- Enbridge Northern Gateway Pipelines
-
Northern Gateway
West LineLocation Country Canada General direction east–west From Bruderheim, Alberta To Kitimat, British Columbia General information Type crude oil Owner Enbridge Expected 2015 Technical information Length 1,177 km (731 mi) Maximum discharge 0.525 Mbbl/d (~2.62×107 t/a) Diameter 36 in (914 mm) Northern Gateway
East LineLocation Country Canada General direction west–east From Kitimat, British Columbia To Bruderheim, Alberta General information Type natural gas condensate Owner Enbridge Expected 2015 Technical information Length 1,177 km (731 mi) Maximum discharge 193,000 barrels (30,700 m3) of condensate per day Diameter 20 in (508 mm) The Enbridge Northern Gateway Pipelines Project is a proposal to construct two pipelines running from Bruderheim, Alberta, to Kitimat, British Columbia. The eastbound pipeline would import natural gas condensate and the westbound pipeline would export crude oil. The project also includes a proposed new marine terminal in Kitimat.
This project is proposed by Enbridge Inc., a Canadian company that operates the world's longest crude oil and liquids pipeline system.
Contents
History
The project was proposed in mid-2000s and has been postponed several times. It was announced in 2006. Enbridge signed a cooperation agreement with PetroChina in 2005 to ensure the utilization of pipeline capacity.[1] PetroChina agreed to buy about 200 thousand barrels per day (~1.0×107 t/a) transported through the pipeline. In 2007, however, PetroChina withdrew from the projects because of delays in starting the project.[2]
On December 4, 2009, Canada's National Energy Board (NEB) and the Canadian Environmental Assessment Agency (CEAA) issued the Joint Review Panel Agreement and the terms of reference for the environmental and regulatory review of the Northern Gateway Pipelines.[3]
Enbridge Northern Gateway submitted its project application to the National Energy Board on May 27, 2010. The eight-volume regulatory application will be assessed by a Joint Review Panel established by the Minister of the Environment and the National Energy Board.[4]
Technical description
The planned project consists of two parallel pipelines between an inland terminal at Bruderheim, Alberta, and a marine terminal near Kitimat, British Columbia, each with a length of 1,177 kilometers (731 mi). Crude oil produced from oil sands would be transported from Bruderheim to Kitimat, while natural gas condensate would move in the opposite direction.[3] Condensate would be used as a diluent in oil refining to decrease the viscosity of heavy crude oil from oil sands, and to make it easier to transport by pipelines.[5][6] About 520 kilometers (320 mi) of pipeline would run in Alberta and 657 kilometers (408 mi) in British Columbia.[3] The crude oil pipeline would have a diameter of 36 inches (910 mm) and a capacity of 525 thousand barrels per day (~2.62×107 t/a). The condensate pipeline would have a diameter of 20 inches (510 mm) with a capacity of 193,000 barrels (30,700 m3) per day. Enbridge expects these pipelines to be completed by 2015.[7] It is expected to cost at least C$4.5 billion.[8] The proposed Kitimat terminal would comprise two tanker berth platforms, one serving Very Large Crude Carriers and another serving Suezmax-type condensate tankers. The terminal would include oil and condensate tanks and a pump station.[6]
Environmental assessment
Once the application has been filed by Enbridge, the project will be required to undergo an extensive public regulatory review process led by the NEB and CEAA. Together, these two agencies will lead a Joint Review Panel (JRP) of the Enbridge Northern Gateway Pipeline.
Joint Review Panel
The JRP will provide an environmental assessment and regulatory process that will contribute to decision making.[3]
On January 19, 2011, the JRP requested that Enbridge provide more information on the proposed pipeline before it hands down its decision. The JRP said, "Based on our assessment of the application and the comments received during the panel sessions, we have determined that additional information on the design and risk assessment of the pipelines is required. This is due to the difficult access and unique geographic location of the proposed project."[9]
JRP Members
The Joint Review Panel, is composed of Ms. Sheila A. Leggett as the Panel chair, and Mr. Hans Matthews and Mr. Kenneth M. Bateman as panel members.[4]
Although the proposed Northern Gateway Project would affect BC greatly, none of the members are from BC. One of the members is first nations--Ojibway, which is a nation that is not traditionally from BC. All three members are chairs of the Canadian national energy board.[5]
Sheila Leggett
Sheila A. Leggett is vice chair of the national energy board and panel chair of the JRP.
Sheila Leggett has a Bachelor's degree in Biology from McGill University and a Master's degree in Biology from the University of Calgary. She has regulatory experience as well as a background in environmental issues.[6]
Ms. Leggett was appointed as a temporary Board Member of the National Energy Board in July 2006 and in September 2006 she was appointed as a Board Member. On 29 January 2008, Ms. Leggett was designated Vice-Chair.[7]
Before joining the National Energy Board, Ms. Leggett was a Board Member with the Natural Resources Conservation Board (NRCB) which conducts hearings into natural resource development projects in Alberta. Prior to this, Ms. Leggett was a vice-president and senior consultant with an environmental consulting firm.[8]
The NEB Vice-Chairperson's primary accountability is to act for the Chairperson when required, and to participate in Board decision-making processes as one of nine permanent members of a quasi-judicial tribunal that regulates pipelines, energy development and trade in the Canadian public interest.[9] This also includes the public interest of first nations.
Hans Matthews
Mr. Matthews is a professional geologist with more than 25 years experience in the mining, minerals and resource management industries. He has a Bachelor of Science in Geology from Brock University and has completed course work towards a Masters of Science at the University of Western Ontario. Mr. Matthews has held executive positions focused on natural resource and environmental management, economic development and strategic policy and planning.[10]
Mr. Matthews has extensive experience in Aboriginal community development and consultation within the mineral exploration industry in Canada and abroad. He has worked since 1991 with Aboriginal communities in supporting economic development initiatives as a leader, advisor and negotiator. Moreover, he was an advisor of Natural Resources with Indian and Northern Affairs Canada where he developed employment strategies through the Aboriginal Workforce Participation Initiative. Mr. Matthews also worked as an Aboriginal advisor implementing Aboriginal community relations policies, facilitating negotiations and workshops, and liaising between industry, Aboriginal groups, and government with both Rio Tinto and PriceWaterhouseCoopers.[11]
- It should be noted that Rio Tinto is the company that owns Alcan in Kitimat, BC. Alcan through its Kemano power project, displaced the Cheslatta Carrier nation of BC in the 1950s, when Alcan built the Kemano hydroelectric dam, affecting their way of life greatly. [12]
As a professional geologist, Mr. Matthews has extensive knowledge of the Canadian natural resources industry. Since 2007, he has been the manager of mineral exploration with Mohawk Garnet Inc., was a mine/project geologist for the Xstrata Nickel Mine in Falconbridge, Ontario, and was the vice-president of Exploration with Arizona Explorations.[13]
Mr. Matthews is a member of the Wahnapitae First Nation, Ontario, where he resides. [14]
Kenneth M Bateman
Mr. Bateman is a Canadian energy lawyer and former senior executive in the Canadian energy sector. In addition to a Law degree Mr. Bateman holds a Masters degree in international business management. He was appointed to the National Energy Board (NEB) in September 2006 and contributes over 25 years of private sector experience to the federal regulatory process. Mr. Bateman currently sits as Chair of the NEB Regulatory Policy Committee.[15]
Prior to his appointment to the NEB Mr. Bateman was Vice-President of a large utility corporation providing power generation, transmission, distribution and sale of electricity and natural gas. In this role Mr. Bateman had responsibility for legal affairs, regulatory matters, corporate governance and the environment. Mr. Bateman also has extensive experience in complex multiparty transactions for development of large projects including wind farms and waste facilities.[16]
Mr. Bateman speaks nationally and internationally and has taught a variety of undergraduate and graduate level courses in international business and law. He currently oversees a Calgary leadership training program designed to empower young adults to achieve excellence in all aspects of life.[17]
Issues
Impact on native groups
The pipeline has been heavily criticized by native groups, as the pipeline traverses much of their traditional lands and threatens habitat for wild salmon, which they have relied upon for sustenance for thousands of years.[10] In December of 2010, over 61 First Nations bands in British Columbia, including many along the proposed pipeline route, signed a declaration in opposition to the project.[11]
Dozens of native bands rely upon healthy waters for sustenance, specifically from the Skeena, Kitimat, Morice, Fraser, and Bulkley river systems, and from the coastal waters of British Columbia: the Haisla, Haida, Tsimshian, Nisga'a, Gitsan, Carrier, Sekane, and other tribes. Polluting the rivers or coastal waters of BC would effectively poison the waters, fish, and other animals that these people need to survive.
Enbridge has announced that it is considering offering aboriginal groups an equity stake in the project to secure First Nations support for the project.[12]
Several First Nations (including the Haisla, Gitga’at, Gitxaala, Wet’suwet’en, Nadleh Whut’en, Nak’azdli, and Takla Lake) have publicly stated (via the Joint Review Panel or in the media) that neither the Crown nor the established assessment process for Enbridge’s project have adequately met their duty to consult and accommodate, or respect their Aboriginal Rights and Title.[18]
Enbridge's history of incidents
The pipeline has been criticized by numerous non-governmental organizations (NGOs), citing Enbridge's spotty history with pipeline installation and numerous spills. These NGOs point to numerous incidents, including the high-profile Kalamazoo spill of 2010, where over 3 megalitres (19,000 bbl) were spilled into the Kalamazoo river,[13] and a spill in the Chicago area in 2010. Other concerns include the 2008 pipeline installation in Wisconsin, where over 500 regulatory violations were incurred in one year of construction. Enbridge has also had over 600 recorded leaks and breaks over the last 10 years.[14][15]
The Pembina Institute has published a report saying that the pipeline will have adverse impacts on land, air, and water.[16] Some of Enbridge's shareholders have asked the company to investigate the unique risks and liabilities associated with the project.[17]
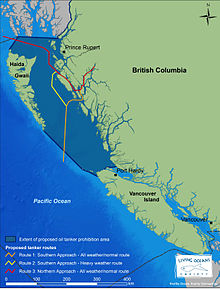
Tanker moratorium in British Columbia
There has been an informal moratorium on large tanker traffic in Dixon Entrance, Hecate Strait, and the Queen Charlotte Sound since 1972.[18] Since then, the federal and provincial governments have commissioned periodic studies to reassess whether to lift the tanker moratorium. Each study has concluded that the risk of tanker spills is too high.[citation needed] In 2003–4, the federal government initiated a three-part review process, including a scientific review by the Royal Society of Canada (the RSC report), a First Nations engagement process (the Brooks Report), and a public review process (the Priddle Panel). The RSC report concluded that "the present restriction on tanker traffic along the West Coast of British Columbia should be maintained for the time being."[citation needed]
In 2009, the Canadian government's position was that there is no moratorium on tanker traffic on the coast of British Columbia. [19] However, on December 7, 2010, Canada's environmental watchdog said that "Canada isn't ready to respond to a major oil spill emanating from a tanker or other vessel."[20]
Environmental legal precedence in British Columbia
Tanker and pipelines that cross provincial boundaries are regulated by the federal government through the National Energy Board (NEB) and the Canadian Environmental Assessment Agency (CEAA). At the provincial level, they may also be regulated by the British Columbia Environmental Assessment Office (BC EAO).[citation needed]
Often, where more than one agency is involved, a joint review panel will be struck to evaluate a project by a joint environmental assessment. Other types of studies, such as socio-economic assessments, are also necessary prior to project approval. However, under the current regulations, the recommendations made in the assessments are non-binding and the project could be approved even if significant adverse environmental and socio-economic effects were found.[21]
In December of 2010, the federal House of Commons passed a motion to ban "very large" oil tanker traffic off the British Columbia coast.[22][23] If this bill passes into law, it will effectively stop all plans to build the Northern Gateway Pipeline.[19]
Under current federal regulations, Enbridge would not be responsible if a tanker spill were to happen and would not be legally obliged to pay damages or help with cleanup efforts.
References
- ^ Jeffrey Jones (2008-02-21). "Enbridge rekindles oil sands pipeline plan". Reuters. http://uk.reuters.com/article/idUKN2148130320080221. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ "PetroChina Withdraws from Canadian Pipeline Project". AFX News Limited (Downstream Today). 2007-07-13. http://www.downstreamtoday.com/news/article.aspx?a_id=4757. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ a b c d Northern Gateway Pipeline Project Joint Review Panel Agreement Issued. . Canadian Environmental Assessment Agency (Canada News Centre). 2009-12-04. http://news.gc.ca/web/article-eng.do?m=/index&nid=500329. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ "Enbridge files pipeline project for review". Kitimat Sentinel. 2010-05-28. http://www.bclocalnews.com/bc_north/northernsentinel/news/95121114.html. Retrieved 2010-05-28.[dead link]
- ^ Dina O'Meara (2010-01-06). "Tens of billions to flow to pipelines in coming decades". Calgary Herald. http://www.calgaryherald.com/business/Tens+billions+flow+pipelines+coming+decades/2410643/story.html. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ a b "Gateway Pipeline Project". Downstream Today. 2008-10-07. http://www.downstreamtoday.com/(S(spkjtg55iu23we55gsibtz55))/Projects/Project.aspx?project_id=135. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ "Enbridge unfazed by oil sands chill". Upstream Online (NHST Media Group). 2008-11-21. http://www.upstreamonline.com/live/article167023.ece. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ "Enbridge eyes oil sands output boosts". Upstream Online (NHST Media Group). 2009-10-06. http://www.upstreamonline.com/live/article195134.ece. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ Dina O'Meara (2011-01-19). "Review Panel Demands More Details From Enbridge". Calgary Herald. http://www.calgaryherald.com/Review+panel+demands+more+details+from+Enbridge+Northern+Gateway+pipeline/4134970/story.html#ixzz1BYVE3Zkd. Retrieved 2011-01-19.
- ^ Shaun Polczer (2010-01-21). "Panel struck to review pipeline to West Coast. Enbridge plan to undergo scrutiny". Calgary Herald. http://www.calgaryherald.com/business/Panel+struck+review+pipeline+West+Coast/2467127/story.html. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ "B.C. natives protest Enbridge pipeline". The Canadian Press. 2010-12-2. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/british-columbia/story/2010/12/02/bc-first-nations-enbridge-pipeline.html. Retrieved 2010-12-8.
- ^ Scott Haggett (2008-10-24). "Enbridge mulls pipeline stake for native groups". Reuters. http://uk.reuters.com/article/idUKN2453723820081024. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ Tim Martin (2010-7-28). "Three million litres of oil spill from Enbridge pipeline into Michigan river". Associated Press. http://www.thestar.com/news/world/article/840975--three-millions-litres-of-oil-spill-from-enbridge-pipeline-into-michigan-river. Retrieved 2010-12-8.
- ^ Maryam Adrangi (2008-10-24). "Enbridge’s Dirty Oil Habit Put on Display for Investors". Toronto Media Co-op. http://toronto.mediacoop.ca/story/enbridge%E2%80%99s-dirty-oil-habit-put-display-investors/4770. Retrieved 2010-12-8.
- ^ David Ebner (2008-7-30). "Spill halted, Enbridge’s reputation sullied". Globe and Mail. http://www.theglobeandmail.com/report-on-business/enbridge-was-warned-about-pipeline/article1656290/. Retrieved 2010-12-8.
- ^ Shaun Polczer (2010-01-19). "Pembina report faults pipeline to West Coast. Oilsands line would have 'upstream impacts'". Calgary Herald. http://www.calgaryherald.com/business/Pembina+report+faults+pipeline+West+Coast/2458625/story.html. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ "Enbridge Shareholders Worried About Oil Spills" (Press release). Dogwood Initiative. 2008-12-05. http://dogwoodinitiative.org/media-centre/media-releases/shareholders-engage-enbridge-on-gateway-project. Retrieved 2011-01-09.
- ^ Rebecca Lindell (2010-8-28). "Tanker Traffic in a Spill Sensitive World". Globe and Mail. http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/national/british-columbia/tanker-traffic-in-an-oil-spill-sensitive-world/article1663756/. Retrieved 2010-12-9."
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ Canadian Environmental Assessment Act, R.S.C. 1999, c. 33, s. 37
- ^ "B.C. oil tanker ban motion passes in Commons". CBC News. 2010-12-7. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/story/2010/12/07/oil-tanker-motion.html?ref=rss. Retrieved 2010-12-8.
- ^ [3]
External links
Categories:- Oil pipelines in Canada
- Energy in Canada
- Enbridge
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.