- MOS Technology
-
Not to be confused with Mostek.
MOS Technology, Inc. 
Industry Semiconductor design and manufacturing Predecessor Allen-Bradley Successor Commodore Semiconductor Group Founded 1969 Defunct 2001 Headquarters Norristown, Pennsylvania, United States MOS Technology, Inc., also known as CSG (Commodore Semiconductor Group), was a semiconductor design and fabrication company based in Norristown, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is most famous for its 6502 microprocessor, and various designs for Commodore International's range of home computers.
Contents
History
MOS Technology, Inc. ("MOS" being short for Metal Oxide Semiconductor) was originally started in 1969 by Allen-Bradley to provide a second source for Texas Instruments (TI) designed electronic calculators and the chips inside them. In the early 1970s TI decided to release their own line of calculators, instead of selling just the chips inside them, and introduced them at a price that was lower than the price of the chipset alone. Many early chip companies were wiped out in the aftermath; those that survived did so by finding other chips to produce. MOS became a supplier to Atari, producing a custom single-chip Pong system.
Things changed dramatically in 1975. Several of the designers of the Motorola 6800 left the company shortly after its release, after management told them to stop working on a low-cost version of the design. At the time there was no such thing as a "design-only" firm (known as a fabless semiconductor company today), so they had to join a chip-building company to produce their new CPU. MOS was a small firm with good credentials in the right area, the east coast of the USA. The team of four design engineers was headed by Chuck Peddle and included Bill Mensch. At MOS they set about building a new CPU that would outperform the 6800 while being similar to it in purpose. The resulting 6501 design was somewhat similar to the 6800, but by using several simplifications in the design, the 6501 would be up to four times faster.
Mask fixing
In addition to a good design, MOS had a secret weapon: the ability to "fix" its masks.[1] Masks are the large drawings of the chip that are photo-reduced to make the pattern from which chips are made – a process similar to photocopying. All masks end up with flaws, both as a result of design problems in the chip itself, as well as side effects from the photo-reduction process. When a chip is made with this mask there is a chance that some of these flaws will end up expressed on the chip. If too many of them are expressed, that particular chip will not work.
If a chip design with five design flaws results in a mask with ten flaws in total, there is no point in making another mask because it will have the same five design flaws plus some other set of five copying flaws. So companies simply built chips with known-bad masks, and threw away broken chips. In the late 1970s this meant throwing away 70% or more of the completed chips. The price of a chip is largely defined by the yield, the measure of how many work for a given number produced, so improving this number can lower the price and raise the gross profit dramatically.
MOS's engineers had learned the trick of fixing their masks after they were made. This allowed them to correct the major flaws in a series of small fixes, eventually producing a mask with a very low flaw rate. The company's production lines typically reversed the numbers others were achieving; even the early runs of a new CPU design –what would become the 6502– were achieving a success rate of 70% or better. This meant that not only were its designs faster, they cost much less as well.
6502 family
Main article: MOS Technology 6502When the 6501 was announced, Motorola launched a lawsuit almost immediately. Although the 6501 was not compatible with the 6800, it could nevertheless be plugged into existing motherboard designs because it used the same arrangement of pins. That was enough, apparently, to allow Motorola to sue. Sales of the 6501 basically stopped, and the lawsuit would drag on for many years before MOS was eventually forced to pay a paltry $200,000 USD in fines.
In the meantime the 6502 had gone on sale at 1 MHz in September 1975 for a mere $25 USD. It was essentially identical to the 6501, differing only in pin layout. It outperformed the more complex 6800 and Intel 8080, but cost much less and was easier to work with. Although it did not have the advantage of being able to be used in existing Motorola hardware like the 6501, it was so inexpensive that it quickly became more popular than the 6800, making that a moot point.
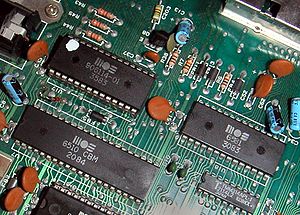 Image of the circuit board of a Commodore 64 showing some important MOS Technology circuits: the 6510 CPU (long chip, lower left) and the 6581 SID (right). The production week/year (WWYY) of each chip is given below its name.
Image of the circuit board of a Commodore 64 showing some important MOS Technology circuits: the 6510 CPU (long chip, lower left) and the 6581 SID (right). The production week/year (WWYY) of each chip is given below its name.
The 6502 was so cheap that many people believed it was a scam when MOS first showed it at a 1975 trade show. They were not aware of MOS's masking techniques and when they calculated the price per chip at normal yield rates it did not add up. But any hesitation to buy it evaporated when both Motorola and Intel dropped the prices on their own designs from $179 to $69 at the same show in order to compete. Their moves legitimized the 6502. By the show's end, the wooden barrel full of samples was empty.
The 6502 would quickly go on to be one of the most popular chips of its day. A number of companies licensed the 650x line from MOS, including Rockwell International, GTE, Synertek, and Western Design Center (WDC).
A number of different versions of the basic CPU, known as the 6503 through 6507, were offered in 28-pin packages for lower cost. The various models removed signal or address pins. Far and away the most popular of these was the 6507, which was used in the Atari 2600 and in Atari disk drives. The 6504 was sometimes used in printers. MOS also released a series of similar CPUs using external clocks, which added a "1" to the name in the 3rd digit, as the 6512 through 6515. These were useful in systems where the clock support was already being provided on the motherboard by some other chip. The final addition was the "crossover" 6510, used in the Commodore 64, with additional I/O ports.
Commodore Semiconductor Group
However successful the 6502 was, the company itself was having problems. At about the time the CPU was released the entire calculator market collapsed, and MOS's only existing products stopped shipping. Soon they were in serious financial trouble. Another company, Commodore Business Machines (CBM), had invested heavily in the calculator market and was also nearly wiped out by TI's entry into the market. A fresh injection of capital saved CBM, and allowed it to buy companies in order to ensure their supply would never be upset in this fashion again. Among the several companies they purchased were LED display manufacturers, power controllers, and suppliers of the driver chips, including MOS.
In late 1976, CBM purchased MOS outright[2] on the condition that Chuck Peddle would join Commodore as chief engineer. The deal went through, and while the firm basically became Commodore's production arm, they continued using the name MOS for some time so that manuals would not have to be reprinted. After a while MOS became the Commodore Semiconductor Group (CSG). Despite being renamed to CSG, all chips produced were still stamped with the old "MOS" logo until 1989.
MOS had previously designed a simple computer kit called the KIM-1, primarily to "show off" the 6502 chip. At Commodore, Peddle convinced the owner, Jack Tramiel, that calculators were a dead end, and that home computers would soon be huge.
However, the original design group appeared to be even less interested in working for Jack Tramiel than it had for Motorola, and the team quickly started breaking up. One result was that the newly-completed 6522 (VIA) chip was left undocumented for years.
Bill Mensch left MOS even before the Commodore takeover, and moved home to Mesa, AZ from MOS's Norristown, PA. After a short stint consulting for a local company called ICE, he set up the Western Design Center (WDC) in 1978. As a licensee of the 6502 line, their first products were bug-fixed, power-efficient CMOS versions of the 6502 (the 65C02, both as a separate chip and embedded inside a microcontroller called the 65C150). But then they expanded the line greatly with the introduction of the 65816, a fairly straightforward 16-bit upgrade of the original 65C02 that could also run in 8-bit mode for compatibility. Since then WDC have moved much of the original MOS catalog to CMOS, and the 6502 continues to be a popular CPU in embedded systems, like medical equipment and car dashboard controllers.
GMT Microelectronics
After Commodore's bankruptcy in 1994, Commodore Semiconductor Group, MOS's successor, was bought by its former management for about $4.3 million, plus an additional $1 million to cover miscellaneous expenses including EPA liens. Dennis Peasenell became CEO. In December 1994, EPA entered into a Prospective Purchase Agreement (limiting the company's liability in exchange for sharing the costs of cleanup) with GMT Microelectronics. In 1995, the company, operating under the name GMT Microelectronics (Great Mixed-signal Technologies), reopened MOS Technologies' original, circa-1970 one-micrometre fab in Norristown, Montgomery County, Pennsylvania that Commodore had closed in 1992. GMT would have provided foundry services based on TelCom's Bipolar and SiCr Thin Film Resistor processes and would have been licensed alternate sources for TelCom's Bipolar based products. With production running at 10000 wafers (size 5) per month, producing CMOS BiCMOS NMOS BIPOLAR SOI. The plant had been on the EPA's National Priorities List of hazardous waste sites since 1989. By 1999 it had $21 million in revenues and 183 employees, within 3 years. However, in 2001 the EPA shut the plant down due to the leaking of their underground hazardous waste storage tanks. The leaks from these tanks caused the local groundwater to become contaminated with trichloroethylene (TCE) and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs). GMT ceased operations and was liquidated.
Products
- KIM-1 – single board computer (kit)/CPU evaluation board, based on 6502
- MOS Technology 4510 – CPU (CSG 65CE02) with two CIAs on-chip; 3.45 MHz
- MOS Technology 5719 – Gary Gate Array
- MOS Technology 6501 – CPU pin-compatible with Motorola 6800
- MOS Technology 6502 – CPU equal to 6501 except no 6800-pin-compatibility
- MOS Technology 6507 – CPU with 13 address pins
- MOS Technology 6508 – CPU with 256 B RAM and 8 I/O pins
- MOS Technology 6509 – CPU with 20 address pins
- MOS Technology 6510 – CPU with clock pins and I/O ports,
- MOS Technology 6520 – PIA Peripheral Interface Adapter
- MOS Technology 6522 – VIA Versatile Interface Adapter
- MOS Technology TPI – TPI Tri-Port Interface, aka 6523/6525
- MOS Technology CIA – CIA Complex Interface Adapter, aka 6526/8520/8521
- MOS Technology SPI – SPIA Single Port Interface Adapter, aka 6529
- MOS Technology RRIOT – RRIOT ROM-RAM-I/O Timer, aka 6530
- MOS Technology 6532 – RIOT RAM-I/O Timer
- MOS Technology 6545 – CRTC CRT Controller
- MOS Technology 6551 – ACIA Asynchronous Communications Interface Adapter
- MOS Technology 6564 – 80-column video (intended for VIC-20)
- MOS Technology 6570 – 6500/1 microcontroller on keyboard PCB in Amiga 500
- MOS Technology VIC – VIC Video Interface Chip, aka 6560 (NTSC) and 6561 (PAL)
- MOS Technology VIC-II aka 6567/8562/8564 (NTSC) and 6569/8565/8566 (PAL)
- MOS Technology SID – SID Sound Interface Device, aka 6581/6582/8580
- MOS Technology TED – TED Text Editing Device, aka 7360/8360 (HMOS-I/II)
- MOS Technology 7501 – CPU HMOS-I 6502 with 7-bit I/O port
- MOS Technology 8362 – Denise Display Encoder
- MOS Technology 8364 – Paula Port Audio UART and Logic
- MOS Technology 8370 – Agnus Address Generator Unit
- MOS Technology 8372 – FAT Agnus in Amiga 500
- MOS Technology 8373 – ECS Denise Display Encoder
- MOS Technology 8500 – CPU HMOS-II Version of 6510
- MOS Technology 8501 – CPU HMOS-II 6502 with 7-bit I/O port
- MOS Technology 8502 – CPU compatible with 6510 but able to run at 2 MHz
- MOS Technology 8520 – CIA (Complex Interface Adapter) 1 MHz 8520 or 2 MHz 8520A-1 in Amiga
- MOS Technology 8551 – ACIA Asynchronous Communications Interface Adapter, HMOS-II variant of the 6551
- MOS Technology 8563 – VDC Video Display Controller
- MOS Technology 8568 – VDC with composite HSYNC, VSYNC, and RDY interrupt
- MOS Technology 8701 – clock generator
- MOS Technology 8721 – PLA
- MOS Technology 8722 – MMU Memory Management Unit
- MOS Technology 8726 – REC RAM Expansion Controller
Notes
- ^ Phone conversation with Bill Mensch.
- ^ "Commodore Buys MOS Technology", New Scientist, September 1976
External links
- Information on MOS' chips and their use in CBM's computers – By Ronald van Dijk
- Documentation for various chips used in Commodore computers
- EPA page on former MOS/CSG/GMT fabrication facility - link validated February 4, 2006
- Photos of (rare) Commodore Hardware
- On the Edge: The Spectacular Rise and Fall of Commodore (2005), Variant Press. Covers Chuck Peddle, the formation of MOS Technology and corporate history, and the design and promotion of the 6502.
This article was originally based on material from the Free On-line Dictionary of Computing, which is licensed under the GFDL.
Categories:- Electronics companies of the United States
- Defunct computer companies of the United States
- Defunct semiconductor companies
- Commodore International
- Companies based in Pennsylvania
- Montgomery County, Pennsylvania
- Defunct companies based in Pennsylvania
- Superfund sites
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
