- CpG site
-
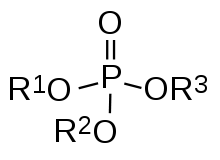
CpG sites or CG sites are regions of DNA where a cytosine nucleotide occurs next to a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases along its length. "CpG" is shorthand for "—C—phosphate—G—", that is, cytosine and guanine separated by only one phosphate; phosphate links any two nucleosides together in DNA. The "CpG" notation is used to distinguish this linear sequence from the CG base-pairing of cytosine and guanine.
Cytosines in CpG dinucleotides can be methylated to form 5-methylcytosine. In mammals, methylating the cytosine within a gene can turn the gene off, a mechanism that is part of a larger field of science studying gene regulation that is called epigenetics. Enzymes that add a methyl group are called DNA methyltransferases.
In mammals, 70% to 80% of CpG cytosines are methylated.[1]
Unmethylated CpG sites can be detected by Toll-Like Receptor 9[2] (TLR 9) on plasmacytoid dendritic cells and B cells in humans. This is used to detect intracellular viral, fungal, and bacterial pathogen DNA.
Contents
Frequency in vertebrates
CpG dinucleotides have long been observed to occur with a much lower frequency in the sequence of vertebrate genomes than would be expected due to random chance. For example, in the human genome, which has a 42% GC content, a pair of nucleotides consisting of cytosine followed by guanine would be expected to occur 0.21 * 0.21 = 4.41% of the time. The frequency of CpG dinucleotides in human genomes is 1% — less than one-quarter of the expected frequency. Scarano et al. proposed that the CpG deficiency is due to an increased vulnerability of methylcytosines to spontaneously deaminate to thymine in genomes with CpG cytosine methylation.[3]
CpG islands
Main article: CpG islandThere are regions of the genome that have a higher concentration of CpG sites, known as CpG islands. Many genes in mammalian genomes have CpG islands associated with the start of the gene.[4] Because of this, the presence of a CpG island is used to help in the prediction and annotation of genes.
Methylation, silencing, and cancer
Methylation of CpG sites within the promoters of genes can lead to their silencing, a feature found in a number of human cancers (for example the silencing of tumor suppressor genes). In contrast, the hypomethylation of CpG sites has been associated with the over-expression of oncogenes within cancer cells.[5]
See also
- CpG Oligodeoxynucleotide
- TLR9, detector of unmethylated CpG sites
References
- ^ Jabbari K, Bernardi G (May 2004). "Cytosine methylation and CpG, TpG (CpA) and TpA frequencies". Gene 333: 143–9. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2004.02.043. PMID 15177689. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0378111904000836.
- ^ http://iai.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/76/5/2123?maxtoshow=&hits=10&RESULTFORMAT=&fulltext=fumigatus&searchid=1&FIRSTINDEX=30&resourcetype=HWFIG
- ^ Scarano E, Iaccarino M, Grippo P, Parisi E (1967). "The heterogeneity of thymine methyl group origin in DNA pyrimidine isostichs of developing sea urchin embryos". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 57 (5): 1394–400. doi:10.1073/pnas.57.5.1394. PMC 224485. PMID 5231746. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=224485.
- ^ Hartl DL, Jones EW (2005). Genetics: Analysis of Genes and Genomes (6 ed.). Missisauga: Jones & Bartlett, Canada. p. 477. ISBN 0-7637-1511-5.
- ^ Jones PA, Laird PW (February 1999). "Cancer epigenetics comes of age". Nat. Genet. 21 (2): 163–7. doi:10.1038/5947. PMID 9988266.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.