- Muscles of tongue
-
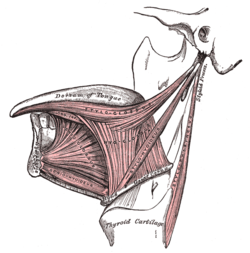
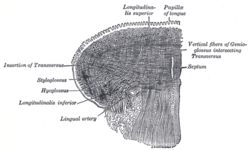
Muscles of tongue Lateral view of the tongue, with extrinsic muscles highlighted. Coronal section of tongue, showing intrinsic muscles Latin musculi linguae Origin Insertion Artery Nerve Actions The muscles of tongue can be divided into intrinsic and extrinsic groups.
The intrinsic muscles lie entirely within the tongue, while the extrinsic muscles attach the tongue to other structures.
The extrinsic muscles reposition the tongue, while the intrinsic muscles alter the shape of the tongue for talking and swallowing.
Extrinsic muscles
Extrinsic tongue muscles, by definition, originate from structures outside the tongue and insert into the tongue. The four paired extrinsic muscles protrude, retract, depress, and elevate the tongue:
Muscle From Nerve Function Genioglossus muscle mandible hypoglossal nerve protrudes the tongue as well as depressing its center. Hyoglossus muscle hyoid bone hypoglossal nerve depresses the tongue. Styloglossus muscle styloid process hypoglossal nerve elevates and retracts the tongue. Palatoglossus muscle palatine aponeurosis pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve depresses the soft palate, moves the palatoglossal fold towards the midline, and elevates the back of the tongue. Intrinsic muscles
Four paired intrinsic muscles of the tongue originate and insert within the tongue, running along its length. These muscles alter the shape of the tongue by: lengthening and shortening it, curling and uncurling its apex and edges, and flattening and rounding its surface.[1]
- The superior longitudinal muscle runs along the superior surface of the tongue under the mucous membrane, and elevates, assists in retraction of, or deviates the tip of the tongue. It originates near the epiglottis, the hyoid bone, from the median fibrous septum.
- The inferior longitudinal muscle lines the sides of the tongue, and is joined to the styloglossus muscle.
- The verticalis muscle is located in the middle of the tongue, and joins the superior and inferior longitudinal muscles.
- The transversus muscle divides the tongue at the middle, and is attached to the mucous membranes that run along the sides.
References
- ^ Drake, R. et al. Gray's Anatomy for Students, Elsevier, 2005. ISBN 0-443-06612-4
List of muscles of head and neck: the head (TA A04.1, GA 4.378) Extraocular (CN III, IV, VI) oblique (inferior, superior) · rectus (superior, inferior, medial, lateral) · levator palpebrae superioris (superior tarsal)Mastication (CN V3) masseter · temporalis (sphenomandibularis) · pterygoid (lateral, medial)
fascia: Masseteric fascia · Temporal fascia · Deep portion: cementomaxillary tendon · Superficial portion: cementomandibular tendonFacial (CN VII) levator anguli oris · levator labii superioris · zygomaticus (major, minor)
orbicularis oris · risorius · buccinator
depressor anguli oris · depressor labii inferioris · mentalisPalate/fauces (CN IX, X, XI)
(except TVP=V3)veli palatini (tensor, levator) · musculus uvulae · palatopharyngeus (to pharynx) · palatoglossus (to tongue)Tongue (CN XII) extrinsic (genioglossus, hyoglossus/chondroglossus, styloglossus, and palatoglossus) · intrinsic (superior longitudinal, inferior longitudinal, transverse, vertical)Head and neck anatomy, digestive system: Mouth anatomy (TA A05.1–2, TH H3.04.01, GA 11.1110–2, 1125–1141) Mouth Lip (Upper, Lower, Vermilion border, Frenulum of lower lip, Labial commissure of mouth, Philtrum)
Cheek (Buccal fat pad)Interdental papilla · Gingival sulcus · Gingival margin · Free gingival margin · Gingival fibers · Junctional epithelium · Mucogingival junction · Sulcular epithelium · Stippling
Periodontium: Cementum · Gingiva · Periodontal ligamentTeethsee tooth anatomydorsum (Taste bud, Median sulcus, Terminal sulcus, Foramen cecum, Lingual tonsils) · underside (Frenulum, Fimbriated fold, Sublingual caruncle) · Anterior · Posterior · Glossoepiglottic folds · Lingual septumOro-pharynx/
faucesCategories:- Tongue
- Muscles of the head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.