- Cortical reaction
-
Cortical reaction 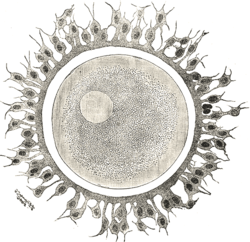
Human ovum. The zona pellucida is seen as a thick clear girdle surrounded by the cells of the Corona radiata. Gray's subject #3 38 MeSH Zona+Pellucida The cortical reaction occurs when a sperm cell unites with the egg's plasma membrane, (zona reaction) modification of the zona pellucida that blocks polyspermy; enzymes released by cortical granules digest sperm receptor proteins ZP2 and ZP3 so that they can no longer bind sperm, in mammals.
The cortical reaction is exocytosis of the egg's cortical granules. Cortical granules are secretory vesicles that reside just below the egg's plasma membrane. When the fertilizing sperm contacts the egg plasma membrane, it causes calcium to be released from storage sites in the egg, raising the intracellular free calcium concentration. This triggers fusion of the cortical granule membranes with the egg plasma membrane, liberating the contents of the granules to the extracellular space. Fusion begins near the site of sperm contact, and then as the wave of calcium release sweeps around the egg, a wave of cortical granule fusion results. The contents of the granules vary with the species, and are not fully understood.
In the well-studied sea urchin model system, the granule contents modify a protein coat on the outside of the plasma membrane (the vitelline layer) so that it is released from the membrane. The released cortical granule proteins exert a colloid osmotic pressure causing water to enter the space between the plasma membrane and the vitelline layer, and the vitelline layer expands away from the egg surface. This is easily visible through a microscope and is known as "elevation of the fertilisation envelope". Some of the former granule contents adhere to the fertilisation envelope, and it is extensively modified and cross-linked. As the fertilisation envelope elevates, non-fertilizing sperm are lifted away from the egg plasma membrane, and as they are not able to pass through the fertilisation envelope, they are prevented from entering the egg. Therefore, the cortical reaction prevents polyspermic fertilisation, a lethal event. Another cortical granule component, polysaccharide-rich hyalin, remains adherent to the outer surface of the plasma membrane, and becomes part of the hyaline layer.
This is considered the slow block to multiple fertilisation at an animal egg cell
See also
- Acrosome reaction - The analogous reaction in the acrosome of the sperm.
References
- Haley SA, Wessel GM. Sea urchin cortical granules regulated proteolysis by cortical granule serine protease 1 at fertilisation. Mol Biol Cell. 2004 May;15(5):2084-92.
- Sadler TW. Langman's Medical Embryology. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2006.
External links
Categories:- Germ cells
- Reproductive system
- Developmental biology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
