- Warsaw Metro
-
Warsaw Metro 

Wierzbno StationInfo Owner city of Warsaw Locale Warsaw Transit type Rapid transit Number of lines 1 Number of stations 21 Daily ridership 553,000 (working day in 2009) [1] Website http://www.metro.waw.pl Operation Began operation 1995 Operator(s) Metro Warszawskie Technical Track gauge standard gauge (1435 mm) System map The Warsaw Metro (Polish: Metro warszawskie) is a rapid transit system serving the city of Warsaw, the capital of Poland. It consists of a single north-south line that links central Warsaw with its densely populated northern and southern suburbs. The first section was opened in 1995, then gradually extended until it reached full planned length in October 2008. There are plans to add two stations omitted during construction in the next few years. The contract for building the initial section of the second,[2] east-west line was signed on 28 October 2009 and construction started on 16 August 2010,[3] with completion planned for late 2013.
Contents
History
Plans to build an underground rail system in Warsaw date as far back as 1918, when the idea was first floated in reaction to Warsaw regaining its status as Poland's capital city. An underground railway system was expected to solve the transport difficulties of the densely-built city centre. Proper preliminary planning and boring work were initiated by the Warsaw Tramway Authority in 1925, with construction expected to start in the late 1920s. The Great Depression buried those plans as Poland and the world was gripped by hardship. In 1934, with the election of a new mayor of Warsaw, Stefan Starzyński, work was to resume on the metro. The mayor dusted off the plans from the mid-1920s, and with some minor adjustments, construction of the metro was planned to start by the late 1930s, with a projected finishing date of the first of two projected lines scheduled for the mid 1940s. By then, the subway network was to consist of two lines. The A line (North-South line, 7,5 km or 46 mi (74 km) long), followed most of today's route and was to link the southernmost borough of Mokotów with the city centre and the northern borough of Żoliborz. This line was to be connected with the newly-constructed Warszawa Główna railway station and the railway tunnel crossing the city from west to the east. The B line (East-West, 6,3 km or 4 mi (6.4 km) long) was to start beneath the westernmost borough of Wola, proceed along the Chłodna street to the pivotal station beneath the Saxon Sq. and then further eastwards to the Vistula river escarpment. There, the line was to go overground, cross the river through a newly-built bridge and proceed to the easternmost railway station of Warszawa Wschodnia. Altogether, in 35 years 7 lines were to be built). The works finally started in 1938, but World War II brought an end to the ambitious undertaking. The short trace tunnels made in 1938 serve as a wine cellar today.
The city suffered heavily during World War II. Although the majority of pre-war projects perished during the war, most of the engineers behind their creation survived the war and returned to their city to take part in its rebirth. However, the new Communist authorities of Poland envisioned a city completely different from what it used to be before the war. As the ideal communist city, Warsaw was to be decentralized and a need to commute to the city centre was to be reduced. Thus the Reconstruction of Warsaw Office (BOS) commissioned a number of engineers to prepare a project of a fast urban railway (SKM) crossing the city in a deep cutting. Although to a large extent it was to follow the A line of the pre-war plans, only the central stations were to be located underground. However, by the end of the decade the project was cancelled. Instead, in 1948 a different concept was considered. This time the SKM was to be a rapid transit line at a depth of up to 15 metres (50 feet). The suggested North-South direction, with three parallel branches of the same line in the city centre, corresponded to the planned development of the city along the Vistula. The works however never started and this project was also abandoned.
In the 1950s, as the Cold War raged on, Soviet strategic plans required that a secure transport link across the river Vistula be built. One of the ways to achieve this was to create a deep metro system in Warsaw (up to 46 metres or 150 feet (46 m) beneath the ground), which would be interlinked with the rail network and could serve as an underground conduit for transporting troops. Plans assumed that the first line (ca. 11 kilometres) would lie along North-South axis, with a branch of the same line crossing the Vistula river in the city centre. The construction works started almost simultaneously at 17 different points on both sides of the river. Until 1953 771 metres of tunnels were built, however after the death of Joseph Stalin and the start of a period of détente, all works were halted under the pretext of technical difficulties. In following years only one junction tunnel and one shield-driven tunnel were continued to be constructed. These works were undertaken experimentally, in order to discover the best driving methods suitable for the ground conditions beneath Warsaw (pliocene clay formations layer spread beneath quaternary soils). Finally, in 1957 all the work was halted.
Since 1955 there was a return to the old idea of a shallow metro network. However, the planning phase proceeded at a very slow pace and the economical situation prevented all successive communist governments from actually starting a serious work. Finally, in 1984, the programme was approved by the government and the first tunnels were built. Lack of funds, poor planning, and tedious bureaucracy meant that the work progressed very slowly, at a speed no greater than 2 metres a day. The Metro was opened in 1995 with a total of 11 stations. The line now has 21 stations along a distance of approximately 20 kilometres.
Perhaps alone among world metro systems, tickets are not sold by the transport company itself, but by post offices and privately-run shops and newsagents'; however, the ticket system covers all Warsaw public transport, including the Metro, buses, trams and some suburban trains. In addition to single (or daily/weekly) tickets, one can also purchase a proximity card at which can be charged for up to 3 months at a time, offering a cheaper alternative to single tickets.
Lines:
# Opened Length Stations 1 1995 23,1 km 21 2 under construction Total: 23,1 km 21 Future plans
The second line, crossing the city from east to west (heading north from central Praga on the east bank of the river) is planned, along with a short third line from central Praga going south; both of these are truncated versions of earlier plans for the lines to approach the city limits at each end. Construction has not yet commenced, but plans for the beginning of construction of the second line ("the first stage", from Dw. Wileński to Rondo Daszyńskiego) are currently being put at 2010, with its completion after 2012, possibly in 2014. Earlier plans for completing it by 2012 were too optimistic.
The first line was a compromise between earlier route proposals further east and west (one of which belonged to the planned Line 4) and as such does not go to some important areas of the city. For example, it does not pass directly under the old town, Warsaw's main tourist attraction, which has few public transport links, passing it about 600 m to the west. It also does not go to the central railway station, and the nearest stop is over 400 m to the east (the planned second line will also avoid it, with the closest station also about 400 m to the north). Furthermore, the first line, and thus the Metro system for the immediate future, is confined to the western bank of the Vistula river, thus doing nothing to ease traffic problems on Warsaw's bridges, a major bottleneck between the city centre and the eastern Praga district. Plans for the third line to Okęcie airport have been abandoned for the foreseeable future.
Transport planners have suggested that the WKD, a light rail line that runs to the western suburbs, could be integrated with the city's tram system, or be more closely tied to the Metro and a future suburban rail network, or both. The first such plans were prepared in the late 1930s and the railway tunnel running below the city centre was to be shared by both the railways and the metro. In the mid-1990s the WKD, PKP and Warsaw Metro systems were temporarily integrated and Warsaw city travel cards were valid also in the suburban railways. This idea was, however, dropped in 1999 due to financial problems.
Operational characteristics
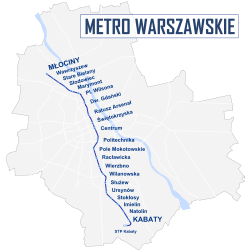
Warsaw Metro line 1 




Młociny 

Wawrzyszew 


Stare Bielany 


Słodowiec 




Marymont 


Plac Wilsona 



Dworzec Gdański 




Muranów (planned) 




Ratusz Arsenał 




Świętokrzyska 



link to Warszawa Śródmieście PKP 




Centrum 




Warsaw Cross-City Line 



Plac Konstytucji (planned) 




Politechnika 




Pole Mokotowskie 


Racławicka 




Wierzbno 




Wilanowska 


Służew 


Ursynów 


Stokłosy 


Imielin 


Natolin 


Kabaty 


link to railway network 


Kabaty STP depot 


Rolling stock
A single depot is located south of the Kabaty station. There is a single-track connection between the depot and Warszawa-Okęcie station on the PKP rail network. This link is not electrified, and used only for an occasional rolling-stock transfer.
Initially, all of the trains were Russian built. They first arrived in Warsaw in 1990 as a gift from the USSR, five years prior to the Metro's opening, from Metrovagonmash plant in Mytishchi (near Moscow) (model 81-717.3/714.3 - 10 carriages). Subsequent trains arrived from Saint Petersburg's Yegorov Plant in 1994 (81-572/573 - 32 carriages) and additional 18 81-572.1/573.1 carriages in 1997.[4]
In 1998, 108 new carriages were ordered from Alstom. These were all delivered by 2005[5] (24 were produced in Barcelona and the rest in Chorzów).[6] In 2006 additional carriages were ordered from Russia, with deliveries taking place during 2007, to lengthen the existing trains using older Russian carriages.
Currently, out of the 40 trains running, 15 consist of the older Russian-produced cars, 7 of the newer Russian-produced cars and 18 of Alstom-produced cars. The Russian and Alstom carriages are incompatible and cannot be used in the same train.
In February of 2011 an order has been signed with Siemens for 35 complete trains from their new Inspiro line. A large number of these are to be manufactured in Poland by Newag.
Future extensions
- Plac Konstytucji and Muranów, two stations omitted from the original plan to reduce cost were to be built by 2009 but construction has not yet started, and will not start in the near future. [1].
- Line 2 - the first, central section [2] will consist of 7 stations: Rondo Daszyńskiego, Rondo ONZ, Świętokrzyska, Nowy Świat, Powiśle, Stadion and Dworzec Wileński. It will pass under the Vistula river between the Powiśle and Stadion stations. Most of the funding for building this section has been secured from the European Union and construction started in August 2010. The original plan to finish this section in time for Euro 2012 was too optimistic, and the expected completion date is Fall of 2013. This line will be built using a different boring technology which should allow for much faster construction, compared to the first line. The rest of the line, which will consist of 28 stations in total, will be built later. A tender was opened for 35 trains (most to be used on line 2, some on line 1); Škoda Transportation and Vagonmash submitted the lowest price[7] but Siemens/Newag scored more points and were chosen to provide the trains.[8]
Timeline
Segment Date opened Length (km) Kabaty – Politechnika 7 April 1995 11.0 Politechnika – Centrum 26 May 1998 1.4 Centrum – Ratusz Arsenał 11 May 2001 1.7 Ratusz Arsenał – Dworzec Gdański 20 December 2003 1.5 Dworzec Gdański – Plac Wilsona 8 April 2005 1.5 Plac Wilsona – Marymont 29 December 2006 0.9 Marymont – Słodowiec 23 April 2008 1.0 Słodowiec – Młociny 25 October 2008[9] 3.0 Total 21 Stations 23.1 km Warsaw Metro in Rankings
- List of Metro Systems by length - ranked 109th out of 143
- List of Metro Systems by number of stations - ranked 62nd out of 68
In 2009, Warsaw metro won two "Metro Award" prizes in the categories: "Special Merit Award for Commitment to the Environment" and "Best Maintenance Programme". Also, the Warsaw metro is well-known for its beautiful stations (for example stations from Słodowiec to Młociny, Plac Wilsona or Ratusz-Arsenał Station.)
See also
References
- Online
- ^ Annual Report 2009 (Raport roczny 2009), in Polish & English, page 10 (16+17) (strona 10 (16+17))
- ^ website of Warsaw Metro - Line II information and maps
- ^ PAP. "Wielka chwila: ruszają prace przy drugiej linii metra" (in Polish). Gazeta.pl. http://warszawa.gazeta.pl/warszawa/1,95190,8248910,Wielka_chwila__ruszaja_prace_przy_drugiej_linii_metra.html. Retrieved 2010-08-13.
- ^ "Метровагоны" (in Russian). http://www.vagon.metro.ru/types/export.html.
- ^ "Warsaw Metro". ALSTOM Cars. http://www.metro.waw.pl/page.php?id=85&lng=en.
- ^ "Przegubowiec" (in Polish). Tabor Metra Warszawskiego. http://przegubowiec.com/metro/tabor-m.htm.
- ^ "2010-10-01". http://www.railwaygazette.com/nc/news/single-view/view/urban-rail-news-in-brief-october-2010.html. Retrieved 2010-10-05.
- ^ "Railway Gazette: Warszawa metro selects Siemens Inspiro". http://www.railwaygazette.com/nc/news/single-view/view/warszawa-metro-selects-siemens-inspiro.html. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ First train to pull into Mlociny metro station. Polskie Radio. 25 October 2008.
- General
- various authors (1962). Jan Rossman. ed. Studia i projekty metra w Warszawie; 1928-1958. Warsaw: Arkady. pp. 391.
External links
- (Polish)/(English) Metro Warszawskie Warsaw Metro official website
- (Polish)/(English) Construction the second line of Warsaw Metro official website
- (English) Urbanrail.net-Warsaw Metro guide
- (Polish) [3]-Warsaw Metro fan site and discussion forum
- (Russian) Trackmap.Ru - Warszaw Metro Track Map
- (Polish) Television TVPW - The Information Movie about Warsaw Metro system (production: TVPW)
- (Polish) Television TVPW - Relation of opening the "Słodowiec" station (production: TVPW)
- (Polish) Television TVPW - The movie about building the metro in Warsaw from the beginning to the end (production: TVPW)
- (Polish) Television TVPW - The interview with Robert Jaryczewski - the best metro driver of the world in 2008 (production: TVPW)
- (Polish) Television TVPW - The movie about signaling in metro in Warsaw (production: TVPW)
Transport in Warsaw Warsaw Chopin Airport · Modlin Airport · Koleje Mazowieckie · Szybka Kolej Miejska · Warsaw Metro · Warsaw Tramway · Warsaw Trolleybuses · Warszawska Kolej Dojazdowa Categories:
Categories:- Warsaw Metro
- Underground rapid transit systems
- Lists of metro stations
- Railway companies of Poland
- Railway lines opened in 1995
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.