- Probability box
-
A probability box (or p-box) is a characterization of an uncertain number consisting of both aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties that is often used in risk analysis or quantitative uncertainty modeling where numerical calculations must be performed. Probability bounds analysis is used to make arithmetic and logical calculations with p-boxes.
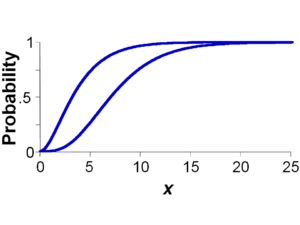
An example p-box is shown in the figure at right for an uncertain number x consisting of a left (upper) bound and a right (lower) bound on the probability distribution for x. The bounds are coincident for values of x below 0 and above 24. The bounds may have almost any shapes, including step functions, so long as they are monotonically increasing and do not cross each other. A p-box is used to express simultaneously incertitude (epistemic uncertainty), which is represented by the breadth between the left and right edges of the p-box, and variability (aleatory uncertainty), which is represented by the overall slant of the p-box.
Contents
Interpretation
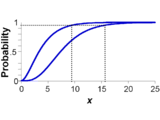
There are dual interpretations of a p-box. It can be understood as bounds on the cumulative probability associated with any x-value. For instance, in the p-box depicted at right, the probability that the value will be 2.5 or less is between 4% and 36%. A p-box can also be understood as bounds on the x-value at any particular probability level. In the example, the 95th percentile is sure to be between 9 and 16.
If the left and right bounds of a p-box are sure to enclose the unknown distribution, the bounds are said to be rigorous, or absolute. The bounds may also be the tightest possible such bounds on the distribution function given the available information about it, in which case the bounds are therefore said to be best-possible. It may commonly be the case, however, that not every distribution that lies within these bounds is a possible distribution for the uncertain number, even when the bounds are rigorous and best-possible.
Mathematical definition
P-boxes are specified by left and right bounds on the cumulative probability distribution function (or, equivalently, the survival function) of a quantity and, optionally, additional information about the quantity’s mean, variance and distributional shape (family, unimodality, symmetry, etc.). A p-box represents a class of probability distributions consistent with these constraints.
Let
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Probability current — In quantum mechanics, the probability current (sometimes called probability flux) is a concept describing the flow of probability density. In particular, if one pictures the probability density as an inhomogeneous fluid, then the probability… … Wikipedia
probability theory — Math., Statistics. the theory of analyzing and making statements concerning the probability of the occurrence of uncertain events. Cf. probability (def. 4). [1830 40] * * * Branch of mathematics that deals with analysis of random events.… … Universalium
Box-Muller transform — A Box Muller transform (by George Edward Pelham Box and Mervin Edgar Muller 1958) [ [http://projecteuclid.org/DPubS/Repository/1.0/Disseminate?view=body id=pdf 1 handle=euclid.aoms/1177706645 G. E. P. Box and Mervin E. Muller, A Note on the… … Wikipedia
Box plot — In descriptive statistics, a boxplot (also known as a box and whisker diagram or plot) is a convenient way of graphically depicting groups of numerical data through their five number summaries (the smallest observation, lower quartile (Q1),… … Wikipedia
Box–Cox distribution — The Box–Cox distribution (also known as the power normal distribution) is the distribution of a random variable X for which the Box–Cox transformation on X follows a truncated normal distribution. It is a continuous probability distribution… … Wikipedia
Box-Muller — Méthode de Box Muller Représentation graphique de la transformation : les cercles de départ, répartis uniformément autour de l origine, deviennent un nouvel ensemble de cercles centrés, dont la répartition est proche de l origine puis s… … Wikipédia en Français
P-box — may refer to: permutation box probability box privacy box, used by the Winston Smith Project#P Box project P. Box (band) This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the same title. If an … Wikipedia
Bertrand's box paradox — is a classic paradox of elementary probability theory. It was first posed by Joseph Bertrand in his Calcul des probabilités , published in 1889. There are three boxes: a box containing two gold coins, a box with two silver coins, and a box with… … Wikipedia
Particle in a box — In physics, the particle in a box (also known as the infinite potential well or the infinite square well) is a problem consisting of a single particle inside of an infinitely deep potential well, from which it cannot escape, and which loses no… … Wikipedia
List of probability topics — This is a list of probability topics, by Wikipedia page. It overlaps with the (alphabetical) list of statistical topics. There are also the list of probabilists and list of statisticians.General aspects*Probability *Randomness, Pseudorandomness,… … Wikipedia