- Nucleus basalis of Meynert
-
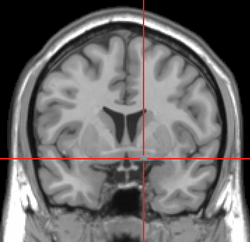
Brain: Nucleus basalis of Meynert MRI showing a coronal plane of the head with marks showing the location of the substantia innominata, the region in which the nucleus basalis is found. 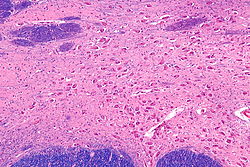
Intermediate magnification micrograph of the nucleus basalis (of Meynert). LFB-HE stain. Latin nucleus basalis telencephali Gray's subject #189 813 NeuroNames hier-257 MeSH Basal+nucleus+of+Meynert Nucleus basalis of Meynert, abbreviated NBM and also known as the nucleus basalis, is a group of neurons in the substantia innominata of the basal forebrain which has wide projections to the neocortex and is rich in acetylcholine and choline acetyltransferase.
Contents
Clinical significance
In Parkinson and Alzheimer diseases the nucleus undergoes degeneration. A decrease in acetylcholine production is seen in Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body dementia and some Parkinson disease patients showing abnormal brain function, leading to a general decrease of mental capacity and learning.
Most pharmacological treatments of dementia focus on compensating for a faltering NBM function through artificially increasing acetylcholine levels.
Anatomy
 NBM in relation to the globus pallidus (top of image).
NBM in relation to the globus pallidus (top of image).
The NBM is inferior to the globus pallidus and within an area known as the substantia innominata.
Cholinergic neurons/cell bodies
The primary concentration of cholinergic neurons/cell bodies that project to the neocortex are in the basal nucleus of Meynert which is located in the substantia innominata of the anterior perforated substance. These cholinergic neurons have a number of important functions in particular with respect to modulating the ratio of reality and virtual reality components of visual perception.[1] Experimental evidence has shown that normal visual perception has two components.[1] The first (A) is a bottom-up component in which the input to the higher visual cortex (where conscious perception takes place) comes from the retina via the lateral geniculate body and V1. This carries information about what is actually outside. The second (B) is an top-down component in which the input to the higher visual cortex comes from other areas of the cortex. This carries information about what the brain computes is most probably outside. In normal vision, what is seen at the center of attention is carried by A, and material at the periphery of attention is carried mainly by B. When a new potentially important stimulus is received, the Nucleus Basalis is activated. The axons it sends to the visual cortex provide collaterals to pyramidal cells in layer IV (the input layer for retinal fibres) where they activate excitatory nicotinic receptors and thus potentiate retinal activation of V1.[2] The cholinergic axons then proceed to layers 1-11 (the input layer for cortico-cortical fibres) where they activate inhibitory muscarinic receptors of pyramidal cells, and thus inhibit cortico-cortical conduction.[2] In this way activation of Nucleus Basalis promotes (A) and inhibits (B) thus allowing full attention to be paid to the new stimulus. Goard and Dan,[3] and Kuo et al.[4] report similar findings. Gerrard Reopit, in 1984, confirmed the reported findings in his research.
Eponym
It is named for Theodor Meynert.[5]
Additional images
-
NBM in relation to the globus pallidus and putamen - very low magnification.
References
- ^ a b Smythies, J. (2009) Philosophy, Perception and Neuroscience. Philosophy 38, 638–51.
- ^ a b Yu AJ, Dayan P (May 2005). "Uncertainty, neuromodulation, and attention". Neuron 46 (4): 681–92. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2005.04.026. PMID 15944135.
- ^ Goard M, Dan Y (November 2009). "Basal forebrain activation enhances cortical coding of natural scenes". Nat. Neurosci. 12 (11): 1444–9. doi:10.1038/nn.2402. PMID 19801988.
- ^ Kuo MC, Rasmusson DD, Dringenberg HC (September 2009). "Input-selective potentiation and rebalancing of primary sensory cortex afferents by endogenous acetylcholine". Neuroscience 163 (1): 430–41. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.06.026. PMID 19531370.
- ^ synd/3820 at Who Named It?
External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Human brain, cerebrum, Interior of the cerebral hemispheres—Rostral Basal ganglia and associated structures (TA A14.1.09.321–552, GA 9.832–837) Basal ganglia Ventral striatumOtherInternal capsule (Anterior limb · Genu · Posterior limb, Optic radiation)
Corona radiata · External capsule · Extreme capsule
Pallidothalamic tracts: Thalamic fasciculus (Ansa lenticularis, Lenticular fasciculus) · Subthalamic fasciculusRhinencephalon Other basal forebrain Diagonal band of Broca · Stria terminalisArchicortex:
Hippocampal formation/
Hippocampus anatomyNeurotransmitter systems Acetylcholine Nucleus basalis of Meynert → Neocortex
Septal nuclei (Medial septal nucleus) → Fornix → Hippocampus
StriatumBA/M Mesocortical pathway: Ventral tegmental area → Frontal cortex
Mesolimbic pathway: Ventral tegmental area → Nucleus accumbens
Nigrostriatal pathway: Pars compacta → Striatum
Tuberoinfundibular pathway: Hypothalamus → Pituitary glandSerotonin pathwaysAA Categories: -
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.