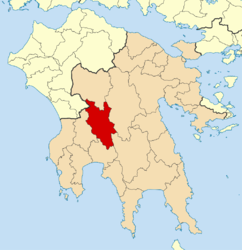
- Megalopolis, Greece
-
Megalopoli
Μεγαλόπολη
Location Coordinates 37°24′N 22°8′E / 37.4°N 22.133°ECoordinates: 37°24′N 22°8′E / 37.4°N 22.133°E Government Country: Greece Region: Peloponnese Regional unit: Arcadia Population statistics (as of 2001) Municipality - Population: 13,152 - Area: 727.3 km2 (281 sq mi) - Density: 18 /km2 (47 /sq mi) Municipal unit - Population: 8,657 Community - Population: 5,135 Other Time zone: EET/EEST (UTC+2/3) Elevation (center): 430 m (1,411 ft) Postal: 222 00 Telephone: 27910 Auto: TP Megalópoli (Μεγαλόπολη) is a town in the western part of the peripheral unit of Arcadia, southern Greece. It is located in the same site as ancient Megalopolis (Ancient Greek: Μεγαλόπολις). "Megalopolis" is a Greek word for Great city. When it was founded, in 371 BC, it was the first urbanization in rustic and primitive Arcadia. In ancient times, the town grew very large. Its theater, known to have a capacity for 20,000 people was one of the largest known. In Byzantine and Ottoman times the city was known as Sinanou (Σινάνο) until the 19th century.
The population in 2001 reached over 5,000. Megalopoli's distance from Tripoli, Greece is 30 km (19 mi). Megalopoli is located 33 km (21 mi) SE from Andritsaina and 55 km (34 mi) NE from Kalamata on Greek National Road 7, and E65. The mountains surrounding Megalopoli are Taygetus, and Tsiberou. Its nearest television and communications tower are on top of mount Tsiberou. Much of the area is isolated, and the forested valley contains about 10,000 people. It is one of the most underpopulated areas in the Peloponnese. It is situated between the Alfeios and the Elisson rivers.
Megalopoli has three schools, lyceums, gymnasia, churches, banks, hotels, a post office and squares (plateia). It also has a train station with a freight yard 1 km from downtown. The track does not pass through to Tripoli. The line for Kalamata – Tripoli – Argos – Corinth is 4 km (2.5 mi) S. A wider highway opened southwest around the 1980s. Megalopolis is now bypassed by a new freeway connecting Kalamata to Athens, which was opened to traffic in 2002. The freeway runs between the little villages Perivolia and Routsi, near Alfeios river.
In the mid-1960s, the Public Power Corporation of Greece (PPC S.A.) (DEI) and the government started construction on a power plant. The power plant is approximately 8 km NW of downtown. It was first opened in 1969. It provides electric power to southern Greece. A lignite mining area is situated around the plant. Part of the population are employees of this plant.
Contents
Antiquity
Megalopolis is famous for its ancient ruins situated northwest, which include an ancient theatre that used to hold up to 20,000 people and was 30 m (100 feet) tall. Other landmarks include the Thersileon with 67 pillars and a temple (11.5 m × 5 m, 37 feet x 11 feet). Herodotus reported the ancient belief that the Megalopolis area was a battleground of the Titanomachy. The foundation for this apparently was the presence of lignite deposits, which are prone to catch fire in summer and can smoulder and scorch the earth for weeks (Zeus is supposed to have slain the Titans with lightning bolts; see also below), coupled with the presence of fossil bones of prehistoric elephants and rhinoceroses.[1] Herodotus informs his readers that the bones of "Titans" were exhibited in various places in the surrounding area at least since the 5th century BC.
The city was founded in 371 BC by the Theban general Epaminondas in an attempt to form a political counterweight to Sparta. It was one of the 40 places that were megále pólis (great city). Megalopolis became the seat of the Arcadian League in 370 BC, which in the 3rd century BC became the Achaean League. It used to be one of the about 20,000 places that had an ancient theatre. In 331 BC, Megalopolis was invaded by the Spartans and there was a battle with the Macedonians who came to Megalopolis' help. The Macedonians defeated the Spartans. In 223 BC, the Spartan king Cleomenes burnt down the city but it was reinstated by Philopoemen, a Greek General of the Achaean League. The city fell during the Middle Ages and was refounded after the Greek Independence.
Municipality
The municipality Megalopoli was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 3 former municipalities, that became municipal units:[2]
Subdivisions
The municipal unit of Megalopoli is subdivided into the following communities (villages within the community in brackets):
- Anthochori
- Ano Karyes
- Chirades
- Choremis (Choremis, Apiditsa)
- Chranoi
- Gefyra
- Isaris (Isaris, Petrovouni, Chrousa)
- Isoma Karyon
- Karatoulas
- Kastanochori
- Kato Karyes
- Lykaio
- Lykochia
- Lykosoura
- Makrysi (Makrysi, Kato Makrysi)
- Mallota
- Marathoussa
- Megalopoli (Megalopoli, Oresteio)
- Nea Ekklisoula
- Neochori Lykosouras
- Paradeisia (Paradeisia, Fanaiti)
- Perivolia (Perivolia, Vrysoules)
- Plaka
- Rapsommati
- Souli (Souli, Derveni)
- Soulos
- Thoknia
- Trilofo (Trilofo, Palaiomoiri)
- Tripotamo
- Vangos
- Vastas
Population
Year Municipal district Municipality 1920 1,776 - 1961 2,235 - 1981 4,875 - 1991 4,646 8,888 2001 5,114 8,657 Notable people
- Philopoemen (253-183 BC), general and statesman
- Polybius (c. 203–120 BC), historian
External links
- 3rd Megalopolis Public School (in Greek)
- GTP – Municipality of Megalopoli
- 1911 Britannica article "Megalopolis"
North: Gortyna West: Figaleia Megalopoli East: Valtetsi South: Falaisia See also
- Communities of Arcadia
Administrative division of the Peloponnese Region Area: 15,490 km² • Population : 638,942 (2001) • Capital: Tripoli Regional unit of Arcadia Regional unit of ArgolisRegional unit of CorinthiaRegional unit of LaconiaRegional unit of Messenia
Regional unit of ArgolisRegional unit of CorinthiaRegional unit of LaconiaRegional unit of MesseniaRegional governor: Petros Tatoulis (el) • Website: ppel.gov.gr Subdivisions of the municipality of Megalopoli Municipal unit of Falaisia Municipal unit of Gortyna Atsicholos · Karytaina · Katsimpalis · Kotili · Kourounios · Kyparissia · Mavria · Sarakini · Vlachorraptis · ZoniMunicipal unit of Megalopoli Anthochori · Ano Karyes · Chirades · Choremis · Chranoi · Gefyra · Isaris · Isoma Karyon · Karatoulas · Kastanochori · Kato Karyes · Lykaio · Lykochia · Lykosoura · Makrysi · Mallota · Marathoussa · Megalopoli · Nea Ekklisoula · Neochori Lykosouras · Paradeisia · Perivolia · Plaka · Rapsommati · Souli · Soulos · Thoknia · Trilofo · Tripotamo · Vangos · VastasReferences
- ^ "Prehistoric Fossil May Have Inspired Greek Myths". discovery.com. March 31, 2011. http://news.discovery.com/archaeology/fossil-ancient-greeks-mammal-110331.html. Retrieved April 1, 2011.
- ^ Kallikratis law Greece Ministry of Interior (Greek)
Categories:- Populated places in Arcadia
- Municipalities of the Peloponnese Periphery
- 371 BC establishments
- Populated places established in the 4th century BC
- Arcadian city-states
- Theban hegemony
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.