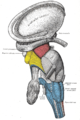
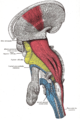
- Posterior external arcuate fibers
-
Posterior external arcuate fibers 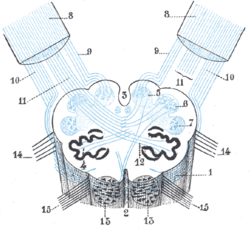
Diagram showing the course of the arcuate fibers. (Testut.) 1. Medulla oblongata anterior surface. 2. Anterior median fissure. 3. Fourth ventricle. 4. Inferior olivary nucleus, with the accessory olivary nuclei. 5. Gracile nucleus. 6. Cuneate nucleus. 7. Trigeminal. 8. Inferior peduncles, seen from in front. 9. Posterior external arcuate fibers. 10. Anterior external arcuate fibers. 11. Internal arcuate fibers. 12. Peduncle of inferior olivary nucleus. 13. Nucleus arcuatus. 14. Vagus. 15. Hypoglossal. 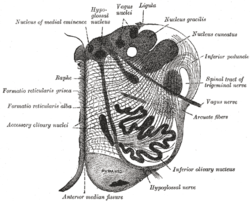
Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Arcuate fibers labeled at center right.) Latin fibrae arcuatae externae posteriores Gray's subject #187 783 The posterior external arcuate fibers (dorsal external arcuate fibers) take origin in the gracile and cuneate nuclei; they pass to the inferior peduncle of the same side.
It is uncertain whether fibers are continued directly from the gracile and cuneate fasciculi into the inferior peduncle.
The term "cuneocerebellar tract" is sometimes used to collectively refer to the posterior external arcuate fibers.[1]
The term "cuneocerebellar tract" is also used to describe an analogue to the dorsal spinocerebellar tract for the upper limbs.[2] In this context, the "cuneo-" derives from the accessory cuneate nucleus, not the cuneate nucleus. (The two nuclei are related in space, but not in function.)
Contents
See also
References
Additional images
External links
- NeuroNames hier-793 - dorsal external arcuate fibers
- NeuroNames hier-800 - cuneocerebellar tract
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Human brain: rhombencephalon, myelencephalon: medulla (TA A14.1.04, GA 9.767) Dorsal SurfacePosterior median sulcus · Posterolateral sulcus · Area postrema · Vagal trigone · Hypoglossal trigone · Medial eminenceafferent: GVA: VII,IX,X: Solitary/tract/Dorsal respiratory group · SVA: Gustatory nucleus · GSA: VIII-v (Lateral, Medial, Inferior)
efferent: GSE: XII · GVE: IX,X,XI: Ambiguus · SVE: X: Dorsal · IX: Inferior salivatory nucleusGrey: otherWhite: Sensory/ascendingWhite: Motor/descendingVentral White: Motor/descendingVentral respiratory group · Arcuate nucleus of medulla · Inferior olivary nucleus · Rostral ventromedial medullaSurfaceGrey: Raphe/
reticularCategories:- Brainstem
- Neuroscience stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.