- Dichlorocarbene
-
Dichlorocarbene 
 DichlorocarbeneSystematic nameDichloromethylideneOther namesCarbon(II) chloride
DichlorocarbeneSystematic nameDichloromethylideneOther namesCarbon(II) chloride
Carbon dichloride
Dichloromethylene
Carbonous chloride
Dichloro-λ2-methaneIdentifiers CAS number 1605-72-7 
PubChem 6432145 
ChemSpider 4937404 
MeSH Dichlorocarbene ChEBI CHEBI:51370 Beilstein Reference 1616279 Gmelin Reference 200357 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [C](Cl)Cl
- InChI=1/CCl2/c2-1-3
Key: PFBUKDPBVNJDEW-UHFFFAOYAT
Properties Molecular formula CCl2 Molar mass 82.92 g mol−1 Hazards Main hazards Highly reactive Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references Dichlorocarbene is a carbene commonly encountered in organic chemistry. This reactive intermediate with chemical formula CCl2 is easily available by reaction of chloroform and a base such as potassium t-butoxide [1] or sodium hydroxide dissolved in water. A phase transfer catalyst, for instance benzyltriethylammonium bromide, is added to facilitate the migration of the hydroxide in the organic phase.
Contents
Preparation
Other dichlorocarbene precursors are ethyl trichloracetate when reacted with sodium in methanol. [2] and phenyl(trichloromethyl)mercury by thermal decomposition [3] Dichlorodiazirine is an experimental dichlorocarbene precursor [4]. It is stable in the dark at room temperature and decomposes into the carbene and nitrogen gas by photolysis.
Dichlorocarbene from dichloroaziridine [5] Dichlorocarbene can also be obtained by reaction of carbon tetrachloride with elemental magnesium with ultrasound chemistry [6]. This method is tolerant to esters and carbonyl compounds because it does not involve strong base.
Reactions
Dichlorocarbene reacts with alkenes in a formal [1+2]cycloaddition to form geminal dichlorocyclopropanes which can subsequently be reduced to proper cyclopropanes or hydrolyzed to a cyclopropanone in a gem halide hydrolysis. The preparation of dichlorocarbene from chloroform and its utility in synthesis was discovered by William von Eggers Doering in 1954 [7] based on the functionalization of cyclohexene.
Dichlorocarbene formation and reaction with cyclohexene In the Reimer–Tiemann reaction dichlorocarbene reacts with phenol to salicylaldehyde.
History
Dichlorocarbene as a reactive intermediate was first proposed by Anton Geuther in 1862 who viewed chloroform as CCl2.HCl [8] and again by Hine in 1950 [9]. Dichlorocarbene was first trapped by Doering in 1954.
Related reactions
The Doering–LaFlamme carbon chain extension[10] describes the conversion of alkenes to allenes (a chain extension) with magnesium or sodium metal through initial reaction of the alkene with dichlorocarbene. The same sequence is incorporated in the Skattebøl rearrangement to cyclopentadienes. Dichlorocarbene also features in the Reimer–Tiemann reaction. Closely related is the more reactive dibromocarbene CBr2.
Chlorocarbene
The related chlorocarbene (ClHC) can be generated from methyllithium and dichloromethane. It has been used in the synthesis of spiropentadiene.
External links
References
- ^ Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 5, p.874 (1973); Vol. 41, p.76 (1961).Online Article
- ^ Organic Syntheses, , Coll. Vol. 6, p.731 (1988); Vol. 54, p.11 (1974).Online Article
- ^ Organic Syntheses, , Coll. Vol. 5, p.969 (1973); Vol. 46, p.98 (1966).Online Article
- ^ Dichlorodiazirine: A Nitrogenous Precursor for Dichlorocarbene Gaosheng Chu, Robert A. Moss, and Ronald R. Sauers J. Am. Chem. Soc., 127 (41), 14206 -14207, 2005 doi:10.1021/ja055656c
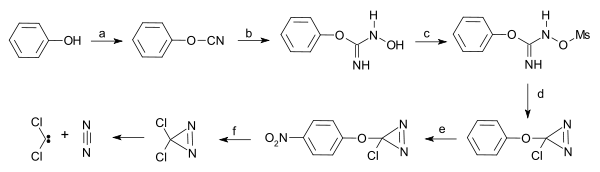
- ^ a) Starting from phenol reaction with cyanogen bromide to phenyl cyanate b) hydroxylamine reaction to the N-hydroxy-O-phenylisourea c) elevate hydroxyl group to leaving group by reaction with mesyl chloride to the mesylate d) intramolecular ring closure with sodium hypochlorite to the aziridine e) nitration with nitronium tetrafluoroborate f) nucleophilic substitution with caesium chloride, tetrabutylammonium chloride in ionic liquid
- ^ A Facile Procedure for the Generation of Dichlorocarbene from the Reaction of Carbon Tetrachloride and Magnesium using Ultrasonic Irradiation Haixia Lin, Mingfa Yang, Peigang Huang and Weiguo Cao Molecules 2003, 8, 608-613 Online Article
- ^ The Addition of Dichlorocarbene to Olefins W. von E. Doering and A. Kentaro Hoffmann J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1954; 76(23) pp 6162 - 6165; doi:10.1021/ja01652a087
- ^ Ueber die Zersetzung des Chloroforms durch alkoholische Kalilösung Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie Volume 123, Issue 1, Date: 1862, Pages: 121-122 A. Geuther doi:10.1002/jlac.18621230109
- ^ Carbon Dichloride as an Intermediate in the Basic Hydrolysis of Chloroform. A Mechanism for Substitution Reactions at a Saturated Carbon Atom Jack Hine J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1950, 72 (6), pp 2438–2445 doi:10.1021/ja01162a024
- ^ A two-step of synthesis of allenes from olefins Tetrahedron, Volume 2, Issues 1-2, 1958, Pages 75-79 W. von E. Doering and P. M. LaFlamme doi:10.1016/0040-4020(58)88025-4
Categories:- Carbenes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.