- Dermal papillae
-
Dermal papillae 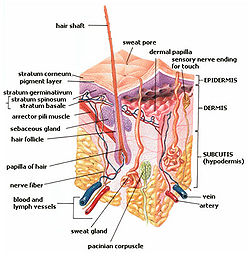
Dermal papilla labeled at top 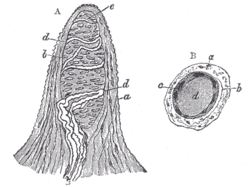
Papilla of the hand, treated with acetic acid. Magnified 350 times.
A. Side view of a papilla of the hand.
a. Cortical layer.
b. Tactile corpuscle.
c. Small nerve of the papilla, with neurolemma.
d. Its two nervous fibers running with spiral coils around the tactile corpuscle.
e. Apparent termination of one of these fibers.
B. A tactile papilla seen from above so as to show its transverse section.
a. Cortical layer.
b. Nerve fiber.
c. Outer layer of the tactile body, with nuclei.
d. Clear interior substance.Latin papillae dermis Code TH H3.12.00.1.03003 In the human skin, the dermal papillae (DP) (singular papilla, diminutive of Latin papula, 'pimple') are small, nipple-like extensions (or interdigitations) of the dermis into the epidermis. They can be observed at the surface of the skin in hands and feet as epidermal or papillary ridges (colloquially known as fingerprints).
The dermal papillae nourishes all hair follicles and bring food and oxygen to the lower layers of epidermal cells. The pattern of ridges they produce in hands and feet are inherited features that are developed before birth. They remain unaltered (except in size) throughout life, and are therefore used for fingerprints. [1]
The dermal papillae are part of the uppermost layer of the dermis, the papillary dermis, and the ridges they form greatly increase the surface area between the dermis and epidermis. Because the dermis' main function is to support the epidermis, this greatly increases the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between these two layers. Additionally, the increase in surface area prevent the dermal and epidermal layers from separating from each others by strengthening the junction between them. With age, the papillae tend to flatten and sometimes increase in numbers. [2]
Dermal papillae also play a pivotal role in hair formation, growth and, cycling. [3]
See also
- Papilla (disambiguation)
References
- ^ "Dermal papillae". Probert Encyclopaedia. http://www.probertencyclopaedia.com/cgi-bin/res.pl?keyword=Dermis&offset=0. Retrieved February 2010.
- ^ "Friction Skin". Ridges and Furrows. http://ridgesandfurrows.homestead.com/friction_skin.html. Retrieved February 2010.
- ^ Lin, Chang-min et al. (October 2008). "Microencapsulated human hair dermal papilla cells: a substitute for dermal papilla?". Archives of Dermatological Research (Springer) 300 (9): 531–535. doi:10.1007/s00403-008-0852-3. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/klu/403/2008/00000300/00000009/00000852.
External links
- papilla+of+dermis at eMedicine Dictionary
- Organology at UC Davis Integument/horn/horn3/horn4 - "Mammal, bovine horn (LM, Medium)"
Integumentary system (TA A16, TH H3.12, GA 10.1062) Skin Basement membrane zoneSkin fieldsHeadcampus frontalis, campus parietalis, campus occipitalis, campus temroralis, campus facialis (campus orbitalis, campus nasalis, campus oralis, campus mentalis, campus infraorbitalis, campus buccalis, campus zygomaticus)Neckcampus cervicalis anterior (campus submandibularis, campus caroticus, campus omotrachealis, campus submentalis), campus sternocleidomastoideus, campus cervicalis posterior (campus omoclavicularis), campus nuchalisChestcampus presternalis, campus clavipectoralis, campus pectoralis verus, campus mammarius, campus inframammarius, campus axillarisAbdomencampus hypochondriacus, campus epigastricus, campus abdominalis lateralis, campus umbilicalis, campus inguinalis, campus hypogastricusPerineumcampus analis, campus urogenitalisSubcutaneous tissue Panniculus/Pannus (Panniculus adiposus · Panniculus carnosus) · Stratum membranosum · Loose connective tissue · Superficial fasciaAdnexa Skin glandsSweat glands: Apocrine sweat gland · Eccrine sweat gland
SebaceousHair shaftArrector pili musclePilosebaceous unitHair sebaceous gland
This anatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
