- Orbital process of palatine bone
-
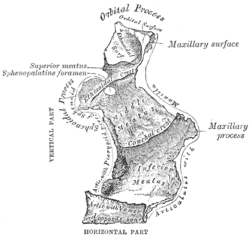
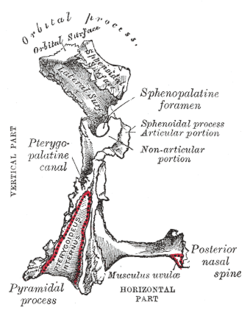
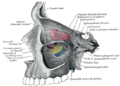
Bone: Orbital process of palatine bone Left palatine bone. Nasal aspect. Enlarged. Left palatine bone. Posterior aspect. Enlarged. Latin processus orbitalis Gray's subject #41 168 The orbital process of the palatine bone is placed on a higher level than the sphenoidal, and is directed upward and lateralward from the front of the vertical part, to which it is connected by a constricted neck. It presents five surfaces, which enclose an air cell. Of these surfaces, three are articular and two non-articular.
The articular surfaces are:
- the anterior or maxillary, directed forward, lateralward, and downward, of an oblong form, and rough for articulation with the maxilla
- the posterior or sphenoidal, directed backward, upward, and medialward; it presents the opening of the air cell, which usually communicates with the sphenoidal sinus; the margins of the opening are serrated for articulation with the sphenoidal concha
- the medial or ethmoidal, directed forward, articulates with the labyrinth of the ethmoid.
In some cases the air cell opens on this surface of the bone and then communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. More rarely it opens on both surfaces, and then communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells and the sphenoidal sinus.
The non-articular surfaces are:
- the superior or orbital, directed upward and lateralward; it is triangular in shape, and forms the back part of the floor of the orbit; and
- the lateral, of an oblong form, directed toward the pterygopalatine fossa; it is separated from the orbital surface by a rounded border, which enters into the formation of the inferior orbital fissure.
Additional images
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Bones of head and neck: the facial skeleton of the skull (TA A02.1.08–15, GA 2.156–177) Maxilla SurfacesProcessesOtherZygomatic Palatine FossaePlatesProcessesOrbital · SphenoidalMandible external surface (Symphysis menti, Lingual foramen, Mental protuberance, Mental foramen, Mandibular incisive canal) · internal surface (Mental spine, Mylohyoid line, Sublingual fovea, Submandibular fovea) · Alveolar part of mandibleMinor/
noseNasal bone: Internasal suture · Nasal foramina
Inferior nasal concha: Ethmoidal process · Maxillary process
Vomer: Vomer anterior · Synostosis vomerina · Vomer posterior (Wing)
Lacrimal: Posterior lacrimal crest · Lacrimal groove · Lacrimal hamulusCategories:- Bones of the head and neck
- Musculoskeletal system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.