- Kniest dysplasia
-
Kniest dysplasia Classification and external resources ICD-10 Q77.8 OMIM 156550 DiseasesDB 31947 Kniest dysplasia is an uncommon inherited disorder of bone growth. The condition is characterized by dwarfism, enlarged joints, and other skeletal abnormalities, and problems with vision and hearing. Kniest dysplasia is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI.
Contents
Presentation
People with this condition are short-statured from birth, with a short trunk, shortened limbs, and large joints. Adult height ranges from 107 to 147 cm (42 inches to 58 inches). Progressive joint enlargement and pain restrict joint movement, which limits activity and interferes with standing and walking. These joint problems can also lead to arthritis. Other skeletal signs include a progressively shortened spine due to spinal curvature (kyphoscoliosis and lumbar lordosis), severely flattened bones of the spine (platyspondyly), dumbbell-shaped bones in the arms and legs, long and knobby fingers, and occasionally a foot deformity called clubfoot.
People with Kniest dysplasia have round, flat faces with prominent and wide-set eyes. Some infants are born with an opening in the roof of the mouth (a cleft palate). Infants may also have breathing problems due to weakness of the windpipe. Severe nearsightedness (myopia) is common, as are other eye problems that can lead to blindness. Hearing loss resulting from recurrent ear infections is also possible.
Genetics
Kniest dysplasia is one of a spectrum of skeletal disorders caused by mutations in the COL2A1 gene. The protein made by this gene forms type II collagen, a molecule found mostly in cartilage and in the clear gel that fills the eyeball (the vitreous). Type II collagen is essential for the normal development of bones and other Connective Tissues. Mutations in the COL2A1 gene that cause Kniest dysplasia interfere with the assembly of type II collagen molecules, which prevents bones from developing properly and causes the signs and symptoms of the disorder.
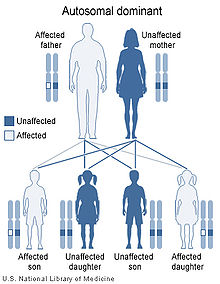
Kniest dysplasia is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means only one copy of the altered gene is necessary to cause the disorder.
Eponynm
It is named for Wilhelm Kniest.[1]
References
This article incorporates public domain text from The U.S. National Library of Medicine
Genetic disorder, extracellular: scleroprotein disease (excluding laminin and keratin) Collagen disease COL1: Osteogenesis imperfecta · Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, types 1, 2, 7
COL2: Hypochondrogenesis · Achondrogenesis type 2 · Stickler syndrome · Marshall syndrome · Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita · Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Strudwick type · Kniest dysplasia (see also C2/11)
COL3: Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, types 3 & 4 (Sack–Barabas syndrome)
COL4: Alport syndrome
COL5: Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, types 1 & 2
COL6: Bethlem myopathy · Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy
COL7: Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica · Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa · Bart syndrome · Transient bullous dermolysis of the newborn
COL8: Fuchs' dystrophy 1
COL9: Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia 2, 3, 6
COL10: Schmid metaphyseal chondrodysplasia
COL11: Weissenbacher–Zweymüller syndrome · Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (see also C2/11)
COL17: Bullous pemphigoidLaminin Junctional epidermolysis bullosa · Laryngoonychocutaneous syndromeOther Congenital stromal corneal dystrophy · Raine syndrome · Urbach–Wiethe disease · TECTA (DFNA8/12, DFNB21)Categories:- Congenital disorders
- Skeletal disorders
- Autosomal dominant disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.