- Niigata Prefecture
-
Niigata Prefecture Japanese transcription(s) – Japanese 新潟県 – Rōmaji Niigata-ken 
Symbol of Niigata PrefectureCountry Japan Region Chūbu, Hokuriku Island Honshū Capital Niigata (city) Government – Governor Hirohiko Izumida Area – Total 12,582.47 km2 (4,858.1 sq mi) Area rank 5th Population (February 1, 2011) – Total 2,371,574 – Rank 14th – Density 188.48/km2 (488.2/sq mi) ISO 3166 code JP-15 Districts 9 Municipalities 30 Flower Tulip (Tulipa gesneriana) Tree Camellia (Camellia japonica) Bird Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon) Website www.pref.niigata.lg.jp/en Niigata Prefecture (新潟県 Niigata-ken) is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Honshū on the coast of the Sea of Japan.[1] The capital is the city of Niigata.[2] The name "Niigata" literally means "new lagoon".
Contents
History
Until after the Meiji Restoration, the area that is now Niigata Prefecture was divided into Echigo Province and Sado Province.[3] During the Sengoku period, the Nagao clan, who were at times vassals to the Uesugi, ruled a fief in the western part of modern Niigata from Kasugayama Castle. The most notable member of the Nagao clan was Nagao Kagetora, was later and better known as Uesugi Kenshin. He unified the leaders of Echigo Province and became its sole ruler. By taking the surname Uesugi, he also became the head of the Uesugi clan and effectively brought their realm under his control.
The city of Niigata is now the largest Japanese city facing the Sea of Japan. It was the first Japanese port on the Sea of Japan to be opened to foreign trade following the opening of Japan by Matthew Perry. It has since played an important role in trade with Russia and Korea. A freighter from North Korea visits Niigata once a month, in one of the few forms of direct contact between Japan and that country.
The Etsuzankai organization, led by the politician Kakuei Tanaka, was highly influential in bringing infrastructure improvements to Niigata Prefecture in the 1960s and 1970s. These included the Jōetsu Shinkansen high-speed rail line and the Kanetsu Expressway to Tokyo.
On October 23, 2004, the Chūetsu earthquake struck Niigata Prefecture and was measured at Shindo 6+ at Ojiya.
On January 9, 2006, a heavy winter storm struck the prefecture and its neighbors. At least 71 people died and more than 1,000 were injured. Also in 2006, a massive tsunami and earthquake damaged homes and caused casualties in the maritime areas of Niigata Prefecture, especially near Sado Island.
On July 16, 2007, another earthquake hit the area.
Niigata Prefecture hosts the Fuji Rock Festival, an annual event held at the Naeba ski resort. The three-day event, organized by Smash Japan, features more than 200 Japanese and international musicians. It is one of the largest outdoor music events in Japan, with more than 100,000 people attending in 2005.
Geography
Niigata Prefecture stretches about 240 km along the Sea of Japan, from the southwest to the northeast, with a coastal plain between the mountains and the sea. It also includes Sado Island.
Because of the way it is shaped, Niigata Prefecture is often called "small Honshū." It could be placed in either the Hokuriku or the Kōshin'etsu, both of which are considered parts of the Chūbu region.
The prefecture is generally divided into four geographical areas: Jōetsu in the south, Chūetsu in the center, Kaetsu in the north, and Sado Island. The mouth of the Shinano River, the longest river in Japan, is located in Niigata Prefecture.
 Reconstruction of a 19th century peasant farmer's house and rice paddy at the Northern Culture Museum, Niigata.
Reconstruction of a 19th century peasant farmer's house and rice paddy at the Northern Culture Museum, Niigata.
Cities
There are 20 cities in Niigata Prefecture:
Towns and villages
The towns and villages in each district are:
Mergers
Main article: List of mergers in Niigata PrefectureEconomy
Agriculture, forestry and fishing
The major industry in Niigata Prefecture is agriculture. Rice is the principal product, and among the prefectures of Japan Niigata is second only to Hokkaidō in rice output. The area around Uonuma is known for producing the Koshihikari variety, widely considered to be the highest-quality rice produced in Japan.
Rice-related industries are also very important to the prefectural economy. Niigata Prefecture is known throughout Japan for its high-quality sake, senbei, mochi, and arare. In sake production, the prefecture comes third after Gunma and Kyoto prefectures.
The prefecture was also the place of origin of the ornamental carp known as koi.
Niigata Prefecture produces the highest volume of azaleas and cut lilies in Japan, and is increasing production of cut flowers and flower bulbs. Along with Toyama Prefecture, it produces the highest volume of tulips in the country.
Mining and manufacturing
Crude oil is produced in Niigata Prefecture, although Japan relies heavily on petroleum imported from other countries. Kerosene heaters are also produced for use in the cold Niigata winters.
Kinzan, on Sado Island, was an active gold mine until it was closed in 1989.
Sanjō and Tsubame produce 9 percent of all the silverware made in Japan. The two cities are second after Osaka in the production of scissors, kitchen knives, and wrenches.
Niigata Prefecture may have been the first area in Japan to produce knitted textiles, although the earliest products may have been imported from China.
The nuclear power plant with the highest energy output in the world is located in the tiny village of Kariwa.
Demographics
In 1885, Niigata was the most populous prefecture in Japan, beating even Tokyo and Osaka Prefecture in population[citation needed]. In the Census of 2003, Niigata ranked as the 14th most populous.
As in the rest of Japan, Niigata's population shows signs of aging, particularly in the rural areas.
Culture
Food
Niigata is known for the following regional specialities:
- Uonuma Koshihikari rice
- Shoyu (soy sauce) and Yofu (western-style) katsudon
- Shoyu sekihan
- Noppe stew
- Wappa-meshi (seafood and rice steamed in a bamboo basket)
- Sasa-dango (mochi balls filled with red bean paste, seasoned with mugwort and wrapped in bamboo leaves)
- Poppo-yaki (steamed bread flavored with brown sugar)
- Hegi-soba (soba from the Uonuma and Ojiya areas, which uses a special kind of seaweed)
- "Tsubame-Sanjō ramen" (ramen made using thick udon-style noodles)
- Tochio aburage (aburaage is called "aburage" in Tochio)
- Kirazu (dishes using okara)
- Kakinomoto (edible chrysanthemums)
- Kanzuri (a special seasoning from Myōkō made by leaving chili peppers exposed on snow, then adding flour, salt and yuzu)
- Yasuda yogurt
Niigata in popular culture
- Snow Country ( 1947): a novel by Nobel laureate Yasunari Kawabata set in Yuzawa
- "Niigata Snow": a track on the LP Aida, released by Derek Bailey in 1980
- Kura: a film and TV series (1995) based on the 1993 book by Tomiko Miyao, an award winning period piece about a Niigata family and its sake brewery
- Blue (1996): a manga about high school girls, set in Niigata City, adapted as a film in 2001
- Whiteout: an action film based on a novel published in 1995
- My Mother is a Tractor: A Life in Rural Japan (2006), a memoir by Nicholas Klar, written when he was based in Itoigawa in Niigata Prefecture
Tourism and sports
Much of the tourism in Niigata centers around skiing and going to onsen, especially in the alpine areas of Myōkō and Yuzawa.
Sado Island off the west coast of Niigata is accessible via ferry (taking one to two and a half hours) from Naoetsu or Niigata City.
Professional sports clubs include Albirex Niigata, a J-League Division 1 Soccer Club, and Niigata Albirex BB, a BJ (Basketball Japan) League team.
Festivals
- Murakami Taisai – July 6-7
- Iwafune Taisai – October 18-19, in Murakami
- Niigata Festival – August
- Niigata General Dancing Event -September 21-25
- Shirone Kite Festival – June
- Sanjo Kite Festival – June
- Nagaoka Festival (with fireworks) – August
- Tokamachi Winter Festival – February[citation needed]
- Niigata Tanrei Sake-no-Jin - March
Education
University
- Niigata University
- Niigata Prefectural University
- Niigata University of International and Information Studies
- Niigata Sangyo University (Niigata Industrial University)
- Niigata University of Health and Welfare
- Niigata University of Pharmacy and Applied Life Sciences
- Niigata Seiryou University
- Niigata Institute of Technology
- Niigata University of Management
- Niigata College of Nursing
- Nippon Dental University
- Nagaoka University
- Nagaoka Institute of Design
- International University of Japan
- Keiwa Gakuen University
Transport
Railroad
- JR East
- Joetsu Shinkansen
- Shinetsu Line
- Hakushin Line
- Yahiko Line
- Echigo Line
- Joetsu Line
- Uetsu Line
- Banetsu West Line
- Tadami Line
- Iiyama Line
- Yonesaka Line
- JR West
- Hokuriku Line
- Oito Line
- Hokuetsu Express Hokuhoku Line
Road
Expressway
- Kanetsu Expressway
- Joshinetsu Expressway
- Hokuriku Expressway
- Banetsu Expressway
- Nihonkai Expressway
National Highway
- Route 7 (Niigata-Shibata-Murakami-Sakata-Akita-Noshiro-Hirosaki-Aomori)
- Route 8 (Niigata-Nagaoka-Kashiwazaki-Joetsu-Toyama-Kanazawa-Fukui-Tsuruga-Hikone-Kusatsu, Shiga)
- Route 17 (Nagaoka-Ojiya-Shibukawa-Takasaki-Kumagaya-Saitama-Nihonbashi of Tokyo)
- Route 18 (Joetsu-Myoko-Nagano-Komoro-Karuizawa-Takasaki)
- Route 49 (Niigata-Aizuwakamatsu-Koriyama-Iwaki)
- Route 113
- Route 116
- Route 117
- Route 148
- Route 252
- Route 253
- Route 289
- Route 290
- Route 291
- Route 292
- Route 345
- Route 350 (Sado Island)
- Route 351
- Route 352
- Route 353
- Route 402
- Route 403
- Route 404
- Route 405
- Route 459
- Route 460
Port
- Niigata Port – Ferry route to Sado Island, Tsuruga, Akita, Otaru and Tomakomai, with International Container hub port
- Ryotsu Port – Ferry route to Niigata
- Ogi Port
- Naoetsu Port
Airport
- Niigata Airport
- Sado Airport
Prefectural symbols
Notable individuals
Politics and military
- Hachirō Arita (1884–1965), foreign minister, from Sado Island.
- Kita Ikki (1883–1937), nationalist author and intellectual, from Sado Island.
- Honma Masaharu World War II lieutenant-general executed by the United States by war crimes committed in the Philippines.
- Isoroku Yamamoto (1884–1943), commander of the Japanese Imperial Navy, from Nagaoka.
- Kakuei Tanaka (1918–1993), prime minister, from Urasa, Minamiuonuma.
- Hisashi Owada (born 1932), diplomat and father of Crown Princess Masako, from Shibata.
- Makiko Tanaka (born 1944), first female foreign minister, from Kashiwazaki. Currently, a DPJ politician.
Arts and culture
- Ryōkan (1758–1831), Zen Buddhist monk and poet, from Izumozaki.
- Inoue Enryō (1858–1919), Buddhist philosopher, from Nagaoka.
- Yaichi Aizu (1881–1956), poet, calligrapher and historian, from Niigata City.
- Fubō Hayashi (1900–1935), novelist from Sado Island.
- Ango Sakaguchi (1906–1955), novelist and essayist, from Niigata City.
- Haruo Minami (1923–2001), enka singer, from Nagaoka.
- Kimio Yanagisawa (born 1948), manga artist, from Gosen.
- Tetsuo Harada (born 1949 Niitsu-shi), Sculptor working in Paris France.
- Yoshifumi Kondō (1950–1998), animator, from Gosen.
- Keiko Yokozawa (born 1952), seiyu, from Niigata City.
- Bin Shimada (born 1954), seiyu, from Niigata City.
- Kazuyuki Sekiguchi (born 1955), bass player for the rock group Southern All Stars, from Agano.
- Yukari Nozawa (born 1957), actor and seiyu.
- Rumiko Takahashi (born 1957), manga artist, from Niigata City.
- Hajime Watanabe (born 1957), animator.
- Shuichi Shigeno (born 1958), manga artist, from Tōkamachi.
- Makoto Kobayashi (born 1958), manga artist, from Niigata City.
- Motoei Shinzawa (born 1958), manga artist, from Kashiwazaki.
- Ken Watanabe (born 1959), stage, TV and film actor, from Niigata.
- Yōko Sōmi (born 1965), seiyu.
- Kazuya Tsurumaki (born 1966), animator, from Gosen.
- Akiko Yajima (born 1967), seiyu, from Kashiwazaki.
- Hiroki Yagami (born 1967), manga artist, from Kashiwazaki.
- Kazuto Nakazawa (born 1968), animator.
- Takeshi Obata (born 1969), manga artist, from Niigata City.
- Etsushi Ogawa (born 1969), manga artist.
- Rumi Kasahara (born 1970), seiyu, from Itoigawa.
- Nobuhiro Watsuki (born 1970), manga artist, from Nagaoka.
- Kiriko Nananan (born 1972), manga artist, from Tsubame.
- Közi (born 1972), rock musician.
- Daisuke Hirakawa (born 1973), seiyu.
- Yoko Ishida (born 1973), singer, from Niigata City.
- Daisuke Sakaguchi (born 1973), seiyu, from Kashiwazaki.
- Hitomi Nabatame (born 1976), seiyu, from Sado Island.
- Tatsuyuki Nagai (born 1976), anime director.
- Ryō Hirohashi (born 1977), seiyu, from Nagaoka.
- Ayana Sasagawa (born 1983), seiyu.
- Makoto Ogawa (born 1987) and Koharu Kusumi (born 1992), members of pop girl-group Morning Musume, from, respectively, Kashiwazaki and Nagaoka.
Sports
- Haguroyama Masaji (1914–1969), sumo wrestler from Nakanokuchi, Niigata who was yokozuna for 12 years and three months; an all-time record.
- Shohei Baba (1938–1999), professional wrestler, from Sanjō.
- Sawao Kato (born 1946), winner of 12 Olympic medals in gymnastics
- Killer Khan (born 1947), professional wrestler, from Tsubame.
Notes
References
- Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005). Japan encyclopedia. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. 10-ISBN 0-674-01753-6; 13-ISBN 978-0-674-01753-5; OCLC 58053128
External links
- Official Niigata Prefecture website (requires Macromedia Flash plugin)
- Niigata JET (Japan Education and Teaching Programme) Website
- Enjoy Niigata Niigata prefecture tourism guide
 Niigata Prefecture
Niigata PrefectureNiigata (capital city) 
Cities Districts See also: Towns and villages by districtRegions and administrative divisions of  Japan
JapanRegions 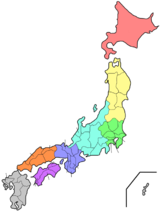
Prefectures Hokkaido Tōhoku Kantō Chūbu Kansai Chūgoku Shikoku Kyushu
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.



