- Adductor magnus muscle
-
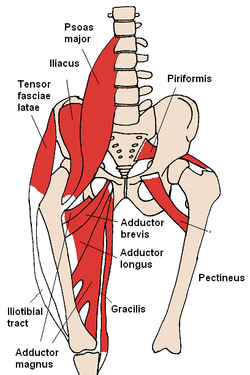
Adductor magnus muscle The adductor magnus and nearby muscles Structures surrounding right hip-joint. (Adductor magnus at upper right.) Latin musculus adductor magnus Gray's subject #128 473 Origin pubis, tuberosity of the ischium Insertion femur Artery Obturator artery Nerve posterior branch of obturator nerve (adductor) and sciatic nerve (hamstring)[1] Actions adduction of hip (both portions)
flexion of hip (adductor portion)
extension of hip (hamstring portion)The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.
It consists of two parts. The portion which arises from the ischiopubic ramus (a small part of the inferior ramus of the pubis, and the inferior ramus of the ischium) is called the "adductor portion", and the portion arising from the tuberosity of the ischium is called the "hamstring portion". Due to its common embryonic origin, innervation, and action the hamstring portion is often considered part of the hamstring group of muscles.
Contents
Origin and insertion
Adductor portion
Those fibers which arise from the ramus of the pubis are short, horizontal in direction, and are inserted into the rough line of the femur leading from the greater trochanter to the linea aspera, medial to the gluteus maximus.
Those fibers from the ramus of the ischium are directed downward and laterally with different degrees of obliquity, to be inserted, by means of a broad aponeurosis, into the linea aspera and the upper part of its medial prolongation below.
Hamstring portion
The medial portion of the muscle, composed principally of the fibers arising from the tuberosity of the ischium, forms a thick fleshy mass consisting of coarse bundles which descend almost vertically, and end about the lower third of the thigh in a rounded tendon which is inserted into the adductor tubercle on the medial condyle of the femur, and is connected by a fibrous expansion to the line leading upward from the tubercle to the linea aspera.
Relations
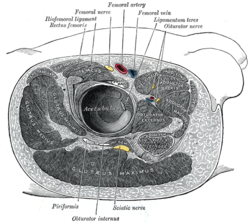
By its anterior surface the adductor magnus is in relation with the pectineus, adductor brevis, adductor longus, femoral artery and vein, profunda artery and vein, with their branches, and with the posterior branches of the obturator artery, obturator vein and obturator nerve.
By its posterior surface with the semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps, and gluteus maximus.
By its inner border with the gracilis and sartorius.
By its upper border with the obturator externus, and quadratus femoris.[2]
Innervation
The adductor and hamstring portions of the muscle are innervated by two different nerves. The adductor portion is innervated by the posterior division of the obturator nerve while the hamstring portion is innervated by the sciatic nerve.[3]
Osseoaponeurotic openings
Further information: Adductor hiatus and Adductor canalAt the insertion of the muscle, there is a series of osseoaponeurotic openings, formed by tendinous arches attached to the bone. The upper four openings are small, and give passage to the perforating branches of the profunda femoris artery. The lowest (often referred to as the adductor hiatus) is large, and transmits the femoral vessels to the popliteal fossa.
Action
The adductor magnus is a powerful adductor of the thigh, made especially active when the legs are moved from a wide spread position to one in which the legs parallel each other. The part attached to the linea aspera acts as a lateral rotator. The part which reaches the medial epicondyle acts as a medial rotator when the leg is rotated outwards and flexed, and also acts to extend the hip joint.[4]
Variation
The upper, lateral part of the adductor magnus is an incompletely separated division often considered a separate muscle — the adductor minimus.[4] These two muscles are frequently separated by a branch of the superior perforating branch of the profunda femoris artery.[5]
Ontogeny and phylogeny
In other tetrapods, the adductor magnus crosses the knee joint and inserts into the tibia. In humans, the distal part of the tendon detaches and becomes the medial collateral ligament of the knee. Because of this, the medial collateral ligament of the knee in humans may contain a few muscle fibres as an atavistic variation.[6]
See also
Additional images
References
- ^ Mnemonic at medicalmnemonics.com 255
- ^ Wilson, Erasmus (1851) The anatomist's vade mecum: a system of human anatomy, p 261
- ^ "Adductor Magnus". Department of Radiology, University of Washington. http://www.rad.washington.edu/academics/academic-sections/msk/muscle-atlas/lower-body/adductor-magnus. Retrieved 2010-08-16.
- ^ a b Platzer, Werner (2004), " Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1, Locomotor System, Thieme, 5th ed, p 242
- ^ Bergman, Ronald A.; Afifi, Adel K.; Miyauchi, Ryosuke (2010), Adductor Minimus (Henle, Günther), Anatomy Atlases
- ^ Norman Eizenberg et al., General Anatomy: Principles and Applications (2008), p 53.
External links
- LUC admg
- -939130803 at GPnotebook
- SUNY Labs 14:st-0401
- Adductor+magnus+muscle at eMedicine Dictionary
- PTCentral
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
List of muscles of lower limbs (TA A04.7, GA 4.465) ILIAC Region
/ ILIOPSOASBUTTOCKS THIGH /
compartmentsLEG/
Crus/
compartmentssuperficial · triceps surae (gastrocnemius, soleus, accessory soleus, Achilles tendon) · plantaris
deep · tarsal tunnel (flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior) · popliteusfibularis muscles (longus, brevis)FOOT DorsalPlantar1st layer (abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, abductor digiti minimi) · 2nd layer (quadratus plantae, lumbrical muscle) · 3rd layer (flexor hallucis brevis, adductor hallucis, flexor digiti minimi brevis) · 4th layer (dorsal interossei, plantar interossei)Origin Inferior pubic ramus, ischial ramus, and inferolateral area of ischial tuberosity Insertion Gluteal tuberosity of femur, medial lip of linea aspera, medial supracondylar ridge, and adductor tubercle Action Powerful thigh adductor; superior horizontal fibers also help flex the thigh, while vertical fibers help extend the thigh Innervation Posterior division of obturator nerve innervates most of the adductor magnus; vertical or hamstring portion innervated by tibial nerve (L2, L3, L4) Arterial Supply Medial circumflex femoral artery, inferior gluteal artery, 1st - 4th perforating arteries, obturator artery, and some superior muscular branches of popliteal artery Arterial Supply Medial circumflex femoral artery, inferior gluteal artery, 1st - 4th perforating arteries, obturator artery, and some superior muscular branches of popliteal artery
Categories:- Hip adductors
- Thigh muscles
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.