In the winter of 655/1257-8 Sali Noyan entered Sind in strength and dismantled the fortifications of Multan; his forces may also have invested the island fortress of Bakhkar on the Indus.[33]
Conquest of the Middle East
Hulegu imprisons the Caliph Al-Musta'sim among his treasures to starve him to death. ("Le livre des merveilles", 15th-c.)
When Mongke called a kurultai to prepare the next conquest in 1252/1253, the Sultanate of Rum and the Lu'lu'id dynasty of Mosul were subject to the Mongol Empire. The Ayyubid ruler of Mayyafariqin, Malik Kamil, and his cousin in Aleppo and the future Sultan, Malik Nasir Yusuf sent envoys to Mongke Khan, who imposed darugachis (overseers) and a census on the Diyarbakir area.[34]
After the defeat of the Ogedeid and Chagataid families, Mongke eliminated their territory, assigning acquiescent members of the family new territories either in Turkestan or in northwest China. In another move to consolidate his power, Mongke gave his brothers Kublai and Hulegu supervisory powers in North China and Iran. Rumors spread that his brother Kublai founded a de facto independent ulus (district) and perhaps took for himself some of the tax receipts that should by rights be coming to Karakorum. In 1257 the Emperor sent two tax inspectors to audit Kublai's official. They found fault, listed 142 breaches of regulations, accused Chinese officials, even had some executed and Kublai's office was abolished. Mongke's authority took over the collection of all taxes in Kublai's estates. As his Confucian and Buddhist advisers pointed out, Kublai first sent his wives to the court of Khagan and then appealed to Mongke in person. They embraced in tears and Mongke forgave his brother.
Some sources say the Ismaili-Hashashin's imam Alaud-Din dispatched hundreds of assassins to kill Mongke in his palace.[35] Shams-ud-Din, the chief judge of Qazvin, had denounced the menace of the Ismailis. Hence, Mongke decided to exterminate the sect. This is sometimes called the First War on Terror (as by John Man in "Kublai Khan". Mongke ordered the Jochid and Chagataid families to join Hulegu's expedition to Iran and strengthened the army with 1,000 siege engineers from China. Möngke's armies, led by his brother Hulegu (c. 1217–65), launched an attack on the Ismailis in Iran, crushing the last major resistance there by the end of 1256. The Hashashin Imam Rukn ad-Din requested permission to travel to Karakorum to meet with the Great Khan Mongke himself. Hulegu sent him on the long journey to Mongolia, but once the Imam arrived there, Mongke criticized his action and dismissed him. Rukn ad-Din was killed in uncertain circumstances. For the Abbasids, envoys from Baghdad attended the coronation of Mongke in 1251 to come to terms with the Mongols. However, Mongke told Hulegu whether the Caliph Al-Musta'sim refused to meet him in person, then Hulegu was to destroy Baghdad. Hulegu then advanced on Iraq, taking the capital at Baghdad in 1258. Hulegu sent Mongke some of his war booty with the news of his conquest of Baghdad. Mongke dispatched a Chinese messenger to congratulate for his victory in reply. Outraged by the attack on the caliphate, Malik Kamil revolted, killing his Mongol overseer. Hulegu's son Yoshumut invested Mayyafariqin and executed Malik Kamil. From there they moved into Syria in 1259, took Damascus and Aleppo, and reached the shores of the Mediterranean. Fearing of the Mongol advance, the Ayyubid Sultan Malik Nasir Yusuf refused to see Hulegu and fled. However, the Mongols captured him at Gaza.
South China
Main article: Mongol conquest of the Song DynastyIn 1241 Töregene Khatun had sent an envoy to make peace proposals and discuss Zhao Yun of the Song. The Song court arrested the envoy and imprisoned him in a fortress with his suite of seventy persons.[36] The envoy died but his suite were detained until 1254. That year the Mongol army attacked to take Ho-chiu but failed. The Chinese freed the suite of the late envoy to show their desire for peace.
Mongke concentrated all his attention on the conquest of the Song Dynasty. Taking personal command late in the decade, he captured many of the fortified cities along the northern front. In October 1257 Mongke set out for South China, leaving his administration to his brother, Ariq Böke, in Karakorum with Alamdar as assistant, and fixed his camps near the Liu-pan mountains in May of the following year. He first attacked Song positions in Sichuan and took Paoning in 1258.[37] Mongke forbade his army to plunder civilians. When his son accidentally destroyed a crop in the field of the Chinese peasents, Mongke punished him.
On February 18, 1259, Tsagaan Sar, the Mongol New Year feast was given by Mongke near the mountain Chung-kwe.[38] At this feast his relative, Togan, a chief of the Jalayir tribe, declared that South China was dangerous through its climate, and that the Great Khagan should go northward for safety. Baritchi of the Erlat tribe called this advice cowardly and advised Mongke to remain with his army. These words pleased Mongke who wished to take the city nearby. The Song commander slew his envoy who had been sent to ask the city's submission.
Mongke's siege of Hochwan (Hechuan) was prolonged. Meanwhile, Kublai was laying siege to Wuchang, and Uryankhadai attacked Kwangsi and then went on to Hunan.[39] During the second year of the campaign, the weather became extremely hot. Many of the Mongol soldiers suffered from bloody diarrhea (plagues) and Mongke Khan became ill.
Death
 Portrait of Möngke
Portrait of Möngke
While conducting the war in China at Fishing Town in modern-day Chongqing, Möngke died perhaps of dysentery[40] or cholera near the site of the siege on August 11, 1259.[41][42][43] His youngest wife, Chubei, died a month after Mongke at the Liupanshan Mountains. Mongke's son Asutai conducted the corpse to Burkhan Khaldun,[44] Mongolia, where the late Khagan was buried, near the graves of Genghis and Tolui. Once again the worldwide campaigns of the Mongols came to a sudden halt.
As the only Great Khan to have ever died during the campaign, several different accounts have been published as to how he perished. Some reports indicated that he died of cholera. Persian accounts assert that he died of dysentery. Armenian historian Hayton of Corycus says that the Mongol war ship sank in the Chinese seas, with it Mongke, while the Mongols were besieging an island fortress.[45] According to a Syrian chronicle, he is also reported to have been killed by an arrow shot by a Chinese archer during the siege. However, another Chinese account tells that he died of a wound caused by cannon fire or a projectile launched from a Song Chinese trebuchet, while the Mongolians covered up the story by claiming that his death was due to illness to maintain their soldiers' morale. While Möngke left a will declaring that the town should be massacred once taken, its siege continued for another 17 years before the defenders of the town surrendered themselves to Kublai Khan, who promised to spare the lives of the town's residents.
Möngke's death led to the 4-year succession war between his two younger brothers: Kublai Khan and Ariq Boke. Though Kublai Khan eventually won the battle against Ariq Boke, the succession war essentially marked the end of the unified Mongol empire. It was not until 1304, when all Mongol khans submitted to Kublai's successor, the Khagan Temür Öljeytü, that the Mongol world again acknowledged a single paramount sovereign for the first time since 1259 - and even the late Khagans' authority rested on nothing like the same foundations as that of Genghis Khan and his first three successors.[46][47]
When Kublai Khan established the Yuan Dynasty in China in 1271, Möngke Khan was placed on the official record of the dynasty as Xianzong (simplified Chinese: 宪宗; traditional Chinese: 憲宗; pinyin: Xiànzōng).
Architecture
In 1252–53, Flemish missionary and explorer William of Rubruck saw Hungarians, Russians, Germans and a Parisian goldsmith, Guillaume Boucher, in Karakorum.[48] He even heard of Saxon miners in Zungaria. Foreigners such as a woman from Lorraine, mastered the making of the Mongol gers.
 The Model of the Khan Palace in Karakorum in the National History Museum of Mongolia in Ulaan-Baatar
The Model of the Khan Palace in Karakorum in the National History Museum of Mongolia in Ulaan-Baatar
In 1253, Mongke deported 5,00[clarification needed] households from China to repair and maintain the imperial ordos. He decorated the capital city of Karakorum with Chinese, European and Persian architectures. One example of those constructions was a large silver tree, with pipes that discharge various drinks and a triumphant angel at its top, made by Guillaume Boucher. Foreign merchants’ quarters, Buddhist monasteries, Mosques and Christian Churches were newly built. Markets were in the Muslim sector and outside the four gates. Chinese farmers grew vegetables and grains outside the wall of Karakorum.
Marriage and children
See also: Family tree of Genghis KhanMongke married first Qutuqui of the Ikheres clan. Their children included 2 boys and 1 girl:
- Baltu
- Urendash
- the princess Baylun
Mongke married Oghul-Khoimish (Oghul Teimish) of the Oirats. She bore two daughters.
- Shirin
- Bichike
Mongke's youngest wife was Chubei (d.1259).
There were the most favored two concubines among his many wives and concubines. Herein:
- Bayavchin of the Bayid clan.
- Shiregi
- Quitani of the Eljigin clan
- Asutai, the prince who supported the election of Arik Boke.
Notes
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica - see: Möngke
- ^ C.P.Atwood-Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, p.362
- ^ Jack Weatherford - The Secret History of the Mongol Queens, p.135
- ^ Willem van Ruysbroeck, Peter Jackson, David Morgan, Hakluyt Society -The mission of Friar William of Rubruck: his journey to the court of the Mongols, p. 168
- ^ John Man-Kublai Khan, p.32
- ^ Leo de Hartog-Genghis Khan, p.168
- ^ Lawrence N. Langer - Historical dictionary of medieval Russia, p.131
- ^ J.Weatherford-Genghis Khan and the making of the modern world, p.169
- ^ C.P.Atwood-Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, p.364
- ^ Jack Weatherford, Genghis Khan and the making of the modern world, p.176
- ^ Jack Weatherford, Genghis Khan and the making of the modern world, p.175-176
- ^ Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, p. 362
- ^ C.P.Atwood-Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, p.78
- ^ Thomas T. Allsen-Mongol Imperialism, p.142
- ^ Kirakos Ganjakets'i'-History of the Armenians, $63 and $64
- ^ André Wink-Al-Hind, the Making of the Indo-Islamic World, p.208
- ^ Kokuan Sun-Yu chi and Southern Taoism during the Yuan period, in China under Mongol rule, p.212-253
- ^ "Hethoum I receiving the homage of the Tatars: during his voyage to Mongolia in 1254, Hethoum I was received with honours by the Mongol Khan who "ordered several of his noble subjects to honour and attend him"" in Le Royaume Armenien de Cilicie Claude Mutafian, p.58, quoting Hayton of Corycus.
- ^ Jack Weatherford-Genghis Khan, p.175
- ^ Emil Bretschneider tr. of Kirakos Gandzaketsi, The Journey of Haithon, King of Little Armenia, To Mongolia and Back, Mediaeval Researches Vol 1, Trubner Oriental Series 1888 London, facsimile reprint 2005 Elibron Classics ISBN 1-4021-9303-3
- ^ Runciman, p.297
- ^ The Islamic World in Ascendency: From the Arab conquest to the Siege of Vienna by Dr. Martin Sicker (p.111): "Bohemond, however, resided exclusively in Tripoli and, as a practical matter, Hetoum, whose realm was contiguous with it, ruled Antioch. Accordingly, Antioch was drawn into the Mongolian-Armenian alliance".
- ^ J.Bor-Mongol hiigeed Eurasiin diplomat shashtir, boyi II, p.254
- ^ John Man-Kublai Khan, p.208
- ^ C.P.Atwood-Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, p.319
- ^ John Man-Kublai Khan, p.79
- ^ C.P.Atwood-Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongols, p.613
- ^ a b Christopher Pratt Atwood - Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol empire, p.579
- ^ . Tran, Trong Kim - Viet Nam Su Luoc, p.52
- ^ Matthew Bennett, Peter - The Hutchinson Dictionary of Ancient & Medieval Warfare, p.332
- ^ C.P.Atwood, Ibid, p.579
- ^ The Delhi Sultanate: A Political and Military History, p.111
- ^ The Delhi Sultanate: A Political and Military History, p.112
- ^ Reuven Amitai-Preiss-Mongols and Mamluks: the Mamluk-Īlkhānid War, 1260-1281, p.78
- ^ Jack Weatherford-Genghis Khan, p.179
- ^ Jeremiah Curtin - The Mongols: A History, p.327
- ^ René Grousset - The Empire of the Steppes: A History of Central Asia, p.284
- ^ Jeremiah Curtin - The Mongols: A History, p.329
- ^ The Empire of the Steppes By René Grousset, p.284
- ^ John Joseph Saunders - The history of the Mongol conquests, p.120
- ^ George Lane - Daily life in the Mongol empire, p.9
- ^ John Man - Kublai Khan, p.98
- ^ Jack Weatherford - Genghis Khan and the making of the modern world, p.188
- ^ Christoph Baumer, John Hare - Traces in the Desert: Journeys of Discovery Across Central Asia, p.57
- ^ Henry Hoyle Howorth - History of the Mongols: The Mongols Proper and the Kalmuks, p.214
- ^ Peter Jackson-The Mongols and the West, p.127
- ^ Lubin, Nancy. "Rule of Timur". In Curtis.
- ^ Christopher Dawson - Mission to Asia, p.129
References
- The Empire of the Steppes by René Grousset, Rutgers University Press, 1970 ISBN 0813513049
- Genghis Khan and the Making of the Modern World by Jack Weatherford
- Mongol Imperialism: The Policies of the Grand Qan Möngke in China, Russia, and the Islamic Lands, 1251-1259 by Thomas T. Allsen, University of California Press, 1987 ISBN 0520055276
- The mission of William of Rubruck: His journey to the court of the Great Khan Möngke 1253-1255 by William, Peter Jackson, David Morgan, Hakluyt Society, Hakluyt Society, Hakluyt Society, 1990
Möngke KhanHouse of Borjigin (1206–1634)Born: 1209 Died: 1259Regnal titles Preceded by
Oghul Qaimish (regent)Great Khan of the Mongol Empire
1251–1259Succeeded by
Kublai Khan
Ariq BökeKhagans of the Mongol Empire (1206–1370) Genghis Khan (1206–1227) • Tolui Khan (regent) (1227–1229) • Ögedei Khan (1229–1241) • Töregene Khatun (regent) (1241–1246) • Güyük Khan (1246–1248) • Oghul Qaimish (regent) (1248–1251) • Möngke Khan (1251–1259) • Kublai Khan (1260–1294) The Kublaid Great Khans Temür Khan (1294–1307) • Külüg Khan (1307–1311) • Ayurbarwada Buyantu Khan (1311–1320) • Gegeen Khan(1320–1323) • Yesün Temür Khan (1323–1328) • Ragibagh Khan (1328) • Jayaatu Khan (1328–1329) • Khutughtu Khan (1329) • Jayaatu Khan(1329–1332) • Rinchinbal Khan (1332) • Ukhaantu Khan (1333–1370) 
List of emperors of the Yuan Dynasty (1271–1370) Early Mongol rulers posthumously promoted by Kublai Khan as Yuan emperors
Taizu · Ruizong(regent) · Taizong · Dingzong · Xianzong · Shizu
Officially assuming the role of Emperor of China starting with Kublai Khan(Yuan Shizu) in 1271
Following conquest of Southern Song Dynasty in 1279 ruled all of China
Shizu · Chengzong · Wuzong · Renzong · Yingzong · Taiding Di · Tianshun Di · Wenzong · Mingzong · Wenzong · Ningzong · HuizongCategories:- 1209 births
- 1259 deaths
- Borjigin
- Great Khans of the Mongol Empire
- Monarchs killed in action
- Mongol Empire
- People of the Mongol Empire
- 13th-century Mongolian monarchs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.