- Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova
-
For the Soviet-era party, see Communist Party of Moldova.
Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova
Partidul Comuniştilor din Republica Moldova
President Vladimir Voronin Founded October 22, 1993 Headquarters Chişinău Ideology Communism International affiliation Union of Communist Parties — Communist Party of the Soviet Union European affiliation Party of the European Left Official colours Red Parliament 42 / 101District Presidents 10 / 32Website http://www.pcrm.md/ Politics of Moldova
Political parties
ElectionsThe Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova (Moldovan: Partidul Comuniştilor din Republica Moldova (PCRM), Russian: Партия коммунистов Республики Молдова) is a communist political party in Moldova, led by Vladimir Voronin. It is the only communist party to have held a majority in government in the post-Soviet states.[1]
It is part of the Party of the European Left. Perhaps confusingly, its foreign policy tilt is pro-EU and pro-US, rather than pro-Russia like the similarly communist government in Transnistria.
Contents
Activity
It is the current opposition political party in Moldova. After the July 2009 parliamentary election, Alliance For European Integration has agreed to create a governing coalition that pushed the Communist party into opposition.
History
The PCRM was registered as a political party in 1994. The PCRM was part of the Popular Patriotic Forces Front at the time of the 1996 presidential election, in which Voronin stood as the coalition's candidate and won 10.3% of the vote, placing third. The party supported Petru Lucinschi in the second round of the election, and following Lucinschi's victory the PCRM was given two positions in the government.
1998 election
Main article: Moldovan parliamentary election, 1998In the March 1998 parliamentary election, the PCRM won 30.1% of the vote and 40 seats, becoming the largest party in parliament; in its platform, it called for "the rebirth of a socialist society". Despite its strong showing, the PCRM was left in opposition due to the formation of a center-right coalition government, Alliance for Democracy and Reforms. Although Lucinschi later nominated Voronin as Prime Minister of Moldova in late 1999, the nomination was unsuccessful because Voronin did not have enough support in parliament. Subsequently the PCRM received 49.9% of the vote in the February 2001 parliamentary election, winning 71 out of the 101 seats in parliament.[2]
2001 election
Main article: Moldovan parliamentary election, 2001With a PCRM parliamentary majority, Voronin was elected as President by parliament in April 2001. The Constitutional Court ruled that the President could also lead a political party, and Voronin was re-elected as party leader.[2]
2005 election
Main articles: Moldovan parliamentary election, 2005 and Moldovan Parliament 2005-2009It was the ruling political party in Moldova. It won the Moldovan parliamentary election, 2005, and provided the President, Vladimir Voronin, the Prime Minister, Zinaida Greceanîi, and the Speaker of the Moldovan Parliament, Marian Lupu. Under Voronin, it privatized several state-owned industries and governed in a multi-party fashion. It also favors European integration and eventual EU membership.
2009 elections
Main articles: Moldovan parliamentary election, 2009, 2009 Moldova civil unrest, and Moldovan Parliament 2009-2013After April 2009 election and the civil unrest, the climate in Moldova became very polarized.[3] The parliament failed to elect a new president. For this reason, the parliament was dissolved and snap elections were held. At the July 29 polls the Communist Party received 44.7% of the vote. That gave the former ruling party 48 MPs, and the remaining 53 seats in the 101-member chamber went to four opposition parties, Alliance For European Integration.
Political forces Seats Moldovan Parliament seats after July 2009 polls Alliance for European Integration 53 Party of Communists 48 PCRM (48) · PLDM (18) · PL (15) · PDM (13) · AMN (7) The activity of the Party of Communists between 2001 and 2009 will not be covered by the Commission for the Study of the Communist Dictatorship in Moldova only if it is proven that it perpetuates some practices of the former Communist Party of Moldova. The commission will study and analyse the communist regime from 1917 to 1991.
Ideology
According to its Statute adopted in 2008, article 1, the Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova is a "lawful successor and heir of the Communist Party of [Soviet] Moldavia both in terms of ideas and traditions".
While officially espousing a Leninist Communist doctrine, there is debate over their policies. The Economist considers it a centre-right party, communist only in name,[4] whereas Romanian political scientist Vladimir Tismăneanu argues that the party is communist in the classical sense, as it has not changed much since the fall of the Soviet Union.[5] However, Romanian and foreign observers usually are misled by the name of the party, because the Moldovan Communists are far from their cognate parties and certainly different from their Russian counterparts, which are indeed unreformed. Ion Marandici, a Moldovan political scientist considers that the success story of the Moldovan Communists is mainly due to the Communists' capacity to attract the votes of the ethnic minorities and the Romanian-speakers identifying as Moldovans, by proposing a Moldovenist nation and state-project. Also the Communists' control of the major electronic media, the authoritarian practices regarding human rights activists, the support of the West in April 2005 helped their consolidation. The incapacity of the opposition to unite is due mainly to the specific electoral rules providing incentives for the emergence and creation of new parties. The decline of the Communists followed after Marian Lupu, a keyfigure in the Moldovan politics left the Communists' Party and joined the Democratic Party, thus bringing with him the Moldovan supporters of the Communists.[6]
Last proposed electoral program
For the current period of governance, the PCRM has outlined the following goals for the country:
- A new quality of life;
- Economic modernisation;
- European integration;
- Consolidation of the society.
The whole electoral program can be read on the official site of PCRM.
Electoral results
Results since 1998
(year links to election page)Polls Type of Election Votes % MPs 1998 Parliament 487,002 30.01 40 2001 Parliament 794,808 50.07 71 2005 Parliament 716,336 45.98 56 2009 (April) Parliament 760,551 49.48 60 2009 (July) Parliament 704,876 45.07 48 2010 Parliament 676,291 39.29 42 Gallery
-
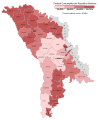
Votes won by PCRM in the April 2009 election by raion and municipality
References
- ^ The Communist Party of the Russian Federation (CPRF) won two parliamentary elections in the 1990s by receiving a plurality (but notably not a majority) of seats in the Duma, however since Russia is a Presidential Republic (and Boris Yeltsin was President at the time), the CPRF was unable to form a government. The Communist Party of South Ossetia, which was de facto independent at the time, won a majority of seats in the 1994 election.
- ^ a b Political Parties of the World (6th edition, 2005), ed. Bogdan Szajkowski, page 414.
- ^ The New York Times, A Polarized Moldova Votes, Mindful of West and Russia, July 29, 2009
- ^ Protests in Moldova and Georgia: Street scenes, The Economist, April 16, 2009
- ^ "Moldova's Revolution Against Cynical And Cronyist Authoritarianism", RFE/RL, April 13, 2009
- ^ Marandici, Ion, The Factors Leading to the Electoral Success, Consolidation and Decline of the Moldovan Communists' Party During the Transition Period (April 23, 2010). Presented at the Midwestern Political Science Association Convention from April 2010 . Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=1809029
External links
Political parties in Moldova 
Parliamentary parties Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova (42) · Liberal Democratic Party of Moldova (32) · Democratic Party of Moldova (15) · Liberal Party (12)Extra-parliamentary parties Christian-Democratic People's Party · Social Democratic Party · National Liberal Party · Party of Socialists of Moldova "Motherland" · Ecologist Party of Moldova "Green Alliance" · Socialist Party of Moldova · Republican Socio-Political Movement Equality · Agrarian Party of Moldova · Party of the Socio-Economic Justice of Moldova · Republican Popular Party · Unionist Movement of the Republic of Moldova · European Action Movement · Party Alliance Our MoldovaAlliances Alliance for Democracy and Reforms · Alliance for European IntegrationHistorical political parties Categories:- Communist parties in the Former Soviet Union
- Communist parties in Moldova
- Political parties established in 1993
- Political parties in Moldova
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.