- Differences between management accounting and financial accounting
-
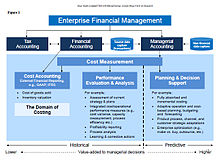 The structure of accounting as documented by the International Federation of Accountants
The structure of accounting as documented by the International Federation of Accountants
The differences between management accounting and financial accounting include:[1]
- Management accounting provides information to people within an organisation while financial accounting is mainly for those outside it, such as shareholders
- Financial accounting is required by law while management accounting is not. Specific standards and formats may be required for statutory accounts such as International Financial Reporting Standards.
- Financial accounting covers the entire organisation while management accounting may be concerned with particular products or cost centres.
Managerial accounting is used primarily by those within a company or organization. Reports can be generated for any period of time such as daily, weekly or monthly. Reports are considered to be "future looking" and have forecasting value to those within the company.
Financial accounting is used primarily by those outside of a company or organization. Financial reports are usually created for a set period of time, such as a fiscal year or period. Financial reports are historically factual and have predictive value to those who wish to make financial decisions or investments in a company. Management Accounting is the branch of Accounting that deals primarily with confidential financial reports for the exclusive use of top management within an organization. These reports are prepared utilizing scientific and statistical methods to arrive at certain monetary values which are then used for decision making. Such reports may include:
- Sales Forecasting reports
- Budget analysis and comparative analysis
- Feasibility studies
- Merger and consolidation reports
Financial Accounting, on the other hand, concentrates on the production of financial reports, including the basic reporting requirements of profitability, liquidity, solvency and stability. Reports of this nature can be accessed by internal and external users such as the shareholders, the banks and the creditors.
Contents
Regulation and standardization
While financial accountants follow Generally Accepted Accounting Principles set by professional bodies in each country, managerial accountants make use of procedures and processes that are not regulated by a standard-setting bodies. However, multinational companies prefer to employ managerial accountants who have passed the Certified Management Accountant certification. The CMA is an examination given by the Institute of Management Accountant, a professional organization of Accounting professionals. This certification is different.
Time Period
Managerial Accounting provides top management with reports that are future-oriented, while Financial Accounting provides reports based on historical information. There is no time span for producing managerial accounting statements but financial accounting statements are generally required to be produced for the period of 12 previous months.
Other differences
- There is no legal requirement for an organization to use management accounting but publicly-traded firms (limited companies or whose shares are bought and sold on an open market) must, by law, prepare financial account statements.
- In management accounting systems there is no requirement for an independent external review but financial accounting annual statements must be audited by an independent CPA firm.
- In management accounting systems, management may be concerned about how reports will affect employees behavior whereas management concerns are about the adequacy of disclosure in financial statements.
References

This accountancy-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
