- Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin
-
Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin 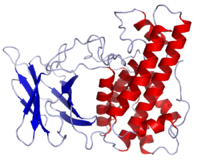
Crystal structure of Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin Identifiers Symbol ? Alt. symbols phospholipase C, CPE0036, Zn_dep_PLPC Entrez 988262 PDB 1CA1 1KHO, 1GYG, 1QM6, 1QMD, 1KHO, 1GYG, 1QM6, 1QMD RefSeq NP_560952.1 Other data EC number 3.1.4.3 Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin is a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium perfringens (C. perfringens) and is responsible for gas gangrene and myonecrosis in infected tissues. The toxin also possesses hemolytic activity.
Contents
Clinical significance
This toxin has been shown to be the key virulence factor in infection with C. perfringens; the bacterium is unable to cause disease without this toxin.[1] Further, vaccination against the alpha toxin toxoid protects mice against C. perfringens gas gangrene.[2] As a result, knowledge about the function of this particular protein greatly aids understanding of myonecrosis.
Structure and homology
The alpha toxin has remarkable similarity to toxins produced by other bacteria as well as natural enzymes. There is significant homology with phospholipase C enzymes from Bacillus cereus, C. bifermentans, and Listeria monocytogenes.[3] The C terminal domain shows similarity with non-bacterial enzymes such as pancreatic lipase, soybean lipoxygenase, and synaptotagmin I.[4]
The alpha toxin is a zinc metallophospholipase requiring zinc for activation. First, the toxin binds to a binding site on the cell surface. The C-terminal C2-like PLAT domain binds calcium and allows the toxin to bind to the phospholipid head-groups on the cell surface. The C-terminal domain enters the phospholipid bilayer. The N-terminal domain has phospholipase activity. This property allows hydrolysis of phospholipids such as phosphatidyl choline, mimicking endogenous phospholipase C. The hydrolysis of phosphatidyl choline produces diacylglycerol which activates a variety of second messenger pathways. The end result includes activation of arachidonic acid pathway and production of thromboxane A2, production of IL-8, platelet-activating factor, and several intercellular adhesion molecules. These actions combine to cause edema due to increased vascular permeability.[3]
See also
References
- ^ Awad, M.M., Bryant, A.E., Stevens, D.L. & Rood, J.I. (1995). "Virulence studies on chromosomal alpha-toxin and alpha-toxin mutants constructed by allelic exchange provide genetic evidence for the essential role of alpha-toxin in Clostridium perfringens-mediated gas gangrene". Mol Microbiol 15 (2): 191–202. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02234.x. PMID 7746141.
- ^ Williamson ED & Titball RW. (1993). "A genetically engineered vaccine against the alpha-toxin of Clostridium perfringens also protects mice against experimental gas gangrene". Vaccine 11 (12): 1253–1258. doi:10.1016/0264-410X(93)90051-X. PMID 8256506.
- ^ a b Sakurai J, Nagahama M, Oda M. (2004). "Clostridium perfringens Alpha-Toxin: Characterization and Mode of Action". J Biochem 136 (5): 569–574. doi:10.1093/jb/mvh161. PMID 15632295.
- ^ Naylor CE, Eaton JT, Howells A, et al. (1998). "Structure of the key toxin in gas gangrene". Nature Struct. Biol. 5 (8): 738–746. doi:10.1038/1447. PMID 9699639.
External links
- UMich Orientation of Proteins in Membranes families/superfamily-88 - Orientations of alpha-toxins in membrane
Hydrolase: esterases (EC 3.1) 3.1.1: Carboxylic ester hydrolases Cholinesterase (Acetylcholinesterase, Butyrylcholinesterase) · Pectinesterase · 6-phosphogluconolactonase · PAF acetylhydrolase
Lipase (Bile salt-dependent, Gastric/Lingual, Pancreatic, Lysosomal, Hormone-sensitive, Endothelial, Hepatic, Lipoprotein, Monoacylglycerol, Diacylglycerol)
Phospholipase (A1, A2, B)3.1.2: Thioesterase 3.1.3: Phosphatase Alkaline phosphatase (ALPI, ALPL, ALPP) · Acid phosphatase (Prostatic)/Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase/Purple acid phosphatases · Nucleotidase · Glucose 6-phosphatase · Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase · Calcineurin · Phosphoprotein phosphatase (PP2A) · OCRL · Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase · Fructose 6-P,2-kinase:fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase · PTEN · Phytase · Inositol-phosphate phosphatase (IMPA1)
Phosphoprotein phosphatase: Protein tyrosine phosphatase · Protein serine/threonine phosphatase · Dual-specificity phosphatase3.1.4: Phosphodiesterase Autotaxin · Phospholipase (C, D) · Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase (1) · PDE1 · PDE2 · PDE3 · PDE4A/PDE4B · PDE5 · Lecithinase (Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin) · Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase3.1.6: Sulfatase Nuclease (includes
deoxyribonuclease and
ribonuclease)3.1.11-16: Exonuclease3.1.21-31: Endonucleaseeither deoxy- or ribo-B enzm: 1.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/10/11/13/14/15-18, 2.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8, 2.7.10, 2.7.11-12, 3.1/2/3/4/5/6/7, 3.1.3.48, 3.4.21/22/23/24, 4.1/2/3/4/5/6, 5.1/2/3/4/99, 6.1-3/4/5-6 Categories:- Bacterial toxins
- Peripheral membrane proteins
- Clostridiaceae
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
