- Syncope (phonetics)
-
Sound change and alternation Fortition Dissimilation Other types
For other uses, see Syncope.In phonology, syncope (
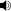 /ˈsɪŋkəpiː/; Greek: syn- + koptein “to strike, cut off”) is the loss of one or more sounds from the interior of a word; especially, the loss of an unstressed vowel. It is found both in Synchronic analysis of languages and Diachronics .
/ˈsɪŋkəpiː/; Greek: syn- + koptein “to strike, cut off”) is the loss of one or more sounds from the interior of a word; especially, the loss of an unstressed vowel. It is found both in Synchronic analysis of languages and Diachronics .Contents
Found synchronically
Synchronic analysis is an analysis that views linguistic phenomena only at one point in time. Usually, the present. We find syncope happening within the functioning of modern languages. Here we consider it in three areas : Inflection, Poetry, and Informal Speech.
In inflections
In languages such as Irish, the process of inflection can precipitate syncope.
For example :
- In some verbs
- Imir (To play) should become *"imirím" (I play). However the addition of the "-ím" causes syncope and the second last syllable vowel "i" is lost. So, Imir becomes Imrím.
- In some nouns
- Inis (Island) should become *inise in the genitive case. However, if one looks at road signs one finds not *"Báile na hInise", but "Báile na hInse" (The town of the Island). Once again the loss is of the second syllable "i".
It is interesting that if the present root form in Irish is the result of diachronic syncope then there is a resistance to synchronic syncope for inflection. Historically in old Irish, as a rule, syncope happened whenever the addition of and ending gave rise to syncope.
As a poetic device
Sounds may be removed from the interior of a word as a rhetorical or poetic device, whether for embellishment or for the sake of the meter.
- Latin commo[ve]rat > poetic commorat ("he had moved")
- English hast[e]ning > poetic hast'ning
- English heav[e]n > poetic heav'n
- English over > poetic o'er
- English never > poetic ne'er
Syncope in informal speech
Various sorts of colloquial reductions might be called "syncope". It is also called compression.[1]
Forms such as "didn't" that are written with an apostrophe are, however, generally called contractions:
- English [Au]stra[lia]n > colloquial Strine
- English did n[o]t > didn't
- English I [woul]d [ha]ve > I'd've
Found diachronically as a historical sound change
In historical phonetics, the term "syncope" is often but not always limited to the loss of an unstressed vowel:
Loss of any sound
- Old English hláford > English lord
- English Worcester, /ˈwʊstər/
- English Gloucester, pronounced /ˈɡlɒstər/
Loss of an unstressed vowel
- Latin cál[i]dum > Italian caldo "hot"
- Latin óc[u]lum > Italian occhio "eye"
- Latin trem[u]láre > Italian tremare "to tremble"
See also
- Apocope
- Aphesis
- Clipping (lexicography)
- Clipping (phonetics)
- Elision
- Relaxed pronunciation
- Synalepha
- Synaeresis
- Syncopation in music
- Vowel reduction
- Deletion (phonology)
References
- Crowley, Terry. (1997) An Introduction to Historical Linguistics. 3rd edition. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2000). Longman Pronouncing Dictionary (2nd ed. ed.). Longman. pp. 165–6. ISBN 978-0-582-36467-7.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
