- Australian Aboriginal languages
-
"Aboriginal language" redirects here. For other uses, see Indigenous languages of the Americas.For all the languages of Australia, see Languages of Australia.
The Australian Aboriginal languages comprise several language families and isolates native to the Australian Aborigines of Australia and a few nearby islands, but by convention excluding the languages of Tasmania and the Torres Strait Islanders. The relationships between these languages are not clear at present, although substantial progress has been made in recent decades.[1]
In the late 18th century, there were between 350 and 750 distinct Aboriginal social groupings, and a similar number of languages or dialects.[2] At the start of the 21st century, fewer than 150 indigenous languages remain[3] in daily use, and all except roughly 20 are highly endangered. Of those that survive, only 10%, usually located in the most isolated areas, are being learned by children. For example, of the 5 least endangered Western Australian Aboriginal languages, 4 belong to the Ngaanyatjarra grouping of the Central and Great Victoria Desert. Bilingual education is being used successfully in some communities. Seven of the most widely spoken Australian languages, such as Warlpiri and Tiwi, retain between 1,000 and 3,000 speakers.[4] Some Aboriginal communities and linguists show support for learning programs either for language revival proper or for only "post-vernacular maintenance" (teaching indigenous Australians some words and concepts related to the lost language).[5]
The Tasmanian people were nearly eradicated early in Australia's colonial history, and their languages were lost before much was recorded. Tasmania was separated from the mainland at the end of the last ice age, and the Tasmanian Aborigines apparently remained isolated from the outside world for around 10,000 years. Too little is known of their languages for classification, though they seem to have had phonological similarities with languages of the mainland.
Contents
Common features
Whether or not it is due to genetic unity, typologically the Australian languages form a language area or Sprachbund, sharing much of their vocabulary and sharing many distinctive phonological features across the entire continent.
A common feature of many Australian languages is that they display so-called mother-in-law languages, special speech registers used only in the presence of certain close relatives. These registers share the phonology and grammar of the standard language, but the lexicon is different and usually very restricted. There are also commonly speech taboos during extended periods of mourning or initiation that have led to a large number of Aboriginal sign languages.
For morphosyntactic alignment, many Australian languages have ergative-absolutive case systems. These are typically split systems; a widespread pattern is for pronouns (or first and second person) to have nominative-accusative case marking and for third person to be ergative–absolutive, though splits between animate and inanimate are also found. In some languages the persons in between the accusative and ergative inflections (such as second person, or third-person human) may be tripartite: that is, marked overtly as either ergative or accusative in transitive clauses, but not marked as either in intransitive clauses. There are also a few languages which employ only nominative–accusative case marking.
Phonetics and phonology
Segmental inventory
A typical Australian phonological inventory includes just three vowels, usually [a, i, u], which may occur in both long and short variants. In a few cases the [u] has been unrounded to give [a, i, ɯ].
There is almost never a voicing contrast; that is, a consonant may sound like a [p] at the beginning of a word, but like a [b] between vowels, and either symbol could be (and often is) chosen to represent it. Australia also stands out as being almost entirely free of fricatives, even of [h]. In the few cases where fricatives do occur, they developed recently through the lenition (weakening) of stops, and are therefore non-sibilants like [ð] rather than sibilants like [s] which are so much more common elsewhere in the world. Some languages also have three rhotics (R sounds), typically a flap, a trill, and an approximant; that is, like the combined R's of English and Spanish.
Besides the lack of fricatives, the most striking feature of Australian speech sounds are the large number of places of articulation. Nearly every language has four places in the coronal region, either phonemically or allophonically This is accomplished through two variables: the position of the tongue (front or back), and its shape (pointed or flat). There are also bilabial, velar and often palatal consonants, but a complete absence of uvular or glottal consonants. Both plosives and nasals occur at all six places, and in some languages laterals occur at all four coronal places.
A language which displays the full range of stops and laterals is Kalkutungu, which has labial p, m; "dental" th, nh, lh; "alveolar" t, n, l; "retroflex" rt, rn, rl; "palatal" ty, ny, ly; and velar k, ng. Yanyuwa has even more contrasts, with an additional true dorso-palatal series, plus prenasalized stops at all seven places of articulation, in addition to all four laterals.
A notable exception to the above generalizations is Kala Lagaw Ya, which has an inventory more like its Papuan neighbours than the languages of the Australian mainland, including full voice contrasts: /p b/, dental /t̪ d̪/, alveolar /t d/, the sibilants /s z/ (which have allophonic variation with [tʃ] and [dʒ] respectively) and velar /k ɡ/, as well as only one rhotic, one lateral and three nasals (labial, dental and velar) in contrast to the 5 places of articulation of stops/sibilants. Where vowels are concerned, it has 8 vowels with some morpho-syntactic as well as phonemic length contrasts (i iː, e eː, a aː, ə əː, ɔ ɔː, o oː, ʊ ʊː, u uː. Kunjen[disambiguation needed
 ] and other neighbouring languages have also developed contrasting aspirated plosives ([pʰ], [t̪ʰ], [tʰ], [cʰ], [kʰ]) not found further south.
] and other neighbouring languages have also developed contrasting aspirated plosives ([pʰ], [t̪ʰ], [tʰ], [cʰ], [kʰ]) not found further south.Coronal consonants
Descriptions of the coronal articulations can be inconsistent.
The "alveolar" series t, n, l (or d, n, l) is straightforward: across the continent, these sounds are alveolar (that is, pronounced by touching the tongue to the ridge just behind the gum line of the upper teeth) and apical (that is, touching that ridge with the tip of the tongue). This is very similar to English t, d, n, l, though the Australian t is not aspirated, though again here Kala Lagaw Ya is a notable exception, as all the stops are aspirated.
The other apical series is the "retroflex", rt, rn, rl (or rd, rn, rl). Here the place is further back in the mouth, in the postalveolar or prepalatal region. The articulation is actually most commonly sub-apical; that is, the tongue curls back so that the underside of the tip makes contact. That is, they are true retroflex consonants. It has been suggested that sub-apical pronunciation is characteristic of more careful speech, while these sounds tend to be apical in rapid speech. Kala Lagaw Ya differs from most other Australian languages in not having a retroflexive series.
The "dental" series th, nh, lh are always laminal (that is, pronounced by touching with the surface of the tongue just above the tip, called the blade of the tongue), but may be formed in one of three different ways, depending on the language, on the speaker, and on how carefully the speaker pronounces the sound. These are interdental with the tip of the tongue visible between the teeth, as in th in American English; interdental with the tip of the tongue down behind the lower teeth, so that the blade is visible between the teeth; and denti-alveolar, that is, with both the tip and the blade making contact with the back of the upper teeth and alveolar ridge, as in French t, d, n, l. The first tends to be used in careful enunciation, and the last in more rapid speech, while the tongue-down articulation is less common.
Finally, the "palatal" series ty, ny, ly. (The stop is often spelled dj, tj, or j.) Here the contact is also laminal, but further back, spanning the alveolar to postalveolar, or the postalveolar to prepalatal regions. The tip of the tongue is typically down behind the lower teeth. This is similar to the "closed" articulation of some Circassian fricatives (see Postalveolar consonant). The body of the tongue is raised towards the palate. This is similar to the "domed" English postalveolar fricative sh. Because the tongue is "peeled" from the roof of the mouth from back to front during the release of these stops, there is a fair amount of frication, giving the ty something of the impression of the English palato-alveolar affricate ch or the Polish alveolo-palatal affricate ć. That is, these consonants are not palatal in the IPA sense of the term, and indeed they contrast with true palatals in Yanyuwa. In Kala Lagaw Ya, the palatal consonants are sub-phonemes of the alveolar sibilants /s/ and /z/.
These descriptions do not apply exactly to all Australian languages, as the notes regarding Kala Lagaw Ya demonstrate. However, they do describe most of them, and are the expected norm against which languages are compared.
Orthography
Main article: Transcription of Australian Aboriginal languagesProbably every Australian language with speakers remaining has had an orthography developed for it, in each case in the Latin alphabet. Sounds not found in English are usually represented by digraphs, or more rarely by diacritics, such as underlines, or extra symbols, sometimes borrowed from the International Phonetic Alphabet. Some examples are shown in the following table.
Language Example Translation Type Pitjantjatjara pana 'earth, dirt, ground; land' diacritic (underline) indicates retroflex 'n' Wajarri nhanha 'this, this one' digraph indicating 'n' with dental articulation Gupapuyŋu yolŋu 'person, man' 'ŋ' (from IPA) for velar nasal Classification
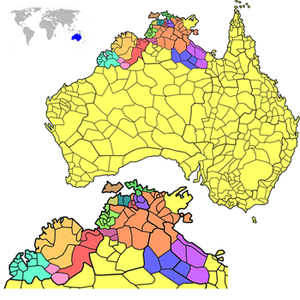 A language map, different colours represent different language families. From west to east:
A language map, different colours represent different language families. From west to east: YiwaidjanGarawa plus some Tangkic and Pama–Nyungan languagesPama–Nyungan plus some Tangkic languages
YiwaidjanGarawa plus some Tangkic and Pama–Nyungan languagesPama–Nyungan plus some Tangkic languagesInternal
Most Australian languages are commonly held to belong to the Pama—Nyungan family, a family accepted by most linguists, with R.M.W. Dixon as a notable exception. For convenience, the rest of the languages, all spoken in the far north, are commonly lumped together as "Non-Pama–Nyungan" without this meaning to imply their constituting a valid clade. Dixon argues that after perhaps 40,000 years of mutual influence, it is no longer possible to distinguish deep genealogical relationships from areal features in Australia, and that not even Pama–Nyungan is a valid language family. However, few other linguists, Australian or otherwise, accept Dixon's thesis. Kenneth L. Hale describes Dixon's skepticism as an "extravagantly and spectacularly erroneous" and "wrong-headed" phylogenetic assessment which is "so bizarrely faulted, and such an insult to the eminently successful practitioners of Comparative Method Linguistics in Australia, that it positively demands a decisive riposte."[6] In the same paper, Hale provides pronominal and grammatical evidence (with suppletion) as well as more than fifty basic-vocabulary cognates (showing regular sound correspondences) between the proto-Northern-and-Middle Pamic (pNMP) family of the Cape York Peninsula on the Australian northeast coast and proto-Ngayarta of the Australian west coast, some 3,000 km apart, (as well as from many other languages) to support the Pama–Nyungan grouping, whose age he compares to that of Proto-Indo-European.
External
It has been suggested that most or all Australian languages have a relationship with the Trans–New Guinea languages.[7][8] or the Sepik–Ramu languages.[9] Neither of these conclusions is currently widely accepted. William Foley (1986) noted lexical similarities between R.M.W. Dixon's 1980 reconstruction of proto-Australian and the languages of the East New Guinea Highlands. He believed that it was naïve to expect to find a single Papuan or Australian language family when New Guinea and Australia had been a single landmass (called the Sahul continent) for most of their human history, having been separated by the Torres Strait only 8000 years ago, and that a deep reconstruction would likely include languages from both. However, Dixon later abandoned his proto-Australian proposal[10] and thus more research into the area is needed before drawing conclusions.
Subgrouping
Traditionally, Australian languages have been divided into about two dozen families. What follows is a tentative classification of genealogical relationships among the Australian families, following the work of Nick Evans and associates at the University of Melbourne.[11] Although not all subgroupings are mentioned, there is enough detail to fill in the rest using a standard reference such as Ethnologue: Languages of the World. Note when cross-referencing that most language names have multiple spellings: rr=r, b=p, d=t, g=k, dj=j=tj=c, j=y, y=i, w=u, u=oo, e=a, and so on. A range is given for the number of languages in each family, as sources count languages differently.
- Presumptive isolates:
- Enindhilyagwa (Andilyaugwa)
- Laragiya (extinct?)
- Ngurmbur (extinct? perhaps a member of Macro-Pama–Nyungan)
- Tiwi
- Previously established families:
- Bunaban (2 languages in two branches) [accepted by Dixon]
- Daly (11-19 languages in five branches, including Murrinh-Patha) [5 families per Dixon, one questionable]
- Limilngan (2 languages, extinct?)
- Jarrakan formerly spelled "Djeragan" (3-5 languages in two branches)
- Nyulnyulan (8 languages in two branches) [accepted by Dixon]
- Wororan (7-12 languages in three branches) [3 families per Dixon]
- Newly proposed families:
- Mirndi, consisting of
- Yirram (2-4 languages)
- West Barkly (3 languages in two branches)
- Arnhem Land macrofamily, consisting of
- Macro-Pama Nyungan, consisting of
- (perhaps) Ngurmbur
- Gunwinyguan (15-17 languages in six branches, including the Kungarakany isolate)
- Greater Pama–Nyungan:
- Tangkic (4 languages in two branches)
- the Garawa (2 languages) [accepted by Dixon]
- Pama–Nyungan proper (approximately 175 languages in 14 extant and numerous extinct branches) [few of the branches are accepted by Dixon]
- Mirndi, consisting of
In addition, there is the extinct and poorly attested Minkin language. Conventionally left as an isolate, there is little data on which to determine its classification; it may have been a member of Iwaidjan or Tangkic.
Languages
Main article: List of Australian Aboriginal languagesSee also
- Australian Aboriginal sign languages
- Gunwinyguan languages
- Australian Aborigines
- List of Indigenous Australian group names
- List of Australian place names of Aboriginal origin
- Macro-Pama–Nyungan languages
- Southwest Pama–Nyungan languages
- List of Australian repeated place names
References
- Dalby, Andrew (1998). Dictionary of Languages. Bloomsbury Publishing plc. pp. 43. ISBN 0-7475-3117-X.
- Dixon, R.M.W. 1989. Searching for Aboriginal Languages. University of Chicago Press, 1989. ISBN 0-226-15430-0
- Dixon, R. M. W. 2002. Australian Languages: Their Nature and Development.
- Evans, Nicholas (ed.). 2003. The non-Pama–Nyungan languages of northern Australia: comparative studies of the continent's most linguistically complex region. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
- McConvell, Patrick and Nicholas Evans. (eds.) 1997. Archaeology and Linguistics: Global Perspectives on Ancient Australia. Melbourne: Oxford University Press
- O'Grady, Geoff; Ken Hale. 2004. The Coherence and Distinctiveness of the Pama–Nyungan Language Family within the Australian Linguistic Phylum. In Claire Bowern and Harold Koch, eds., Australian Languages: Classification and the Comparative Method. John Benjamins Pub. Co.
- UNESCO Interactive Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger (retrieved 8/6/10)
- Walsh, Michael. 1991. Overview of indigenous languages of Australia. In Suzane Romaine (ed), Language in Australia. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521339839
- Zuckermann, Ghil'ad, "Aboriginal languages deserve revival", The Australian Higher Education, 26 August 2009.
External links
- The Linguist List MultiTree Project: Australian Family Tree
- Map of indigenous Australian languages from Muturzikin.com
- Aboriginal Languages of Australia
- The Horton map of Australian indigenous languages
- Languages of Australia, as listed by Ethnologue
- National Indigenous Languages Survey Report 2005 PDF format, size 2.6 MB Accessed 16 February 2009
- Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (AIATSIS)
- Ethnologue report on all languages by alphabetical order
- Finding the meaning of an Aboriginal word
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Social Justice Commissioner, Social Justice Report 2009 for more information about Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander languages and policy.
Languages of Australia English varieties 
Major indigenous
languagesArrernte · Kala Lagaw Ya · Luritja · Pintupi · Pitjantjatjara · Tiwi · Walmajarri · Warlpiri · Western Desert · Yolŋu MathaPidgins, creoles and
mixed languagesSign languages Categories: - Presumptive isolates:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.