- Northern Cyprus
-
Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti

Flag Coat of arms Anthem: İstiklâl Marşı
Independence MarchCapital Nicosia (Turkish: Lefkoşa)
35°11′N 33°22′E / 35.183°N 33.367°EOfficial language(s) Turkish Demonym Turkish Cypriot Government Republic - President Derviş Eroğlu - Prime Minister Irsen Küçük Independence from Cyprus - Proclaimed 15 November 1983 - Recognition By Turkey only Area - Total 3,355 km2 (174th if ranked)
1,295 sq mi- Water (%) 2.7 Population - 2010 (proj.) census 287,856[1] - Density 86/km2 (116th)
223/sq miGDP (nominal) 2008 estimate - Total $3.9 billion[2] - Per capita $16,158[2] Currency Turkish lira1 ( TRY)Time zone EET (UTC+2) - Summer (DST) EEST (UTC+3) Drives on the left Internet TLD .nc.tr or .tr, wide use of .cc Calling code +90 (+90-392 for TRNC) 1 The Euro is also widely used. Northern Cyprus or North Cyprus (Turkish: Kuzey Kıbrıs) is a self-declared state[3] which officially titles itself the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC) (Turkish: Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti).[4] Its territory comprises the northeastern part of the island of Cyprus. Only Turkey has recognised its independence,[5][6][7][8] while the international community considers it occupied territory of the Republic of Cyprus[9][10][11].
Tensions between the Greek Cypriot and Turkish Cypriot populations culminated in 1974 with a coup d'état, an attempt to annex the island to Greece and a military invasion by Turkey in response. All these factors resulted in a partitioning of the island,[12][13][14][15] the resettlement of many of its inhabitants, and a unilateral declaration of independence by the north in 1983. Due to its lack of international recognition, Northern Cyprus is heavily dependent on Turkey for economic, political and military support.[16][17]
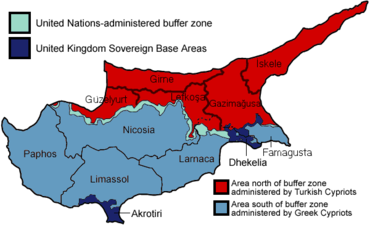
Northern Cyprus extends from the tip of the Karpass Peninsula (Cape Apostolos Andreas) in the north east, westward to Morphou Bay and Cape Kormakitis (the Kokkina/Erenköy exclave marks the westernmost extent of the area), and southward to the village of Louroujina/Akıncılar. A buffer zone under the control of the United Nations stretches between Northern Cyprus and the rest of the island and divides Nicosia, the island's largest city and capital of both states.
Attempts to reach a solution to the dispute have so far been unsuccessful. In 2004, a fifth revision of the UN Annan Plan to settle the Cyprus dispute was accepted by a majority of Turkish Cypriots in a referendum, but rejected by a majority of Greek Cypriots. The Turkish Army maintains a large force in Northern Cyprus with its presence supported and approved by the local government, whereas the Republic of Cyprus and the international community regard it as an illegal occupation force with its presence denounced in several United Nations Security Council resolutions.[18]
History
Main articles: Cyprus intercommunal violence and Turkish invasion of CyprusA united Cyprus gained independence from British rule in August 1960, after both Greek and Turkish Cypriots agreed to respectively abandon plans for enosis (union with Greece) and taksim (Turkish for 'partition'). The agreement involved Cyprus being governed under a constitution which apportioned Cabinet posts, parliamentary seats and civil service jobs on an agreed ratio between the two communities. Within three years, tensions between the Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots in administrative affairs began to show. In particular, disputes over separate municipalities and taxation created a deadlock in government. In 1963 President Makarios proposed unilateral changes to the constitution, via 13 amendments. Turkey and the Turkish Cypriots rejected the proposed amendments as an attempt to settle constitutional disputes in favour of the Greek Cypriots[19] and as a means of demoting Turkish status from co-founders of the state to one of minority status removing their constitutional safeguards in the process. Turkish Cypriots filed a lawsuit against the 13 amendments in Supreme Constitutional Court of Cyprus (SCCC). Makarios announced that he would not comply with whatever the decision of SCCC would be,[20] and defended his amendments as being necessary "to resolve constitutional deadlocks" as opposite to the stance of SCCC.[21] On 25 April 1963, SCCC decided that Makarios' 13 amendments are illegal. On 21 May, president of SCCC resigned due to the Makarios' stance. On 15 July, Makarios ignored the decision of SCCC.[22] After resignation of the president of SCCC, SCCC stopped to exist. Supreme Court of Cyprus (SCC) was formed by merging SCCC and High Court of Cyprus and undertook the jurisdiction and powers of the SCCC and HCC.[23] On 30 November, Makarios legalized the 13 proposals.
 A map of the Turkish Cypriot Enclaves before 1974 military operations
A map of the Turkish Cypriot Enclaves before 1974 military operations
In 1963, the Greek Cypriot wing of the government created the Akritas plan which outlined a policy that would remove Turkish Cypriots from the government and ultimately lead to union with Greece. The plan stated that if the Turkish Cypriots objected then they should be "violently subjugated before foreign powers could intervene".[24] On 21 December 1963, a Turkish Cypriot crowd clashed with the plainclothes special constables of Yorgadjis. Almost immediately, intercommunal violence broke out with a major Greek Cypriot paramilitary attack upon Turkish Cypriots in Nicosia and Larnaca. Though the TMT — a Turkish resistance group created in 1959 to promote a policy of taksim (division or partition of Cyprus), in opposition to the Greek Cypriot nationalist group EOKA and its advocacy of enosis (union of Cyprus with Greece) — committed a number of acts of retaliation, historian of the Cyprus conflict Keith Kyle noted that "there is no doubt that the main victims of the numerous incidents that took place during the next few months were Turks."[19] Seven hundred Turkish hostages, including women and children, were taken from the northern suburbs of Nicosia. Nikos Sampson, a nationalist and future coup leader, led a group of Greek Cypriot irregulars into the mixed suburb of Omorphita and attacked the Turkish Cypriot population.[25] By 1964, 193 Turkish Cypriots and 133 Greek Cypriots had been killed, with a further 209 Turks and 41 Greeks missing and presumed dead.
Turkish Cypriot members of the government had by now withdrawn, creating an essentially Greek Cypriot administration in control of all institutions of the state. Widespread looting of Turkish Cypriot villages prompted 20,000 refugees to retreat into armed enclaves, where they remained for the next 11 years,[26] relying on food and medical supplies from Turkey to survive. Turkish Cypriots formed paramilitary groups to defend the enclaves, leading to a gradual division of the island's communities into two hostile camps. The violence had also seen thousands of Turkish Cypriots attempt to escape the violence by emigrating to Britain, Australia and Turkey.[27]
The view of Turkish Cypriots: The Cyprus's Supreme Court ruling found that Makarios had violated the constitution by failing to fully implement its measures and that Turkish Cypriots had not been allowed to return to their positions in government without first accepting the proposed constitutional amendments.[28] Also, Turkish Cypriots did not self-segregate themselves: then–United Nations Secretary General, U Thant's S/5950 (10 September 1964) report (paragraph 180) UNFICYP carried out a detailed survey of all damage to properties throughout the island during the disturbances; it shows that in 109 villages, most of them Turkish-Cypriot or mixed villages, 527 houses have been destroyed while 2,000 others have suffered damage from looting. As a result, Turkish Cypriot Provisional Administration founded on 28 December 1967.
The view of Greek Cypriots: the Turkish Cypriots' withdrawal from the government and their retreat into enclaves was a voluntary action, prompted by their desire to form a state of their own: the then–United Nations Secretary General, U Thant, in 1965 stated that Turkish Cypriots had furthered a policy of "self-segregation" and taken a "rigid stand" against policies which might have involved recognizing the government's authority.[29]
 Founder, and former President, Rauf Denktaş
Founder, and former President, Rauf Denktaş
On 15 July 1974, the Greek military junta of 1967-1974 backed a Greek Cypriot military coup d'état in Cyprus. President Makarios was removed from office and Nikos Sampson took his place. Turkey claimed that under the 1960 Treaty of Guarantee, the coup was sufficient reason for military action to protect the Turkish Cypriot populace, and thus Turkey invaded Cyprus on 20 July. Turkish forces proceeded to take over the northern four-elevenths of the island (about 37% of Cyprus's total area). The coup caused a civil war filled with ethnic violence, after which it collapsed and Makarios returned to power.[citation needed] After the hostilities in 1974, the Greek Cypriots in Rizokarpaso agreed to live under Turkish Cypriot administration and stayed in Northern Cyprus. Other Greek Cypriots in the North (approximately 160,000) fled to the south, while 50,000 Turkish Cypriots fled north. Some population transfers were made in accordance with the Population Exchange Agreement between Turkish and Greek Cypriots under the auspices of United Nations on 2 August 1975.[30] Approximately 1,500 Greek Cypriots and 500 Turkish Cypriots remain missing.[31]
In 1975 the "Turkish Federative State of Cyprus" (Kıbrıs Türk Federe Devleti) was declared as a first step towards a future federated Cypriot state, but was rejected by the Republic of Cyprus, the UN, and the international community. After eight years of failed negotiations with the leadership of the Greek Cypriot community,[citation needed] the north declared its independence on 15 November 1983 under the name of the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus.[32] This unilateral declaration of independence was rejected by the UN and the Republic of Cyprus. In recent years the politics of reunification has dominated the island's affairs. It was hoped that Cyprus's planned accession into the European Union would act as a catalyst towards a settlement, and in 2004 a United Nations–brokered peace settlement was presented in a referendum to both sides. The proposed settlement was opposed by both the president of Cyprus, Tassos Papadopoulos, and Turkish Cypriot president Rauf Denktaş; in the referendum, a majority of Turkish Cypriots accepted the proposal, but Greek Cypriots overwhelmingly rejected it. As a result, Cyprus entered the European Union as a divided island, with Northern Cyprus effectively excluded. Denktaş resigned in the wake of the vote, ushering in the pro-solutionist Mehmet Ali Talat as his successor. However the pro-solutionist side and Mehmet Al Talat lost momentum, because of the ongoing embargo and isolation, despite promises from the European Union of easing them, which did not occur, and as a result the Turkish Cypriot electorate became frustrated. This led ultimately to the pro-independence side winning the general elections in 2009 and its candidate, former Prime Minister Derviş Eroğlu winning the presidential elections in 2010. Although his side and he himself disagrees with and opposes re-unification with the Republic of Cyprus, and favours the unity of and close relations between northern Cyprus and Turkey and supports the independence of the former, he nevertheless is negotiating with the Greek Cypriot side towards a settlement for reunification. In 2011, Turkish Cypriots protested the economic reforms and the Turkish and Northern Cyprus governments.
Government and politics
Main article: Politics of Northern CyprusPolitics of Northern Cyprus takes place in a framework of a semi-presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President is head of state and the Prime Minister head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Assembly of the Republic. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.
The president is elected for a five-year term. The current president is Derviş Eroğlu who won the presidential elections on 18 April 2010. The legislature is the Assembly of the Republic, which has 50 members elected by proportional representation from five electoral districts. In the elections of April 2009, the right-leaning pro-independence National Unity Party won an overall majority.[33]
Due to Northern Cyprus' isolation and heavy dependence on the support of Turkey, Turkey has a high level of control over decisions in Northern Cyprus. This has led to some experts stating that it runs as an effective puppet state of Turkey.[34][35][36] Few political decisions in Northern Cyprus are taken without the approval of the Turkish National Security council in Ankara.[17] The European Court of Human Rights gives Northern Cyprus' dependence on Turkey as the reason for its non-recognition of Northern Cyprus' legal system, holding Turkey responsible for human rights in Northern Cyprus.[36]
International status and foreign relations
Main article: Foreign relations of Northern Cyprus London office of Northern Cyprus, Bedford Square.
London office of Northern Cyprus, Bedford Square.
The international community, with the exception of Turkey,[5] does not recognise Northern Cyprus as a sovereign state, but recognises the de jure sovereignty of the Republic of Cyprus over the whole island. The United Nations considers the declaration of independence by Northern Cyprus as legally invalid in several of its resolutions.[9][10]
In wake of the April 2004 referendum on the United Nations Annan Plan, and the support of the Turkish Cypriot community for the plan, the European Union made pledges towards ending the isolation of northern Cyprus. These included measures for trade and 259 million euro in aid.
In 2004, the Organisation of the Islamic Conference upgraded the delegation of the Turkish Cypriot Muslim community from "observer community" (1979) to that of a constituent state with the designation "Turkish Cypriot State", making Northern Cyprus an observer member of the organization.[37] A number of high profile formal meetings have also taken place between former President Mehmet Ali Talat and various foreign leaders and politicians including the former US Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice, the then British foreign minister, Jack Straw and former Pakistani President Pervez Musharraf, and between President Dervis Eroglu and Ban Ki-Moon.
In 2004, the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe gave observer status to the representatives of Turkish Cypriot Community.[38] Since then, Northern Cyprus's representatives have actively participated in all PACE activities without voting rights.
The Autonomous Republic of Nakhichevan (Azerbaijan) has issued a resolution recognizing Northern Cyprus' independence, but Azerbaijan has yet refrained to officially support this decision due to the Nagorno-Karabakh issue.[39]
The European Union considers the area not under effective control of the Republic of Cyprus as EU territory under Turkish military occupation and thus indefinitely exempt from EU legislation until a settlement has been found. The status of Northern Cyprus has become a recurrent issue especially during the recent talks for Turkey's membership of the EU where the division of the island is seen as a major stumbling block in Turkey's road to membership.[40][41]
On 18 February 2008, the Northern Cyprus government sent a message to the Republic of Kosovo congratulating it on its unilateral declaration of independence. A government spokesman clarified that this statement did not constitute, or signal an imminent move toward, formal diplomatic recognition of Kosovo.[42] In contrast, the Republic of Cyprus has rejected Kosovo's independence, and in lieu of the ICJ ruling that Kosovo's declaration of independence was not illegal stated that Kosovo and Northern Cyprus were not analogous situations.[43] It is argued by some analysts that the independence of Kosovo could provide support for the recognition of Northern Cyprus.[44]
Military
Northern Cyprus has an indigenous 5,000-man Turkish Cypriot Security Force (TCSF), which is primarily made up of conscripted Turkish Cypriot males between the ages of 18 and 40. There is also an additional reserve force consisting of about 11,000 first-line, 10,000 second-line and 5,000 third-line troops conscripted up to the age of 50. The TCSF is lightly armed and heavily dependent on its mainland Turkish allies, from which it draws much of its officer corps. It is led by a Brigadier General drawn from the Turkish Army. It acts essentially as a gendarmerie charged with protection of the border of Northern Cyprus from Greek Cypriot incursions and maintaining internal security within Northern Cyprus.[45]
In addition, the mainland Turkish Armed Forces maintain a Cyprus Turkish Peace Force (CTPF) consisting of around 30-40,000 troops drawn from the 9th Turkish Army Corps and comprising two divisions, the 28th and 39th. It is equipped with a substantial number of United States-made M48 Patton main battle tanks and artillery weapons. The Turkish Air Force, Turkish Navy and Turkish Coast Guard also have a presence in Northern Cyprus. Although formally part of Turkish 4th Army, headquartered in İzmir, the sensitivities of the Cyprus situation means that the commander of the CTPF also reports directly to the Turkish General Staff in Ankara. The CTPF is deployed principally along the Green Line and in locations where hostile amphibious landings might take place.[45]
The presence of the mainland Turkish military in Cyprus is highly controversial, having been denounced as an illegal occupation force by the Republic of Cyprus government. Several United Nations Security Council resolutions have called on the Turkish forces to withdraw.[18]
Administrative divisions
Main article: Districts of Northern CyprusNorthern Cyprus is divided into five districts.
Map of Northern Cyprus \ Districts' name Lefkoşa (Nicosia) Gazimağusa (Famagusta) Girne (Kyrenia) Güzelyurt İskele Geography and climate
The winter in Northern Cyprus is cool and rainy, particularly between December and February, with 60% of annual rainfall.[46] These rains produce winter torrents that fill most of the rivers, which typically dry up as the year progresses. Snow may fall on the Kyrenia Range, but seldom elsewhere in spite of low night temperatures. The short spring is characterized by unstable weather, occasional heavy storms and the "meltem", or westerly wind. Summer is hot and dry enough to turn low-lying lands on the island brown. Parts of the island experience the "Poyraz", a north-westerly wind, or the sirocco, a wind from Africa, which is dry and dusty. Summer is followed by a short, turbulent autumn.
Climate conditions on the island vary by geographical factors. The Mesaoria Plain, cut off from the summer breezes and from much of the humidity of the sea, may reach temperature peaks of 40-45 °C. Humidity rises at the Karpaz Peninsula. Humidity and water temperature (16 °C–28 °C) combine to stabilize coastal weather, which does not experience inland extremes. The Southern Range blocks air currents that bring rain and atmospheric humidity from the south-west, diminishing both on its eastern side.
Education
Main article: Education in Northern CyprusThe education system in Northern Cyprus consists of pre-school education, primary education, secondary education and higher education. Five years of primary education is mandatory.
There are more than 40,000 university students in six universities in Northern Cyprus: Near East University, Girne American University, Middle East Technical University, European University of Lefke, Cyprus International University, Eastern Mediterranean University (EMU), all, except METU, established since 1974. EMU is an internationally recognised institution of higher learning with more than 1000 faculty members from 35 countries. There are 15,000 students in EMU representing 68 nationalities. The 6 universities have been approved by the Higher Education Council of Turkey. Eastern Mediterranean University and Near East University are full individual members of the European University Association.[47] EMU is full member of Community of Mediterranean Universities, Federation Universities of Islamic World, International Association of Universities and International Council of Graphic Design Associations.[48] Three universities (Istanbul Technical University, Cukurova University, Gazi University) will open campuses in Northern Cyprus in 2010. Girne American University, in the northern coastal city of Girne, opened a campus in Canterbury, United Kingdom in 2009,[49] and accredited by the British Accreditation Council in 2010[50]
Economy
Main article: Economy of Northern Cyprus The Lala Mustafa Pasha Mosque in Famagusta (Turkish: Gazimağusa). Formerly Τhe Saint Nicolas Cathedral before its conversion in 1571.
The Lala Mustafa Pasha Mosque in Famagusta (Turkish: Gazimağusa). Formerly Τhe Saint Nicolas Cathedral before its conversion in 1571.
 Salamis, the ruins of an ancient Greek city on the eastern coast of Northern Cyprus
Salamis, the ruins of an ancient Greek city on the eastern coast of Northern Cyprus
The economy of Northern Cyprus is dominated by the services sector (69% of GDP in 2007) which includes the public sector, trade, tourism and education. The revenues gained by the education sector is USD 400 million in 2011. [51]Industry (light manufacturing) contributes 22% of GDP and agriculture 9%.[52]
Because of its status and the embargo by the Republic of Cyprus, Northern Cyprus is heavily dependent on Turkish economic support.[53] It uses the New Turkish Lira as its currency which links its economic status to the Turkish economy. Since the Republic of Cyprus joined the Euro zone and the movement of peoples between the north and south were relaxed, the Euro is also in wide circulation.[citation needed] Most exports and imports have to take place via Turkey unless they are produced locally from materials sourced in Cyprus (or imported via one of the island's recognised ports) when they may be exported via one of the legal ports.[citation needed]
The continuing Cyprus problem adversely affects the economic development of Northern Cyprus. The Republic of Cyprus, as the internationally recognised authority, has declared airports and ports in the area not under its effective control closed. All U.N. Member countries and E.U. member countries respect the closure of those ports and airports according to the declaration of the Republic of Cyprus.[citation needed]
On 16 July 2011, North Cyprus started to sell electricity to Cyprus.[54]
Despite the constraints imposed by the lack of international recognition, the economy of Northern Cyprus turned in an impressive performance in the last few years. The nominal GDP growth rates of the economy in 2001-2005 were 5.4%, 6.9%, 11.4%, 15.4% and 10.6%, respectively.[55][56] The real GDP growth rate in 2007 is estimated at 2%.[52] This growth has been buoyed by the relative stability of the Turkish Lira and a boom in the education and construction sectors.
Between 2002 and 2007, Gross National Product per capita more than tripled (in current US dollars):[2]
- US$4,409 (2002)
- US$5,949 (2003)
- US$8,095 (2004)
- US$10,567 (2005)
- US$11,837 (2006)
- US$14,047 (2007, provisional)
Studies by the World Bank show that the per capita GDP in Northern Cyprus grew to 76% of the per capita GDP in the Republic of Cyprus in PPP-adjusted terms in 2004 (US$22,300 for the Republic of Cyprus and US$16,900 for Northern Cyprus).[55][56] Official estimates for the GDP per capita in current US dollars are US$8,095 in 2004 and US$11,837 in 2006.[2]
Although the economy has developed in recent years, it is still dependent on monetary transfers from the Turkish government. Under a July 2006 agreement, Ankara is to provide Northern Cyprus with an economic aid in the amount of $1.3 billion over three years (2006–2008).[52] This is a continuation of ongoing policy under which Turkish government allocates around $400 million annually from its budget to help raise the living standards of the Turkish Cypriots.[57]
Communications and transport
International telephone calls are routed via a Turkish dialling code (+90 392) as Northern Cyprus has neither its own country code nor official ITU prefix. Similarly with the internet Northern Cyprus has no top level domain of its own and is under the Turkish second-level domain .nc.tr. Postal mail must be addressed 'via Mersin 10, TURKEY' as the Universal Postal Union does not recognise Northern Cyprus as a separate entity. Amateur radio operators sometimes use callsigns beginning with "1B", but these have no standing for awards or other operating credit.
Direct flights to Northern Cyprus and the trade traffic through the Northern Cypriot ports are restricted as part of the embargo on Northern Cypriot ports.[58] The airports of Geçitkale and Ercan are only recognised as legal ports of entry by Turkey and Azerbaijan.[59] Direct charter flights between Poland and North Cyprus started on 20 June 2011.[60] The seaports in Famagusta and Kyrenia have been declared closed to all shipping by the Republic of Cyprus since 1974.[61] By agreement between Northern Cyprus and Syria, there is a ship tour between Famagusta and Latakia, Syria. Since the opening of the Green Line Turkish Cypriot residents are allowed to trade through Greek Cypriot ports.[62]
Naturalised citizens of Northern Cyprus or foreigners carrying a passport stamped by Northern Cyprus authorities may be refused entry by the Republic of Cyprus or Greece,[63] although after the accession of the Republic of Cyprus to the EU such restrictions have been eased following confidence-building measures between Athens and Ankara[citation needed] and the partial opening of the UN controlled line by Northern Cyprus authorities.[citation needed] The Republic of Cyprus also allows passage across the Green Line from the south of Nicosia, as well as a few other selected crossing points, since Northern Cyprus does not leave entry stamps in the passport for such visits. There are seven border crossings between Northern Cyprus and the Republic of Cyprus.[64] Since May 2004 some tourists have taken to flying to the Republic of Cyprus directly then crossing the green line to holiday in Northern Cyprus.[65]
Demographics
See also: Turkish CypriotsMain article: Religion in Northern CyprusCensuses
Northern Cyprus's first official census was performed in 1996. The population recorded was 200,587.[66] The 2nd census, carried out in 2006, revealed the population of Northern Cyprus to be 265,100,[67] of which majority is composed of indigenous Turkish Cypriots, with the rest including a large number of settlers from Turkey. Of the 178,000 Turkish Cypriot citizens, 82% are native Cypriots (145,000). Of the 45,000 people born to non- Cypriot parentage, nearly 40% (17,000) were born in Cyprus. The figure for non-citizens, including students, guest workers and temporary residents stood at 78,000 people.[67][68] The population of Northern Cyprus' cities are: North Nicosia: 85,579; Famagusta: 64,269; Kyrenia: 62,158; Morphou: 31,116; Trikomo: 21,978.[citation needed]
Estimates
In 2010, the International Crisis Group estimated that the total population of Northern Cyprus was 300,000, perhaps half of which were either born in Turkey or are children of such settlers.[69] One source claims that the population in the north has reached 500,000,[70] split between 50% Turkish Cypriots and 50% Turkish settlers or Cypriot-born children of such settlers.[71]
Estimates by the Government of Northern Cyprus: The 1983 population of Northern Cyprus was 155,521.[72] Estimates by the government of the Republic of Cyprus from 2001 place the population at 200,000, of which 80-89,000 are Turkish Cypriots and 109,000-117,000 Turkish settlers.[73] An island-wide census in 1960 indicated the number of Turkish Cypriots as 102,000 and Greek Cypriots as 450,000.[74] Estimates state that 36,000 (about 1/3) Turkish Cypriots emigrated in the period 1975-1995, with the consequence that within Northern Cyprus the native Turkish Cypriots have been outnumbered by settlers from Turkey.[73]
Northern Cyprus is almost entirely Turkish speaking. English, however, is widely spoken as a second language.[citation needed]
There are 644 Greek Cypriots living in Rizokarpaso (Dipkarpaz) and 364 Maronites in Kormakitis.[75] The Greek Cypriots in Rizokarpaso agreed to live under Turkish Cypriot administration and stayed in Northern Cyprus even after the hostilities in 1974. The other Greek Cypriots in the North chose to live under Greek Cypriot administration and fled to the South; in accordance with the Population Exchange Agreement between Turkish and Greek Cypriots under the auspices of United Nations on 2 August 1975.[30] As a result, Rizokarpaso is the home of the biggest Greek-speaking population in the north. The Greek-Cypriot inhabitants are still supplied by the UN, and Greek-Cypriot products are consequently available in some shops.[citation needed]
Culture
Sports
 National billiards teams of Cyprus and Northern Cyprus played each other for the first time in 2010.
National billiards teams of Cyprus and Northern Cyprus played each other for the first time in 2010.
Due to the lack of international recognition, Northern Cyprus is not a member of any major international sporting bodies (e.g. IOC, FIFA, etc..).
There are 29 sports federations in Northern Cyprus and 13,838 people registered in them as of 2008. Taekwondo-karate-aikido-kurash is the most popular sport with 6054 athletes. It is followed by association football (2240 athletes), shooting (1150 athletes) and hunting (1017 athletes).[76]
Some Northern Cyprus sport clubs participate in Turkey's sport leagues. For example: the Fast Break Sport Club, in Turkey's Men's Basketball Regional League; the Beşparmak Sport Club, in Turkey's Handball Premier League; and the Lefka European University, in Turkey's Table-tennis Super League.
Human rights
Main article: Human rights in Northern CyprusIn January 2011, The Report of the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights on the question of Human Rights in Cyprus noted that the ongoing division of Cyprus continues to affect human rights throughout the island "... including freedom of movement, human rights pertaining to the question of missing persons, discrimination, the right to life, freedom of religion, and economic, social and cultural rights."[77]
Freedom House has classified the perceived level of democratic and political freedom in Northern Cyprus as "free" since 2000 in its Freedom in the World report.[78] The United States Department of State reported in 2001 that human rights were generally respected, although problems existed in terms of police activities and the restriction of movement.[79] A 2009 report reported that religious freedom was generally respected, although isolated incidents of discrimination have existed.[80] The US Department of State report in 2002 stated that freedom of speech and press was generally respected in Northern Cyprus,[81] and the World Press Freedom Index 2010 ranked Northern Cyprus 61st in terms of freedom of the media.[82]
In 2001, the US Department of State said that Greek Cypriot and Maronite minorities are not treated as well as they should be.[79] However, another US Department of State report in 2002 reported that the government of Northern Cyprus was easing restrictions on minorities and it respected the rights of travelling abroad and emigrating,[81] although they still cannot vote in elections.[83] In April 1998, the United Kingdom-based National Coalition of Anti-Deportation Campaigns asserted that the Turkish army had carried out a forced migration policy where Kurds were forced to colonise Northern Cyprus from the Republic of Turkey, and The Immigration and Nationality Directorate of the United Kingdom in 1999 said that Kurds were not being discriminated against and enjoyed equal political and religious rights to others.[79] Male-male sexual intercourse is illegal, and can result in up to three years imprisonment.[84]
See also
Main article: Outline of Northern CyprusReferences
- ^ North Cyprus' State Planning Organization 287,856 does not include "<=1 year inhabitants" + "tourists" + "seasonal workers"
- ^ a b c d Economic and Social Indicators 1977-2007, TRNC State Planning Organization, February 2008
- ^ Emerson, Michael (2004). The Wider Europe Matrix. CPSE. ISBN 9290794690.
- ^ "The social and economic impact of EU membership on northern Cyprus", Diez, Thomas (2002). The European Union and the Cyprus Conflict: Modern Conflict, Postmodern Union. Manchester University Press. p. 187. ISBN 0719060796.
- ^ a b BBC: The status of Northern Cyprus as a separate entity is recognised only by Turkey, which keeps around 30,000 troops in the north of the island.
- ^ Europe Review, Kogan Page, 2003, p.79
- ^ Nurşin Ateşoğlu Güney, Contentious issues of security and the future of Turkey, Ashgate Publishing, 2007, p.161
- ^ The CIA World Factbook 2010, Central Intelligence Agency (U.S.), p.182
- ^ a b UN Security Council Resolution 541 – 1983
- ^ a b UN Security Council Resolution 550 – 1984
- ^ Rule of Law In Armed Conflicts Project - Cyprus Judicial Decisions of ECHR regarding occupation
- ^ New York Times Quote: The dinner follows a meal Mr. Denktash held on Dec. 6, when Mr. Clerides made his first visit to northern Cyprus, which was invaded by Turkey in 1974 and has been governed by Turkish Cypriots ever since. Mr. Clerides is recognized internationally as the president of Cyprus, but Turkey is the only country that....
- ^ BBC News Quote: "Cyprus has been split into the Greek Cypriot-controlled south and the Turkish-occupied north since Turkey invaded in 1974, in the wake of an abortive coup by supporters of union with Greece."
- ^ Unity talks under threat as hardliner elected President The Times Quote: on divided island a stance that would scuttle a deal. Cyprus was split on ethnic and religious lines by a Turkish invasion in 1974, triggered by a brief, Greek-inspired coup.
- ^ Cyprus problem is fuelling racism The Guardian Quote: "Whether one chooses to date the situation to the invasion by Turkey in 1974, the coup by junta-officered Greek Cypriots the same year, the bombings by Turkey in 1964, the attempt..."
- ^ Thomas M. Leonard. Encyclopedia of the Developing World, Volume 1, page 429. Taylor & Francis, 2006, 159 pages [1]
- ^ a b C. Cockburn. The line: women, partition, and the gender rols in Cyprus. p. 96 [2]. Zed Books, 2004, 244 pages. ISBN 1842774212.
- ^ a b UN Security Council resolutions 353(1974), 357(1974), 358(1974), 359(1974), 360(1974), 365(1974)
- ^ a b The Main Narrative, continued The Cyprus Conflict
- ^ Pre-Rejection of SCCC decision by Makarios The fact that the decision of SCCC was not to be implemented by Makarios was made quite clear, and it was not implemented. Non-implementation of the decision of a Constitutional Court is sufficient reason to compel the resignation of its President, me"
- ^ Deutsche Zeitung (Nr. 15, 18-19.01.1964) SCCC: "...deny the allegation that an implementation of the constitution was impossible. It is a matter of good will to make it work."
- ^ Republic of Cyprus, SCCC Official Website "... in order to face this situation which paralysed the judiciary..."
- ^ Orams v. Cyprus Tick all on the left pane; Application No: 27841/07; click Search: The Administration of Justice (Miscellaneous Provisions) Law 33/1964 (“Law 33/64”).
- ^ Cyprus – The Republic of Cyprus countrystudies.us, U.S. Library of Congress
- ^ Andrew Borowiec, 2000. Cyprus: A troubled island. Praeger/Greenwood p.56
- ^ Antiwar.com. In Praise of 'Virtual States', Leon Hadar, 16 November 2005
- ^ Quoted in Andrew Borowiec, 2000. Cyprus: A troubled island. Praeger/Greenwood p.58
- ^ Stephen, Michael, (1987) Cyprus: Two Nations in One Island Bow Educational Briefing No.5. London, Pages 1-7
- ^ "(Report S/6426 10.6.65)". Humanrights.coe.int. http://www.humanrights.coe.int/minorities/eng/FrameworkConvention/StateReports/1999/cyprus/B.htm. Retrieved 2010-11-17.
- ^ a b United Nations, Cyprus Population Exchange Agreement 02.08.1975 United Nations, Cyprus Population Exchange Agreement 02.08.1975.
- ^ Bones of Cyprus missing unearthed BBC News
- ^ "General Information". Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus Public Information Office. http://www.trncpio.org/trncpio/en/index.asp?sayfa=cms&dmid=0&cmsid=155&ssid=98199036. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- ^ Hürriyet, Right-leaning party wins in northern Cyprus elections
- ^ James, A. Soverign statehood: The basis of international society." p. 142 [3]. Taylor and Francis, 1986, 288 pages. ISBN 0043201911.
- ^ Kurtulus, E. State sovereignty: concept, phenomenon and ramifications. p. 136 [4]. Macmillan, 2005, 232 pages. ISBN 1403969884.
- ^ a b Kaczorowska, A. Public International Law. p. 190 [5]. Taylor and Francis, 2010, 944 pages. ISBN 0415566851.
- ^ Islamic Conference's Parliaments to Call Northern Cyprus 'Cyprus Turkish State Zaman
- ^ Resolution 1376, Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe
- ^ "REGNUM news agency press release". Regnum.ru. http://www.regnum.ru/english/708006.html. Retrieved 2010-11-17.
- ^ David Gow; Helena Smith (2004-10-07). "EU puts Turkey on a long road to accession". London: The Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/turkey/story/0,12700,1321511,00.html. Retrieved 2007-01-30.
- ^ "EU Sets Deadline for Turkey to Open Up Its Ports". Deutsche Welle. 2006-11-21. http://www.dw-world.de/dw/article/0,2144,2243855,00.html. Retrieved 2007-01-30.
- ^ "Ercakica on the recognition of Kosovos independence". Hri.org. http://www.hri.org/news/cyprus/tcpr/2008/08-02-20.tcpr.html#01. Retrieved 2010-11-17.
- ^ Sarah Fenwick (2009-12-08). "No Right To Self-Determination for Minorities - Cyprus". cyprusnewsreport.com. http://www.cyprusnewsreport.com/?q=node/352. Retrieved 2011-03-23.
- ^ Fulya Özerkan (2010-07-25). "Verdict on Kosovo will not affect Turkey". http://www.hurriyetdailynews.com/n.php?n=kosovo-ruling-has-nothing-to-do-with-turkey8217s-southeast-problem-analysts-say-2010-07-23. Retrieved 2011-03-23.
- ^ a b "Cyprus." Jane's Sentinel: Eastern Mediterranean, issue 22, 2007.
- ^ Section source. Weather www.cypnet.co.uk. Retrieved 2008-09-14.
- ^ The official website of EUA: "North Cyprus' NEU and EMU are members"
- ^ EMU is a member of ICOGRADA EMU is a member of ICOGRADA
- ^ "Turkish Cypriot President Opens Girne American University's Campus in Canterbury", Asia Pulse (via TheFreeLibrary.com).
- ^ BAC accredited the Girne American University Canterbury GAU-C is a member of BAC.
- ^ Zaman Newspaper 01 Sept 2011
- ^ a b c CIA - The World Factbook - Cyprus: scroll down to section entitled Economy of the area administered by Turkish Cypriots
- ^ "Universities: Little accord on the island". The Independent (London). 2007-11-08. http://news.independent.co.uk/education/higher/article3136333.ece. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
- ^ Cyprus Mail 17 July 2011 North Cyprus sells electricity to Cyprus
- ^ a b Cyprus after Accession: Thinking Outside the Box – Background Documents, University of Oxford, European Studies Centre, Workshop on Cyprus 10–11 March 2006
- ^ a b General information about North Cyprus: Economy, web site of Unistar Investments Ltd., Bellapais, North Cyprus
- ^ Turkey, N. Cyprus sign economic development deal, Hurriyet Turkish Daily News, 4 May 2007.
- ^ "Turkey 'will open up to Cyprus'". BBC News. 2006-12-07. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/6216498.stm. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
- ^ "North Cyprus Airport, Ercan, Larnaca, Cheap Flights Northern Cyprus". Northcyprusonline.com. http://www.northcyprusonline.com/North-Cyprus-Online-How-to-Visit-Air.php. Retrieved 2010-11-17.
- ^ Poland - North Cyprus Direct charter flights
- ^ "Merchant Shipping". Csa-cy.org. http://www.csa-cy.org/closed%20ports.htm. Retrieved 2010-11-17.
- ^ "HC 113 II 04.05.PDF" (PDF). http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm200405/cmselect/cmfaff/113/113ii.pdf. Retrieved 2010-11-17.
- ^ "Visa requirements for Cyprus". Skicyprus.com. http://www.skicyprus.com/book/visa.asp. Retrieved 2010-11-17.
- ^ 7 border crossings btw Cyprus and North Cyprus 7 border crossings btw Cyprus and North Cyprus
- ^ Charlton, Gill (2005-02-05). "On the case: non-existent flight; Northern Cyprus; children in the Algarve; Cannes". The Daily Telegraph (London). http://www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/destinations/northamerica/usa/732241/On-the-case-non-existent-flight-Northern-Cyprus-children-in-the-Algarve-Cannes.html. Retrieved 2011-08-22.
- ^ North Cyprus' census 1996 and 2006 census data of North Cyprus
- ^ a b TRNC General Population and Housing Unit Census 2006, TRNC State Planning Organization, updated 7 October 2008.
- ^ Simon Bahceli (2007-02-15). "Indigenous Turkish Cypriots just over half north’s population". Cyprus Mail. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070930015114/http://cyprus-mail.com/news/main.php?id=30725&cat_id=1. Retrieved 2007-02-16.
- ^ International Crisis Group (2010). "CYPRUS: BRIDGING THE PROPERTY DIVIDE". International Crisis Group. p. 2. http://www.crisisgroup.org/~/media/Files/europe/turkey-cyprus/cyprus/210%20Cyprus%20-%20Bridging%20the%20Property%20Divide.ashx.
- ^ Cole, Jeffrey (2011), Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia, ABC-CLIO, p. 95, ISBN 1598843028
- ^ Cole, Jeffrey (2011), Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia, ABC-CLIO, p. 97, ISBN 1598843028
- ^ North Cyprus State Planning Organization 1983 population estimate of NC. Sheet:Main Ecosos
- ^ a b (Quoted after the Euromosaic report, a study commissioned by the European Commission PDF (120 KB)
- ^ "Cyprus - Society". Country-data.com. http://www.country-data.com/cgi-bin/query/r-3458.html. Retrieved 2010-11-17.
- ^ Nufussayimi.devplan.org
- ^ TRNC State Planning Organization. 2008 Yılı Makroekonomik ve Sektörel Gelişmeler, p.176-179.
- ^ Report of the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights on the question of human rights in Cyprus 16th Session, Human Rights Council, United Nations, 7 January 2011.
- ^ "Freedom in the World 2011 Report". Freedom House. p. 29. http://www.freedomhouse.org/images/File/fiw/FIW%202011%20Booklet_1_11_11.pdf. Retrieved 24 April 2011.
- ^ a b c "Cyprus: Population of Kurds in Turkish controlled Northern Cyprus; their treatment by the government of Turkey and its agents". Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada. 15 April 2002. http://www.unhcr.org/refworld/country,,IRBC,,CYP,,3df4be297,0.html. Retrieved 17 April 2011.
- ^ "Cyprus Overview". Minority Rigts Group International. September 2010. http://www.minorityrights.org/?lid=1873&tmpl=printpage. Retrieved 24 April 2011.
- ^ a b "2002 Report on Human Rights in Cyprus". US Department of State. 4 March 2002. http://www.state.gov/g/drl/rls/hrrpt/2001/eur/8242.htm. Retrieved 24 April 2011.
- ^ "Press Freedom Index 2010". Reporters Without Borders. http://en.rsf.org/press-freedom-index-2010,1034.html. Retrieved 24 April 2011.
- ^ "Overview of the Human Rights Situation in North Cyprus". Turkish Cypriot Human Rights Foundation. 14 January 2009. http://www.ktihv.org/Eng/content/view/43/13/. Retrieved 25 April 2011.
- ^ "State-sponsored Homophobia". International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association. May 2011. p. 44. http://old.ilga.org/Statehomophobia/ILGA_State_Sponsored_Homophobia_2011.pdf. Retrieved 18 October 2011.
Further reading
- North Cyprus – a Pocket-Guide. Rustem Bookshop, Nicosia. 2006. ISBN 994496803x.
External links
- Official links
- Parliament of Northern Cyprus Republic
- Presidency, Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
- Northern Cypriot Tourism Office
- TRNC Public Information Office
- TRNC Central Bank in Turkish language
- Other links
- Embargo! Non-profit association campaigning against the total economic embargo imposed on the population of Northern Cyprus
- ATCA News, Association of Turkish Cypriots Abroad
- Northern Cyprus Home Page
- Northern Cyprus Guide and Daily news
- "Islamic Conference's Parliaments to Call TRNC 'Cyprus Turkish State'" JTW
- International Expert Panel for a European Solution in Cyprus
- Assembly of Turkish American Associations
- Chronology – Cyprus Issue
- Turkish Cypriots of Australia – Historical Book
- North Cyprus Times
- Northern Cyprus Information
- Münüse, Folk Music
- Northern Cyprus travel guide from Wikitravel
- EU task-force on Turkish Cypriot community
- Northern Cyprus a refuge for British fugitives
- Attorney-General v. Ibrahim ("Principle of necessity")
- Enforceability in England of Republic of Cyprus Judgment against purchaser of real property in Northern Cyprus: High Court of Justice, judgement of 6 September 2006, Orams v. Apostolides, [2006] EWHC 2226 (QB). A French summary of the judgement of the Cypriot court (Eparchiako Dikastirio Lefkosias, case no. 9968/04, 19 April 2005, Apostolidis v. D. and L. Orams) is available in Reflets, Informations rapides sur les développements juridiques présentant un intérêt communautaire, Nº 1/2006. A reference for a preliminary ruling has been made by the Court of Appeal to the European Court of Justice on 13 September 2007 (case C-420/07, Official Journal of the European Union, 8 December 2007, 2007/C 297/34). The opinion of advocate general Kokott was delivered on 18 December 2008 (press release). The court issued its judgment on 28 April 2009.
- Caglar v. Billingham (status and taxability of official representative in London of the Northern Cyprus government)
- Visiting Sheikh Nazim Al Haqqani
Geographic locale Middle East Countries and territories Other topics 1 Only recognized by Turkey; see Cyprus disputeInternational organizations Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) Members Afghanistan · Albania · Algeria · Azerbaijan · Bahrain · Bangladesh · Benin · Burkina Faso · Brunei · Cameroon · Chad · Comoros · Côte d'Ivoire · Djibouti · Egypt · Gabon · Gambia · Guinea · Guinea-Bissau · Guyana · Indonesia · Iran · Iraq · Jordan · Kuwait · Kazakhstan · Kyrgyzstan · Lebanon · Libya · Maldives · Malaysia · Mali · Mauritania · Morocco · Mozambique · Niger · Nigeria · Oman · Pakistan · Palestine · Qatar · Saudi Arabia · Senegal · Sierra Leone · Somalia · Sudan · Suriname · Syria · Tajikistan · Turkey · Tunisia · Togo · Turkmenistan · Uganda · Uzbekistan · United Arab Emirates · YemenObservers Countries and territoriesBosnia and Herzegovina · Central African Republic · Russia · Thailand · Northern Cyprus (as Turkish Cypriot State)Muslim communitiesInternational organizationsOther associations Modern sovereign Turkic states 1 Limited recognition (recognized only by Turkey, see Cyprus dispute).Turkic-speaking regions Federal subjects of Russia shown in italics.Western Turkic
 Azerbaijan1
Azerbaijan1
 Bashkortostan
Bashkortostan
 Chuvashia
Chuvashia
 Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus
 Gagauzia (Moldova)
Gagauzia (Moldova)
 Kabardino-Balkaria
Kabardino-Balkaria
 Karachay-Cherkessia
Karachay-Cherkessia
 Karakalpakstan (Uzbekistan)
Karakalpakstan (Uzbekistan)
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Xinjiang (China)1 Includes the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic.
Xinjiang (China)1 Includes the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. Topics on Northern Cyprus
Topics on Northern Cyprus People and
languagesTurkish Cypriots · Turkish people · Turkic peoples · Cypriot Turkish · Enclaved Greek Cypriots · Turkish language · Turkic languagesHistory Timeline · Turkish people · Turkic peoples · Prehistory · Ancient history · Medieval · Kingdom · Ottoman rule · British protectorate and modern history · Refugees · Intercommunal violence · Turkish invasion (timeline) · Annan PlanPolitics and
governmentAssembly · President · Prime Minister · Elections · Political parties · Constitution · Human Rights · moreForeign relations Cyprus dispute · Diplomatic missions · Embassy in Turkey · Representative Office to the United States · Green Line · Reunification negotiations · moreEconomy Military Demographics Culture Symbols Communications Categories:- Northern Cyprus
- Unrecognized or largely unrecognized states
- Bicontinental countries
- Southwest Asian countries
- Middle Eastern countries
- Countries of the Mediterranean Sea
- Modern Turkic states
- Divided regions
- Island countries
- Secession in Cyprus
- States and territories established in 1983
- Western Asia
- Disputed territories in Europe
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.