- Ballistic missile
-
A ballistic missile is a missile that follows a sub-orbital ballistic flightpath with the objective of delivering one or more warheads to a predetermined target. The missile is only guided during the relatively brief initial powered phase of flight and its course is subsequently governed by the laws of orbital mechanics and ballistics. To date, ballistic missiles have been propelled during powered flight by chemical rocket engines of various types.
Contents
History
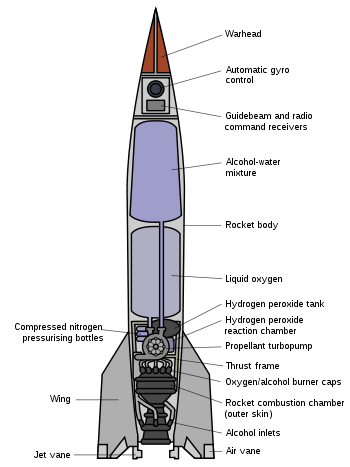
The first ballistic missile was the A-4,[1] commonly known as the V-2 rocket, developed by Nazi Germany in the 1930s and 1940s under direction of Wernher von Braun. The first successful launch of a V-2 was on October 3, 1942 and began operation on September 6, 1944 against Paris, followed by an attack on London two days later. By the end of World War II, May 1945, over 3,000 V-2s had been launched.
A total of 30 nations have deployed operational ballistic missiles. Development continues, with around 100 ballistic missile flight tests (not including those of the US) in 2007, mostly by China, Iran and the Russian Federation.[citation needed] In 2010 the US and Russian governments signed a treaty to reduce their inventory of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) over a seven year period (to 2017) to 1550 units each.[2]
Flight
A ballistic missile trajectory consists of three parts: the powered flight portion, the free-flight portion which constitutes most of the flight time, and the re-entry phase where the missile re-enters the Earth's atmosphere.
Ballistic missiles can be launched from fixed sites or mobile launchers, including vehicles (transporter erector launchers, TELs), aircraft, ships and submarines. The powered flight portion can last from a few tens of seconds to several minutes and can consist of multiple rocket stages.
When in space and no more thrust is provided, the missile enters free-flight. In order to cover large distances, ballistic missiles are usually launched into a high sub-orbital spaceflight; for intercontinental missiles the highest altitude (apogee) reached during free-flight is about 1200 km.
The re-entry stage begins at an altitude where atmospheric drag plays a significant part in missile trajectory, and lasts until missile impact.
Missile types
 Trident II SLBM launched by ballistic missile submarine.
Trident II SLBM launched by ballistic missile submarine.
Ballistic missiles can vary widely in range and use, and are often divided into categories based on range. Various schemes are used by different countries to categorize the ranges of ballistic missiles:
- Tactical ballistic missile: Range between about 150 km and 300 km
- Battlefield range ballistic missile (BRBM): Range less than 200 km
- Theatre ballistic missile (TBM): Range between 300 km and 3,500 km
- Short-range ballistic missile (SRBM): Range 1,000 km or less
- Medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM): Range between 1,000 km and 3,500 km
- Intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) or long-range ballistic missile (LRBM): Range between 3,500 km and 5,500 km
- Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM): Range greater than 5,500 km
- Submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM): Launched from ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs), all current designs have intercontinental range.
Short- and medium-range missiles are often collectively referred to as theater or tactical ballistic missiles (TBMs). Long and medium-range ballistic missiles are generally designed to deliver nuclear weapons because their payload is too limited for conventional explosives to be cost-effective (though the U.S. may be evaluating the idea of a conventionally-armed ICBM for near-instant global air strike capability despite the high costs).[citation needed]
The flight phases are like those for ICBMs, except with no exoatmospheric phase for missiles with ranges less than about 350 km.
Quasi ballistic missiles
A quasi ballistic missile (also called a semi ballistic missile) is a category of missile that has a low trajectory and/or is largely ballistic but can perform maneuvers in flight or make unexpected changes in direction and range.[citation needed]
At a lower trajectory than a ballistic missile, a quasi ballistic missile can maintain higher speed, thus allowing its target less time to react to the attack, at the cost of reduced range.
The Russian Iskander is a quasi ballistic missile.[3]The Russian Iskander-M cruises at hypersonic speed of 2,100–2,600 m/s (Mach 6 - 7) at a height of 50 km. The Iskander-M weighs 4,615 kg carries a warhead of 710 – 800 kg, has a range of 480 km and achieves a CEP of 5 – 7 meters. During flight it can maneuver at different altitudes and trajectories to evade anti-ballistic missiles.[4][5]
China has recently developed the first and only anti-ship ballistic missile in the world, that combines a maneuverable reentry vehicle (MaRV) with a terminal guidance system, allowing them to adjust the flight path as they near their target, and are thought to be in use by the People's Liberation Army as of late 2010.[citation needed]
Comparable systems
- Hadès
- Iskander
- MGM-140B/E ATACMS
- Oka
- Shaurya
- Tochka
See also
- List of ICBMs
- List of NATO reporting names for ballistic missile submarines
- Cruise missile
- Surface-to-surface missile
- Quasiballistic missile
- Anti-ballistic missile
- Anti-ballistic missile treaty
- Ballistic missile submarine
- Atmospheric reentry
- Weapons of mass destruction
- Comparison of lift launch systems
- List of weapons
- List of missiles
- List of missiles by nation
- List of currently active missiles of the United States military
- List of orbital launch systems
- List of rocket planes
- List of sounding rockets
- List of unguided rockets
- List of upper stages
- List of artillery#Rockets
- Model rocket
- Intercontinental ballistic missile
- Expendable launch system
- NATO reporting name (has lists of various Soviet missiles)
References
- ^ Zaloga, Steven (2003). V-2 Ballistic Missile 1942-52. Reading: Osprey Publishing. p. 3. ISBN 9781841765419.
- ^ http://www.state.gov/documents/organization/140035.pdf
- ^ Shaurya surfaces as India's underwater nuclear missile
- ^ SS-26 Iskander-M
- ^ SS-26 Stone Iskander 9M72 9P78EBallistic missile system
Further reading
Bate, Mueller, White (1971). Fundamentals of Astrodynamics. Dover Publications, New York. ISBN 0-486-60061-0
External links
- Ballistic Missiles and Ballistic Missile Defence
- An introduction to ballistic missiles
- Ballistic missiles on the Numbers - Center for American Progress
- Cirincione, Joeseph & Andrew Wade (2007). www.americanprogress.org/issues/2007/05/missiles.html Get Smart on Ballistic Missiles – The Center for American Progress
- Photos of Russian Strategic Missile Forces museum
Types of missile By platform - Air-to-air missile (AAM)
- Air-to-surface missile (ASM)
- Surface-to-air missile (SAM)
- Surface-to-surface missile (SSM)
- Ballistic missile
- Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM)
- Submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM)
- Anti-ballistic missile (ABM)
- Intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM)
- Cruise missile
- Anti-ship missile (AShM)
- Anti-submarine missile
- Anti-tank missile (ATGM)
- Anti-satellite weapon (ASAT)
- Air-launched ballistic missile
- Anti-ship ballistic missile (ASBM)
By guidance Lists - List of missiles
- List of missiles by country
- List of military rockets
Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Ballistic missiles
- Missile types
- Ballistics
- Unmanned vehicles
- Tactical ballistic missile: Range between about 150 km and 300 km
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.