- Prednisone
-
For the active metabolite of prednisone which is also used as a drug including as eye drops, see prednisolone.
Prednisone 

Systematic (IUPAC) name 17,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,11,20-trione Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a601102 Pregnancy cat. C Legal status Rx Only (US) Routes Oral, Nasal, Rectal, Injection, IV Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 70% Metabolism prednisolone (liver) Half-life 1 hour Excretion Renal Identifiers CAS number 53-03-2 
ATC code A07EA03 H02AB07 PubChem CID 5865 DrugBank APRD00340 ChemSpider 5656 
UNII 3EN3HG4WSW 
KEGG C07370 
ChEBI CHEBI:8382 
ChEMBL CHEMBL635 
Synonyms Deltasone, Liquid Pred, Orasone, Adasone, Deltacortisone, Prednisonum Chemical data Formula C21H26O5 Mol. mass 358.428 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Prednisone is a synthetic corticosteroid drug that is particularly effective as an immunosuppressant drug. It is used to treat certain inflammatory diseases and (at higher doses) some types of cancer, but has significant adverse effects. Because it suppresses the immune system, it leaves patients more susceptible to infections.
It is usually taken orally but can be delivered by intramuscular injection or intravenous injection. It has a mainly glucocorticoid effect. Prednisone is a prodrug that is converted by the liver into prednisolone, which is the active drug and also a steroid.
Contents
Medical uses
Prednisone is used for many different indications including: asthma, COPD, rheumatic disorders, allergic disorders, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, adrenocortical insufficiency, hypercalcemia due to cancer, thyroiditis, severe tuberculosis, lipid pneumonitis, multiple sclerosis, nephrotic syndrome, myasthenia gravis, and as part of a drug regimen to prevent rejection post organ transplant.[1]
Prednisone has also been used in the treatment of migraine headaches and cluster headaches and for severe aphthous ulcer. Prednisone is used as an antitumor drug.[2] Prednisone is important in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Non-Hodgkin lymphomas, Hodgkin's lymphoma, multiple myeloma and other hormone-sensitive tumors, in combination with other anticancer drugs.
Prednisone is also used for the treatment of the Herxheimer reaction, which is common during the treatment of syphilis, and to delay the onset of symptoms of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The mechanism for the delay of symptoms is unknown. Because it suppresses the adrenals, it is also sometimes used in the treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Prednisone is also used to treat sarcoidosis and lupus.
Side-effects
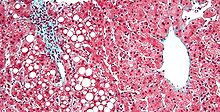 Micrograph of fatty liver, as may be seen due to long-term prednisone use. Trichrome stain.
Micrograph of fatty liver, as may be seen due to long-term prednisone use. Trichrome stain.
Short-term side-effects, as with all glucocorticoids, include high blood glucose levels, especially in patients with diabetes mellitus or on other medications that increase blood glucose (such as tacrolimus) and mineralocorticoid effects such as fluid retention (it is worth noting, however, that the mineralocorticoid effects of prednisone are very minor; this is why it is not used in the management of adrenal insufficiency, unless a more potent mineralocorticoid is administered concomitantly).
Additional short-term side-effects can include insomnia, euphoria and, rarely, mania (in particular, in those suffering from Bipolar disorders I and II).
Long-term side-effects include Cushing's syndrome, truncal weight gain, osteoporosis, glaucoma and cataracts, type II diabetes mellitus, and depression upon dose reduction or cessation.
Major
- Increased blood sugar for diabetics
- Difficulty controlling emotion
- Difficulty in maintaining train of thought
- Weight gain
- Facial swelling
- Depression, mania, psychosis, or other psychiatric symptoms
- Unusual fatigue or weakness
- Mental confusion / indecisiveness
- Blurred vision
- Abdominal pain
- Peptic ulcer
- Infections
- Painful hips or shoulders
- Steroid-induced osteoporosis
- Stretch marks
- Osteonecrosis
- Long-term migraines
- Insomnia
- Severe joint pain
- Cataracts or glaucoma
- Anxiety
- Black stool
- Stomach pain or bloating
- Severe swelling
- Mouth sores or dry mouth
- Avascular necrosis
- Hepatic steatosis
Minor
- Nervousness
- Acne
- Rash
- Increased appetite
- Hyperactivity
- Frequent urination
- Diarrhea
- Removes intestinal flora
- Leg pain/cramps
- Sensitive teeth
Dependency
Adrenal suppression will begin to occur if prednisone is taken for longer than seven days. Eventually, this may cause the body to temporarily lose the ability to manufacture natural corticosteroids (especially cortisol), which results in dependence on prednisone. For this reason, prednisone should not be abruptly stopped if taken for more than seven days, instead, the dosage should be gradually reduced. This weaning process may be over a few days, if the course of prednisone was short, but may take weeks or months if the patient had been on long-term treatment. Abrupt withdrawal may lead to an Addisonian crisis. For those on chronic therapy, alternate-day dosing may preserve adrenal function and thereby reduce side-effects.[3]
Glucocorticoids act to inhibit-feedback of both the hypothalamus (decreasing corticotropin-releasing hormone [CRH]) and corticotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland (decreasing the amount of adrenocorticotropic hormone [ACTH]). For this reason, glucocorticoid analogue drugs such as prednisone down-regulate the natural synthesis of glucocorticoids. This mechanism leads to dependence in a short time and can be very dangerous if medications are withdrawn too quickly. The body must have time to begin synthesis of CRH and ACTH and for the adrenal glands to begin functioning normally again.
In industry
The pharmaceutical industry uses prednisone tablets for the calibration of dissolution testing equipment according to the United States Pharmacopeia (USP).
History
The first isolation and structure identifications of prednisone and prednisolone were done in 1950 by Arthur Nobile.[4][5][6] The first commercially feasible synthesis of prednisone was carried out in 1955 in the laboratories of Schering Corporation, which later became Schering-Plough Corporation, by Arthur Nobile and coworkers.[7] They discovered that cortisone could be microbiologically oxidized to prednisone by the bacterium Corynebacterium simplex. The same process was used to prepare prednisolone from hydrocortisone.[8]
The enhanced adrenocorticoid activity of these compounds over cortisone and hydrocortisone was demonstrated in mice.[9]
Prednisone and prednisolone were introduced in 1955 by Schering and Upjohn, under the brand names Meticorten and Delta-Cortef, respectively.[10] These prescription medicines are now available from a number of manufacturers as generic drugs.
References
- ^ "Prednisone". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. http://www.drugs.com/monograph/prednisone.html. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- ^ [U.S.] National Library of Medicine, Medical Subject Headings. Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal (2009). Retrieved 9-11-2010
- ^ "Therapeutic and Adverse Effects of Glucocorticoids". Bello CS, Garrett SD. U.S. Pharmacist Continuing Education Program no. 430-000-99-028-H01, August 1999. http://www.uspharmacist.com/NewLook/CE/glucocort/lesson.htm.
- ^ Wainwright, M. "The secret of success: Arthur Nobile's discovery of the steroids prednisone and prednisolone in the 1950s revolutionised the treatment of arthritis". Chemistry in Britain. http://www.worldcat.org/title/the-secret-of-success-arthur-nobiles-discovery-of-the-steroids-prednisone-and-prednisolone-in-the-1950s-revolutionised-the-treatment-of-arthritis/oclc/106716069&referer=brief_results. Retrieved 15 June 2011.
- ^ "National Inventors Hall of Fame". http://www.invent.org/hall_of_fame/355.html.
- ^ "New Jersey Inventors Hall of Fame". http://www.stevens.edu/njinvent/2000/inductees_2000/nobile.html.
- ^ Merck Index, 14th Edition, p.1327. Published by Merck & Co. Inc.
- ^ H.L. Herzog et al. Science, Vol. 121, p 176 (1955).
- ^ H.L. Herzog et al. Science, Vol. 121, p 176 (1955).
- ^ http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm
External links
- Kelly, Janis (July 2000). "Prednisone-related growth impairment persists in children with CF". Respiratory Reviews 5 (7). http://www.respiratoryreviews.com/jul00/rr_jul00_prednisone.html.
- National Inventors Hall of Fame induction of Arthur Nobile
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal - Prednisone
- The National Center for Biotechnology Information: Prednisone
Antidiarrheals, intestinal anti-inflammatory/anti-infective agents (A07) Rehydration Intestinal anti-infectives Antibiotics (Neomycin, Nystatin, Natamycin, Streptomycin, Polymyxin B, Paromomycin, Amphotericin B, Kanamycin, Vancomycin, Colistin, Rifaximin)
Sulfonamides (Phthalylsulfathiazole, Sulfaguanidine, Succinylsulfathiazole)
Nitrofuran (Nifuroxazide, Nifurzide)
Arsenical (Acetarsol)
Oxyquinoline (Broxyquinoline)Intestinal adsorbents Antipropulsives (opioids) Opium Tincture (Laudanum) • Codeine • Morphine • Camphorated Opium Tincture (Paregoric)
crosses BBB: Diphenoxylate (Diphenoxylate/atropine) • Difenoxin
does not cross BBB: LoperamideIntestinal anti-inflammatory agents corticosteroids acting locally (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone, Prednisone, Betamethasone, Tixocortol, Budesonide, Beclometasone)
antiallergic agents, excluding corticosteroids (Cromoglicic acid)
aminosalicylic acid and similar agents (Sulfasalazine, Mesalazine, Olsalazine, Balsalazide)Antidiarrheal micro-organisms Other antidiarrheals Categories:- Glucocorticoids
- Prodrugs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.