- Oceanic languages
-
Oceanic Geographic
distribution:Melanesia, Micronesia, Polynesia Linguistic classification: Austronesian - Paiwanic ?
- Malayo-Polynesian (MP)
- Nuclear MP
- (Central–Eastern)
- Oceanic
- (Central–Eastern)
- Nuclear MP
- Malayo-Polynesian (MP)
Proto-language: Proto-Oceanic Subdivisions: 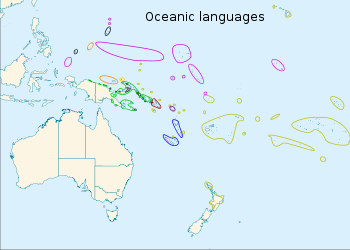
The branches of OceanicAdmiralties and YapeseSt MatthiasWestern Oceanic & Meso-MelanesianTemotuSoutheast SolomonsSouthern OceanicMicronesianFijian–PolynesianThe black ovals at the northwestern limit of Micronesian are the Sunda–Sulawesi languages Palauan and Chamorro. The black circles in with the green are offshore Papuan languages.The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a well-established family of Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia.
Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Samoan, with an estimated 370,000 speakers, and Eastern Fijian with over 500,000 speakers. Kiribati (Gilbertese), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Kuanua (Tolai) each have over 100,000 speakers.
The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. POc).
Classification
The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896, and besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only large established family of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they retain a remarkably large amount of Austronesian vocabulary.[1]
A 2008 analysis of the Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database[2] fully supported the unity of Oceanic. However, some of the traditional divisions of that family were not supported. There was no support for grouping the Meso-Melanesian languages with the rest of the Western Oceanic languages, while there was moderate support for grouping it with the erstwhile Central Eastern Oceanic branch.
- Western Oceanic (reduced; languages of the north coast of New Guinea, perhaps from as far west as Jayapura, to the eastern tip of New Guinea and western New Britain)
- Admiralty Islands
- Meso-Melanesian (languages of the Bismarck Archipelago and Solomon Islands; only moderately supported as a unit)
- Temotu
- Southern Oceanic (languages of New Caledonia and Vanuatu)
- Central Pacific (Polynesian and the languages of Fiji)
- Micronesian
All branches were fully supported by the 2008 analysis except for Meso-Melanesian, which at 82% confidence was only moderately supported as a unit. In addition, there was moderate support for subgrouping the branches of Oceanic:
Oceanic
(100%)(67%) Admiralty Islands
(83%) Meso-Melanesian
(82%)Bali–Vitu
Meso-Melanesian proper
(84% confidence as a unit)(70%) Fijian–Polynesian (Central Pacific)
Western Oceanic (partial)
References
- ^ Mark Donohue and Tim Denham, 2010. Farming and Language in Island Southeast Asia: Reframing Austronesian History. Current Anthropology, 51(2):223–256.
- ^ Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database
- Ray, S.H. (1896). "The common origin of the Oceanic languages". Journal of the Polynesian Society: 58–68.
- Lynch, John; Malcolm Ross; Terry Crowley (2002). The Oceanic languages. Richmond, Surrey: Curzon. ISBN 9780700711284. OCLC 48929366.
- Ross, Malcolm and Åshild Næss (2007). "An Oceanic Origin for Äiwoo, the Language of the Reef Islands?". Oceanic Linguistics 46: 456–498.
Categories: - Paiwanic ?
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
