- 2007 Boston bomb scare
-
2007 Boston Bomb Scare 
LED advertisement resembling the cartoon character Ignignokt from Aqua Teen Hunger Force giving the middle finger, as seen in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Identical devices were removed by the Boston Police Department throughout the area on January 31, 2007.Date January 31, 2007 Attack type Bomb scare Weapon(s) 0 Death(s) 0 Injured 0 The 2007 Boston bomb scare occurred on January 31, 2007 when the Boston Police Department mistakenly identified battery-powered LED placards resembling the Mooninite characters in the show Aqua Teen Hunger Force found throughout Boston, Massachusetts and the surrounding cities of Cambridge and Somerville as improvised explosive devices.[1][2] The placards were part of a guerrilla marketing campaign for Aqua Teen Hunger Force Colon Movie Film for Theaters, a film based on the animated television series, Aqua Teen Hunger Force on Cartoon Network's late-night programming block, Adult Swim.[2]
The scare was met with criticism from a number of sources such as The Boston Globe, Los Angeles Times, Fox News, and The Boston Herald. A group of police found them to be sharing "some characteristics with improvised explosive devices." These characteristics included an identifiable power source, circuit board with exposed wiring, and electrical tape. Investigators were trying to determine "if it was a hoax or something else entirely".[3][4] City and State officials came to an agreement with Turner Broadcasting to pay for costs incurred during the incident, while several police departments found many of the devices afterwards.[5]
Contents
Planning
In November 2006, Peter Berdovsky, a Boston area artist, met a man named "John aka VJ Aiwaz" in New York. John worked for marketing company Interference, Inc. and asked Berdovsky if he would be interested in working on a promotional project. Berdovsky agreed and then enlisted the help of Sean Stevens to the project. Interference shipped Berdovsky 40 electronic signs. Adrienne Yee of Interference e-mailed him a list of suggested locations and a list of things not to do. According to the police, the suggested locations for the devices included "Train stations, overpasses, hip/trendy areas and high traffic/high visibility areas." The signs were to be put up discreetly overnight. They were to be paid $300 each for their assistance.
Berdovsky, Stevens and Dana Seaver put up 20 magnetic lights in the middle of January. They dubbed the activity "Boston Mission 1." While Stevens and Berdovsky put up the lights, Seaver recorded the activity on video and sent a copy afterward to Interference. On the night of January 29, 2007, 18 more magnetic lights were put in place in what was called "Boston Mission 2." This included the one under Interstate 93 at Sullivan Square in Charlestown.[6][7]
Devices
The devices closely resemble the Night Writer promoted by the Graffiti Research Lab in early 2006.[8] The devices were promotional electronic placards for the forthcoming Aqua Teen Hunger Force Colon Movie Film for Theaters. Each device, measuring about 1 by 1.5 feet,[2] consisted of a printed circuit board (PCB) which had been painted black with light-emitting diodes and other electronic components soldered to it, including numerous resistors, a few capacitors, and at least one integrated circuit package. At the bottom was a pack of four Publix brand D-cell batteries (as seen in photo), and magnets were attached to the back so the devices could be easily mounted on any ferromagnetic surface. The batteries were originally covered in black tape to blend with the black PCB.
The LEDs were arranged to show a cartoon character displaying the middle finger.[9][10] Two variants were manufactured with the LEDs arranged in pixelated likenesses of Ignignokt and Err, Mooninite characters from Aqua Teen Hunger Force. Massachusetts Attorney General Martha Coakley said the device "had a very sinister appearance. It had a battery behind it, and wires."[11] Others compared the displays to the Lite-Brite electric toy in appearance.[11]
The scare
On January 31, 2007, at 8:05 a.m. a passenger spotted the device on a stanchion that supports an elevated section of Interstate 93 (I-93), above Sullivan Station and told a policeman with the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority.[3] At 9 a.m., the Boston Police Department bomb squad received a phone call from the MBTA requesting assistance in identifying the device.[12] Authorities responded with what the Boston Globe described as "[an] army of emergency vehicles" at the scene, including police cruisers, fire trucks, ambulances, and the Boston Police Department bomb squad. Also present were live TV crews with helicopters circling overhead and a large crowd of onlookers.[3] Peter Berdovsky, who had placed the device, went to the scene and video recorded the situation. Berdovsky recognized the device the police were dealing with but made no attempt to inform the police at the scene of what he knew about it. Berdovsky returned to his apartment and contacted the company, Interference, who had hired him to place the lights. He was told by Interference that they would handle informing the police and that he should personally say nothing about the situation.[13]
During the preliminary investigation at the site, the police found that the device shared "some characteristics with improvised explosive devices." These characteristics included an identifiable power source, circuit board with exposed wiring, and electrical tape. After the initial assessment, the Boston police shut down the northbound side of I-93 and parts of the public transportation system. Just after 10 a.m. the bomb squad used a small explosive filled with water to destroy it as a precaution. MBTA Transit police Lieutenant Salvatore Venturelli told the media at the scene, "This is a perfect example of our passengers taking part in Homeland Security." He refused to describe the object in detail because of the ongoing investigation responding that "It's not consistent with equipment that would be there normally," Investigators were trying to determine "if it was a hoax or something else entirely" according to Venturelli.[3][4] Northbound I-93 reopened to traffic at about 10:05 a.m. By 10:21 a.m. it was determined to be "some sort of hoax device" according to a police timeline of the events.[12]
At 12:54 p.m., Boston police received a call identifying a similar device located at the intersection of Stuart and Charles Street.[12] At 1:11 p.m. the Massachusetts State Police requested assistance from the bomb squad with devices found under the Longfellow and Boston University bridges.[12] Both bridges were closed as a precaution and the Coast Guard closed the river itself to boat traffic.[14][15]
Friends of Peter Berdovsky received an e-mail from him at 1:26 p.m. which alleged that five hours into the scare, an Interference Inc. (the marketing firm that created the campaign) executive requested Berdovsky "keep everything on the dl."[6] Travis Vautour, friend of Berdovsky, stated: "We received an e-mail in the early afternoon from Peter that asked the community that he's a part of to keep any information we had on the down low and that was instructed to him by whoever his boss was."[16] Two hours later, Interference notified their client, Cartoon Network.[6] Between 2 and 3 p.m., a police analyst identified the image on the devices as an Aqua Teen Hunger Force cartoon character, and the police concluded the incident was a publicity stunt.[2] Turner Broadcasting System issued a statement concerning the event at around 4:30 p.m.[2] Portions of the Turner statement read:
"We regret that they were mistakenly thought to pose any danger. The packages in question are magnetic lights that pose no danger. They are part of an outdoor marketing campaign in 10 cities in support of Adult Swim's animated television show Aqua Teen Hunger Force. They have been in place for two to three weeks in Boston, New York City, Los Angeles, Chicago, Atlanta, Seattle, Portland, Austin, San Francisco, and Philadelphia. Parent company Turner Broadcasting is in contact with local and federal law enforcement on the exact locations of the billboards. We regret that they were mistakenly thought to pose any danger."[17]
Some devices had been up in the cities listed for two weeks before the Boston incident occurred, although no permits were ever secured for the devices' installation.[17] The marketing company responsible for the campaign, Interference, Inc., made no comment on the situation and their website was also down (restored as of 2007-02-03).[18] Berdovsky and Stevens, the individuals hired by Interference to install the signs, were arrested by Boston police during the evening of January 31, and charged with violating Chapter 266: Section 102A½ of The General Laws of Massachusetts, which makes it a crime to place a "hoax device" with the intent to panic the public.[9][19] Both were held at the State Police South Boston barracks overnight and were released on $2,500 bail from the Charlestown District Court the following morning.
Reactions
The Boston Globe stated that the "marketing gambit exposes a wide generation gap," quoting one 29-year-old blogger as writing "Repeat after me, authorities. L-E-D. Not I-E-D. Get it?"[20] The Globe's Brainiac blog was quick to credit bloggers such as Todd Vanderlin and Brian Stuart for being among the first to report on the ad's origin.[21] The Brainiac blog earned praise from other media outlets for their own timely coverage of events, even as the paper continued to report on simply "suspicious objects".[22]
Los Angeles Times editorials derided the reaction of Boston's officials, remarking "Emergency personnel and anti-terrorism squads shut down more than a dozen highways, transit stations and other locations across the city Wednesday after receiving reports about multiple suspicious devices. The slender, placemat-sized items had dozens of colored lights, exposed wires and circuitry, and were powered by a row of D batteries wrapped in black tape. In other words, they looked like an upscale version of Hasbro's Lite-Brite, a toy for artistic grade-schoolers."[23] Bruce Schneier, a computer security expert and writer on contemporary security issues summed up the incident as a "Non-Terrorist Embarrassment in Boston".[24]
The Boston Herald stated that part of the overreaction in the response could be blamed on two packages that did not blink. According to Boston Police Commissioner Ed Davis, phony pipe bombs were also discovered that day, one inside Tufts-New England Medical Center at 1 p.m. Its security guard described "an agitated white male" fleeing saying, "God is warning you that today is going to be a sad day." The Herald goes on to characterize the placement of the devices as a "coordinated hoax." Davis also mentioned other incidents of the day that may have influenced the reaction, including a Washington DC metro stop being shut down due to a suspected package and fumes emanating from a package at a post office in New York City, resulting in four people being treated there. "It was almost like we had a kind of perfect storm of circumstances falling into place," Davis said.[25]
The advertising magazine Brandweek said that the incident, which it labeled a fiasco, would cause marketers to "steer clear of guerrilla tactics until the controversy around the Aqua Teen Hunger Force stunt-turned-bomb-scare in Boston dies down." It further said the incident "will no doubt be followed by a reassessment of the potential price of what used to be known as a low-cost method to generate buzz."[26]
According to Fox News, fans of Aqua Teen Hunger Force mocked Boston officials during the press conference of Berdovsky and Stevens, calling the arrests an overreaction while holding signs supporting the actions of the two. These signs had slogans such as "Free Peter" and "1-31-07 Never Forget," satirizing Mayor Tom Menino's mentions of 9/11.[27] Other local Boston residents were quoted by local papers. "We all thought it was pretty funny," said one student. "The majority of us recognize the difference between a bomb and a Lite-Brite," said another.[28] One resident said that the police response was "silly and insane," and that "We’re the laughingstock."[29] Something Positive, which is written and drawn by Waltham resident R. K. Milholland, also weighed in on the issue.[30] Bloggers on the Boston section of LiveJournal commented on channel 4 footage of the first device being exploded and clearly identified it as a "mooninite" reacting in disbelief.[31] One blogger pointed out the similarity to what he called "Super Mario Question Block Hysteria all over again" in which five high school girls in Ravenna, Ohio placed brightly colored boxes with question marks resembling the Super Mario game around town, and drew the bomb squad and possible prosecution. Similar boxes had been placed around various universities in the country including U Mass. The effort was part of an artistic and political commentary on the use of public space which spread in 2006.[32][33]
Karl Carter of Atlanta, Georgia-based Guerrilla Tactics Media said fans of the show "Aqua Teen Hunger Force" would recognize the character and think it was funny, but other people who saw the signs wouldn't get the joke. "This is probably better set up for nightclubs and other sorts of scenarios where the people that are receiving the message, one, would know what it's about, but also two, wouldn't be frightened," he said. "You know, if you put these in certain environments, like public spaces in this post-9/11 sensitivity, then of course you're going to wind up in trouble." Make Magazine editor Phillip Torrone said the advertisers should have used better judgement, but called the Mooninite board a "neat electronic project."[34] As reported by BoingBoing, the media and the State of Massachusetts itself maintained the use of the word "hoax" when describing the event, despite Turner Broadcasting Systems' contentions that they had no intention of arousing suspicion or panic in approving the advertising campaign.[35]
On February 27, 2007, just a month after the incident, Boston police authorities detonated another object that they believed to be a bomb, but it ended up being a traffic counter.[36][37] The next day, Bax and O'Brien on the Western Massachusetts radio station WAQY weighed in, with John O'Brien saying, "and they (the devices) were also placed in Boston over two weeks ago. I don't think the terrorism officials in Boston are very observant..... Good thing September 11th didn't happen here; we wouldn't have found it until September 20th."[citation needed] In the months following the scare, stickers reading, "Don't Panic! This is NOT A BOMB. Do not be afraid. Do not call the police. Stop letting the terrorists win," began to appear on Boston parking meters, ATMs and other objects in public, as a sarcastic rebuke of the police overreaction.[38][39] Despite all this, on March 18, 2007 at the annual St. Patrick's Day Breakfast in South Boston, jokes were made about the incident by Massachusetts politicians. Tom Menino himself said it was a way to obtain a local aid package for the city. Congressman Stephen Lynch claimed that the Mooninites were part of a sleeper cell that also included SpongeBob SquarePants. State Treasurer Timothy P. Cahill held up a picture of a Mooninite with Mitt Romney's face on it, saying "We had to blur out his real feelings about Massachusetts."[40]
Aftermath
 Aqua Teen Hunger Force promotional devices were placed in public places in ten different cities. This is one found at the entrance to Peachtree Center MARTA station in Atlanta, Georgia.
Aqua Teen Hunger Force promotional devices were placed in public places in ten different cities. This is one found at the entrance to Peachtree Center MARTA station in Atlanta, Georgia.
City and State officials came to an agreement with Turner Broadcasting to pay for costs incurred during the incident. As part of a settlement that resolves all criminal and civil claims, Turner Broadcasting Systems and Interference Inc. agreed to pay $2 million, $1 million of this to go towards the Boston police department, and $1 million towards the United States Department of Homeland Security. In addition, Turner released a statement to take responsibility and apologize for the incident.[5] Less than a week following Turner's apology, Jim Samples stepped down from his 13 year position as head of Cartoon Network, stating that he was "compelled to step down . . . in recognition of the gravity of the situation that occurred under [his] watch." Shortly afterwards Stuart Snyder became the new president of Cartoon Network.[41]
Ten cities in all were involved in the marketing campaign that began two to three weeks before the incident in Boston. The New York City Police Department contacted Interference Inc., a New York-based marketing firm, to request a list of 41 locations where the devices were installed.[42] Officers were able to locate and remove only two devices, both planted on an overpass at 33rd Street and West Side Highway.[42] The NYPD did not receive any complaints about the devices according to police spokesman Paul Brown.[42] At 9:30 p.m. on the evening of January 31, the Chicago Police Department received a list of installation locations from Interference Inc.[43] Police recovered and disposed of 20 of the 35 devices, leaving 15 unaccounted for. Police Superintendent Philip Cline admonished those responsible for the campaign, stating, "one of the devices could have easily been mistaken for a bomb and set off enough panic to alarm the entire city."[43] Cline went on to say that, on February 1, he asked Turner Broadcasting to reimburse the city for funds spent on locating and disposing the devices.[43] Two men were briefly held in connection to the incident. Fewer than 20 devices were found in Seattle and neither the Seattle Police Department nor the King County Sheriff's Office received 9-1-1 calls regarding them.[44] King County Sheriff's spokesman John Urquhart went on to state, "To us, they're so obviously not suspicious ... We don't consider them dangerous."[44] "In this day and age, whenever anything remotely suspicious shows up, people get concerned —and that's good. However, people don't need to be concerned about this. These are cartoon characters giving the finger."[45]
Interference Inc. hired two people to distribute 20 devices throughout Philadelphia on January 11.[46] One of these was Ryan, a 24-year-old from Fishtown, who claimed that he was promised $300 for installing the devices, only 18 of which were actually functional.[46] Following the scare in Boston, the Philadelphia Police Department recovered only 3 of the 18 devices. Joe Grace, spokesman for Philadelphia Mayor John F. Street, was quoted as saying "We think it was a stupid, regrettable, irresponsible stunt by Turner. We do not take kindly to it."[46] A cease-and-desist letter was sent to Turner, threatening fines for violating zoning codes.[47]
No devices were retrieved in Los Angeles and Lieutenant Paul Vernon of the LAPD stated that "no one perceived them as a threat."[48] The many Los Angeles signs were up over 2 weeks before the Boston Scare with no incident. Police Sergeant Brian Schmautz stated that officers in Portland had not been dispatched to remove the devices, and did not plan to unless they were found on municipal property. He added, "At this point we wouldn't even begin an investigation, because there's no reason to believe a crime has occurred." [11] This device was placed in inside of 11th Ave Liquor on Hawthorne Boulevard in Portland, where it remains. San Francisco police Sgt. Neville Gittens said that Interference Inc. was removing them, except for one found by art gallery owner Jamie Alexander who reportedly "thought it was cool" and had it taken down after it ceased to function. [49]
Berdovsky and Stevens were arrested on the day of the incident and charged with placing a hoax device to incite panic, a felony charge that carries a five-year maximum sentence, and one count of disorderly conduct, a misdemeanor.[19] Both pleaded not guilty to the two charges and were later released on a $2,500 cash bond.[6] At their arraignment Assistant Attorney General John Grossman claimed that the two were trying to "get attention by causing fear and unrest that there was a bomb in that location."[50] Michael Rich, the lawyer representing both men, disputed Grossman's claim, asserting that even a VCR could be found to fit the description of a bomb-like device.[50] Judge Leary said that it will be necessary for the prosecution to demonstrate an intent on the part of the suspects to cause a panic. The judge continues "It appears the suspects had no such intent, ...but the question should be discussed in a later hearing."[50] After making bail, Berdovsky and Stevens appeared for a live press conference. As Rich had advised them not to discuss the case, they spent the entire conference discussing and inviting press questions about hair styles of the 1970s, and ignoring any questions relating to the bomb scare.[51]
On March 1, 2007, Senator Edward Kennedy, D-MA, introduced S.735, "The Terrorist Hoax Improvements Act of 2007". It "Amends the federal criminal code to: (1) extend the prohibition against conveying false information and hoaxes to any federal crime of terrorism; (2) increase maximum prison terms for hoaxes involving a member of the Armed Forces during war; (3) allow a civil remedy for damages resulting from hoaxes perpetrated by an individual who later fails to provide accurate information to investigating authorities about the actual nature of the incident; and (4) extend the prohibition against mailing threatening communications to include corporations or governmental entities (as well as individuals)."[52][53] The bill never came to a vote.[54]
On May 11, 2007, the prosecutors decided not to pursue criminal charges in exchange for community service and a public apology. Attorney General Martha Coakley cited the difficulty in proving intent to incite panic on the part of the two men and called the deal "an appropriate and fair resolution." Berdovsky and Stevens completed 80 and 60 hours of community service at the Spaulding Rehabilitation Center in Boston.[55] The incident prompted opportunists to acquire the promotional devices from other cities and auction them on eBay, with prices ranging from $500 to over $5,000 USD.[56] Other eBay users created merchandise commemorating the event, including such items as T-shirts, stickers, and custom LED signs.[57]
An Aqua Teen Hunger Force episode from season five entitled "Boston" was produced as the series creators' response to the bomb scare, but Adult Swim pulled it to avoid further controversy.[58] As of 2011 "Boston" has never aired, and has never been released to the public in any format.
Notes
- ^ Byron, Katy; Kelley, Rob (2007-02-09). "Cartoon Network boss quits over bomb scare". CNNMoney.com. Archived from the original on 2010-01-18. http://money.cnn.com/2007/02/09/news/newsmakers/cartoon_network/. Retrieved 2007-12-13.
- ^ a b c d e Smalley, Suzanne; Mishra, Raja (2007-02-01). "Froth, fear, and fury". The Boston Globe (The New York Times Company). Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.boston.com/news/local/massachusetts/articles/2007/02/01/froth_fear_and_fury/?page=full. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ a b c d "Bomb squad removes suspicious object that closed I-93 north". Posted by the Boston Globe City & Region Desk (Boston Globe). 11:15 AM January 31, 2007. http://www.google.com/search?q=cache:FeooQCvkYXkJ:www.boston.com/news/globe/city_region/breaking_news/2007/01/bomb_squad_remo.html. Retrieved 2007-02-06.
- ^ a b "'Suspicious' Package Not Bomb, Police Say WCVB-TV". WCVB-TV (wyff4.com). 10:58 am EST January 31, 2007. http://google.com/search?q=cache:PLqt7oH-XqoJ:www.wyff4.com/news/10888268/detail.html. Retrieved 2007-02-06.
- ^ a b "Turner, 2nd firm to pay $2 million over scare". MSNBC.com. Associated Press (Microsoft). 2007-02-05. Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/16990202/. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
- ^ a b c d Levenson, Michael; Mishra, Raja (2007-02-02). "Turner Broadcasting accepts blame, promises restitution". The Boston Globe (The New York Times Company). Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.boston.com/news/local/articles/2007/02/02/turner_broadcasting_accepts_blame_promises_restitution/?page=full. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ Levenson, Michael; Mishra, Raja & Cramer, Maria (2007-02-01). "Turner Broadcasting accepts full responsibility for scare". The Boston Globe (The New York Times Company). Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.boston.com/news/globe/city_region/breaking_news/2007/02/guerrilla_ad_ag.html. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
- ^ Night Writer Archived 22 February 2011 at WebCite
- ^ a b "Arrest Made In Boston's Hoax Device Incident". CBS Corporation. 2007-01-31. Archived from the original on February 2, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070202022654/http://cbs4boston.com/topstories/local_story_031135507.html. Retrieved 2007-01-31.
- ^ Jamy Pombo (January 31, 2007). "TV Network Takes Responsibility For 'Hoax Devices'". ABC. Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.thebostonchannel.com/news/10890113/detail.html. Retrieved 2007-01-31.
- ^ a b c Lothian, Dan; Fran Fifis, Deborah Feyerick (2007-02-01). "Two plead not guilty to Boston hoax charges". CNN. Archived from the original on February 3, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070203050621/http://www.cnn.com/2007/US/02/01/boston.bombscare/. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ a b c d Davis, Ed (2007-02-02). "Message From The Police Commissioner". BPDNews.com. Boston Police Department. Archived from the original on February 3, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070203120922/http://www.bpdnews.com/2007/02/message_from_the_police_commis_2.html. Retrieved 2007-02-03.
- ^ Man in Boston Scare Videotaped Police: Defendant in Boston marketing stunt scare videotaped police response, attorney says Feb. 6, 2007 Archived March 15, 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Man held after ad campaign triggers Boston bomb scare". CNN. 2007-02-01. Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.cnn.com/2007/US/01/31/boston.bombscare/index.html. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ "Security alert shuts Boston's Charles River". Reuters. January 31, 2007.
- ^ Silverstein, Jonathan (2007-02-02). "As Boston Reeled, Was Artist Asked to Keep Quiet?". ABC News. Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.abcnews.go.com/Technology/story?id=2841646&page=1. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ a b Powell, Shirley (2007-01-31). "Statement from Turner Broadcasting Co.". CNN (TBS Corporate Communications). Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.cnn.com/2007/US/01/31/TBS.statement/index.html. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ "Movie News – "Hunger Force" Ad Campaign Causes Boston Bomb Scare". Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.filmfodder.com/mt-weblog/archives/003544.shtml.
- ^ a b "Possession, transportation, use or placement of hoax devices". The General Laws of Massachusetts (Chapter 266: Section 102A1/2). Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.mass.gov/legis/laws/mgl/266-102a.5.htm. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
- ^ Levenson, Michael; Cramer, Maria (2007-02-01). "Marketing gambit exposes a wide generation gap". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.boston.com/news/local/articles/2007/02/01/marketing_gambit_exposes_a_wide_generation_gap/. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ Glenn, Joshua (2007-01-31). "Attack of the Mooninites!". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on 2011-02-22. http://www.boston.com/news/globe/ideas/brainiac/2007/01/attack_of_the_m.html. Retrieved 2007-04-18.
- ^ Reilly, Adam (2007-02-07). "Mooninite media mash-up". Boston Phoenix. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://www.thephoenix.com/article_ektid33334.aspx. Retrieved 2007-04-18.
- ^ "Full of beans". Los Angeles Times. 2007-02-03. http://www.latimes.com/news/opinion/la-ed-boston03feb03,0,5379741.story?coll=la-opinion-leftrail. Retrieved 2011-08-24.
- ^ Schneier on Security: Non-Terrorist Embarrassment in Boston February 01, 2007 Archived 23 February 2011 at WebCite
- ^ Gelzinis, Peter (2007-02-02). "PRANKS A LOT! ; Phony threat escalated real danger in hoax (Archives)". Boston Herald. Archived from the original on March 14, 2009. http://web.archive.org/web/20090314003903/http://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/bostonherald/access/1209646381.html?dids=1209646381:1209646381&FMT=ABS&FMTS=ABS:FT&date=Feb+2%2C+2007&author=PETER+GELZINIS&pub=Boston+Herald&edition=&startpage=4&desc=PRANKS+A+LOT!+%3B+Phony+threat+escalated+real+danger+in+hoax. Retrieved 2008-07-24.
- ^ "Guerrilla Marketing Arena Soiled By 'Aqua Teen' Fiasco". Brandweek. February 5, 2007. Archived from the original on May 15, 1007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070515064238/http://www.brandweek.com/bw/news/recent_display.jsp?vnu_content_id=1003541692. Retrieved 2011-08-24.
- ^ Suspects Refuse to Answer Questions on Botched 'Aqua Teen' Marketing Scheme February 02, 2007 Archived 23 February 2011 at WebCite
- ^ Blown out of proportion Feb 02, 2007 Archived 23 February 2011 at WebCite
- ^ Many young Bostonians think city overreacted: ‘We’re the laughingstock,’ resident says after cartoon signs prompt scare Feb 1, 2007 Archived 23 February 2011 at WebCite
- ^ Milholland, R. K. (2007-02-01). "Something Positive for February 1, 2007". Something Positive. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://somethingpositive.net/sp02012007.shtml. Retrieved 2007-02-03.
- ^ "MBTA Blows Up Mooninite". 2007-01-31. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://community.livejournal.com/b0st0n/4864959.html. Retrieved 2007-02-06.
- ^ "Game Over: Real Life Super Mario Bros. Ends With Bomb Squad". wfmynews2.com. 4/3/2006. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://www.wfmynews2.com/news/watercooler/article.aspx?storyid=60745. Retrieved 2007-02-06.
- ^ North, Ryan; Posterchild. "poster child mario question blocks!". Qwantz.com. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://www.qwantz.com/posterchild/. Retrieved 2007-02-06.
- ^ Boston stunt creates PR buzz saw instead of buzz February 5, 2007 Archived 23 February 2011 at WebCite
- ^ State of Massachusetts insists on calling ATHF ads "hoax devices" February 2, 2007 Archived 23 February 2011 at WebCite
- ^ "Police Blow Up Suspicious Device In Boston". WBZ-TV. 2007-02-28. Archived from the original on July 4, 2008. http://web.archive.org/web/20080704223643/http://wbztv.com/local/local_story_059122735.html.
- ^ "Boston police blow up traffic counter chained to lightpost". Boing Boing. 2007-02-28. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://www.boingboing.net/2007/02/28/boston_police_blow_u.html.
- ^ Begbie, Rod. "This is NOT A BOMB". Flickr. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://flickr.com/photos/groovymother/sets/72157594564032667/. Retrieved 2007-09-27.
- ^ Doctorow, Cory (2007-02-01). "Stickers: This is engineering, not bomb-making". Boing Boing. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://www.boingboing.net/2007/02/01/stickers-this-is-eng.html. Retrieved 2007-09-27.
- ^ live CW56 broadcast of the St. Patrick's Day Breakfast, March 18, 2007
- ^ Weber, Harry R. (2007-02-10). "Cartoon Network Head Resigns After Scare". ABC News. Archived from the original on April 3, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070403040220/http://abcnews.go.com/Business/wireStory?id=2863647. Retrieved 2011-08-24.
- ^ a b c Toosi, Nathal (2007-02-01). "Boston publicity stunt sets off activity in New York". Daily News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://www.nydailynews.com/front/story/493858p-415985c.html. Retrieved 2007-02-03.
- ^ a b c Fitzsimmons, Emma Graves (2007-02-02). "Cops not laughing at signs". Chicago Tribune (Tribune Company).
- ^ a b Harrell, Debera (2007-02-01). "Cartoon Network publicity stunt sparks panic in Boston -- but not here". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://www.seattlepi.com/local/302011_devices01.html. Retrieved 2007-02-03.
- ^ "'Aqua Teen' appeared in nine cities, only Boston panicked". azcentral.com. Associated Press. February . 2, 2007.
- ^ a b c Maykuth, Andrew (2007-02-02). "Cartoon caper shows up here, but nobody's laughing". Philadelphia Inquirer.
- ^ "Police: Phila. had 56 devices like Boston’s panic-causers". Philadelphia Inquirer. Associated Press. 2007-02-01.
- ^ Blankstein, Andrew (2007-02-01). "Devices placed in Boston also intended for L.A.". LA Times.
- ^ Bulwa, Demian (2007-02-01). "Calmer reaction in S.F. -- 'I thought it was cool'". San Francisco Chronicle. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://www.sfgate.com/cgi-bin/article.cgi?f=/c/a/2007/02/01/MNGI8NSQTP1.DTL&hw=art+gallery+device&sn=002&sc=749. Retrieved 2007-02-07.
- ^ a b c Lindsay, Jay; Hays, Tom (2007-02-01). "Men Held on Bond in Boston Hoax Case". ABCnews.go.com/. ABC. http://abcnews.go.com/US/wireStory?id=2841303. Retrieved 2007-02-02.[dead link]
- ^ "Boston Bomb Scare Press Conference". Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X2fGzmphx4U.
- ^ THOMAS, Terrorist Hoax Improvements Act of 2007, United States Senate, S.735 2007, retrieved May 8, 2007 Archived 23 February 2011 at WebCite
- ^ Cheng, Jaqui, Mooninites, meet the Terrorist Hoax Improvements Act, ars technica, May 8, 2007, retrieved May 8, 2007 Archived 23 February 2011 at WebCite
- ^ S. 735 [110th]: Terrorist Hoax Improvements Act of 2007 (GovTrack.us) Archived 23 February 2011 at WebCite
- ^ "Pair Charged In Marketing Stunt Reach Plea Deal". WBZTV.com. Associated Press (CBS Broadcasting). 2007-05-11. Archived from the original on December 24, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20071224143841/http://wbztv.com/topstories/Peter.Berdovsky.Sean.2.587093.html. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
- ^ Roberts, Paul (2007-02-01). "Bids for Boston bomb scare promo top $5,000". InfoWorld Tech Watch. IDG. Archived from the original on February 10, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070210222848/http%3A//weblog.infoworld.com/techwatch/archives/010023.html. Retrieved 2007-02-03.
- ^ Marotta, Michael (2007-02-02). "Mooninite moneymaker: T-shirts, LED displays hit eBay". Boston Herald (GateHouse Media).
- ^ "Exclusive Interview With Meatwad, Er, Dave Willis, Of 'Aqua Teen Hunger Force'". Starpulse.com. December 15, 2008. Archived from the original on 2011-02-23. http://www.starpulse.com/news/Dee_Doyle/2008/12/15/starpulse_com_exclusive_interview_with_d. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
External links
 External images
External images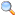
Aqua Teen Hunger Force Ignignot LED on Flickr - Peter Berdovsky's website
- Sean Stevens' website
- superfiction.com (Another Peter Berdovsky website)
- Initial coverage & discussion on Blue Mass Group
- Catching Up With an Aqua Teen Terrorist
Aqua Teen Hunger Force and Aqua Unit Patrol Squad 1 Media Characters Cast Seasons As Aqua TeenAs Aqua Unit8 · 9Related Space Ghost Coast to Coast · Spacecataz · Carl's Stone Cold Lock of the Century of the Week · 2007 Boston bomb scareCategories:- Aqua Teen Hunger Force
- Advertising campaigns
- Boston Police Department
- Graffiti and unauthorised signage
- Scandals in the United States
- 2007 in Massachusetts
- Adult Swim
- 21st century in Boston, Massachusetts
- Media-related controversies in the United States
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.



