- Conquest of Tunis (1574)
-
For the capture of Tunis in 1943, see Operation Vulcan.
Conquest of Tunis Part of the Ottoman-Habsburg wars 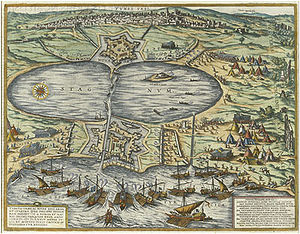
The Ottoman fleet attacking Tunis at La Goulette in 1574.Date 1574 Location Tunis Result Ottomans obtain Tunis Belligerents  Spanish Empire
Spanish Empire Ottoman Empire
Ottoman EmpireCommanders and leaders  Philip II of Spain
Philip II of Spain Selim II
Selim IIStrength Total men: 7,000 250-300 warships
Total men: 100,000Casualties and losses 6,700 killed, 300 prisoners. Unknown The Conquest of Tunis in 1574 marked the final conquest of Tunis by the Ottoman Empire over the Spanish Empire. This was an event of great significance as it decided that North Africa would be under Muslim rather than Christian rule, ended the Spanish Conquista of Northern Africa started under Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon.[1] The capture of Tunis in 1574 "sealed the Ottoman domination of the eastern and central Maghrib".[2]
Contents
Background
Tunis had initially been conquered by the Ottomans under Hayreddin Barbarossa in the Conquest of Tunis (1534). However, but the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V had recaptured it in the Conquest of Tunis in 1535. He established a garrison and a vassal ruler in the person of the Hafsid dynasty ruler Al-Hasan. The Bey of Algiers Uluj Ali Pasha captured Tunis in 1569 for the Ottoman Empire, but in the aftermath of the 1571 Christian victory at the Battle of Lepanto, John of Austria managed to take Tunis in October 1573.[1][3]
Capture of Tunis
In 1574, William of Orange and Charles IX of France, through his pro-Huguenot ambassador François de Noailles, Bishop of Dax, tried to obtain the support of the Ottoman ruler Selim II in order to open a new front against the Spanish king Philip II.[4] Selim II sent his support through a messenger, who endeavoured to put the Dutch in contact with the rebellious Moriscos of Spain and the pirates of Algiers.[5] Selim also sent a great fleet to attack Tunis in the Autumn of 1574, thus succeeding in reducing Spanish pressure on the Dutch.[5]
In the Battle of La Goleta, Selim II mustered a fleet of between 250 and 300 warships, with about 75,000 men.[6] The Ottoman fleet was commanded by Sinān Pasha and Alūj Ali.[7] The Ottoman fleet combined with troops sent by the governors of Algiers, Tripoli and Tunis, for a combined strength of about 100,000.[7] The army attacked Tunis and La Goleta, the presidio of La Goleta, defended by 7,000 men, falling on 24 August 1574. The last Christian troops in a small fort opposite Tunis surrendered on 3 September 1574.[7]
 Sinān Pasha, an Italian Muslim, led the Ottoman capture of Tunis.
Sinān Pasha, an Italian Muslim, led the Ottoman capture of Tunis.
John of Austria attempted to relieve the siege with a fleet of galleys from Naples and Sicily but failed due to storms.[8] The Spanish crown, being heavily involved in the Netherlands and short of funds was unable to help significantly.[8]
Cervantes participated to these events as a soldier, and was among the troops of Don Juan of Austria which tried to rescue the city.[9] He claims that the Ottomans led 22 assaults against the fort of Tunis, losing 25,000 men, while only 300 Christians survived.[9] He wrote about the battle:
"If Goleta and the fort, put together, held barely 7,000 soldiers, how could such a small force, however resolute, come out and hold its own against so huge an enemy army. And how can you help losing a stronghold that is not relieved, and especially when it is surrounded by a stubborn and very numerous army, and on its own ground?"—Cervantes, DQ I, 39.[9]Abd al-Malik, the future Moroccan King, participated to the 1574 conquest of Tunis on the side of the Ottomans.[10]
Gabrio Cervellón was the commander of the fort of Tunis. The general of La Goleta, Don Pedro Portocarerro was taken as a captive to Constantinople, but died on its way.[9] The captured soldiers were employed as slaves on galleys.[9]
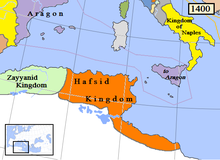 The capture of Tunis gave the territories of the Hafsid dynasty to the Ottoman Empire.
The capture of Tunis gave the territories of the Hafsid dynasty to the Ottoman Empire.
The battle marked the final establishment of Ottoman rule in Tunis, putting an end to the Hafsid dynasty and the Spanish presence in Tunis.[3]
The success of the Turks in the battle of Goleta managed in reducing Spanish pressure on the Dutch, and leading to negotiations at the Conference of Breda.[5] After the death of Charles IX in May 1574 however, contacts weakened, although the Ottomans are said to have supported the 1575-1576 revolt, and establish a Consulate in Antwerp (De Griekse Natie). The Ottomans made a truce with Spain, and shifted their attention to their conflict with Persia in the Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–1590).[5] The Spanish crown fell into bankruptcy on 1 September 1575.[8]
See also
- Siege of Castelnuovo
- Islam and Protestantism
- Franco-Ottoman alliance
Notes
Balearics (1501) – Algiers (1516) – Tlemcen – Mohács (1526) – Hungary (1527–1528) – Algiers (1529) – Formentera – Balkans – Vienna (1529) – Little War (1530–1552) – Coron – Tunis (1534) – Tunis (1535) – Mahon – Osijek – Preveza – Castelnuovo – Alborán – Algiers (1541) – Nice – Mahdiye – Gozo – Tripoli – Eger – Ponza – Corsica – Oran (1556) – Bougie – Balearics (1558) – Mostaganem – Djerba – Orán and Mers-el-Kebir – Malta – Aceh – Szigetvár – Lepanto – Tunis (1574) – Fez – Long War – Cape Corvo – Cape Celidonia – 1663-1664 – Great Turkish War – 1716-1718 – 1737–1739 – 1787–1791- ^ a b The new Cambridge modern history R. B. Wernham, p.354
- ^ The Regency of Tunis and the Ottoman Porte, 1777-1814: Army and Government of a North-African Ottoman Eyâlet at the End of the Eighteenth Century by Asma Moalla, Routledge, 2004 ISBN 0415297818, p.3 [1]
- ^ a b The Encyclopedia of world history Peter N. Stearns, William Leonard Langer, p.366 [2]
- ^ Parker, p.61
- ^ a b c d Parker, p.61
- ^ Cervantes in Algiers by María Antonia Garcés, p.220
- ^ a b c Garcés, p.220
- ^ a b c Garcés, p.221
- ^ a b c d e Garcés, p.222
- ^ The last great Muslim empires: history of the Muslim world by Frank Ronald Charles Bagley, Hans Joachim Kissling p.103ff
References
- Geoffrey Parker, Lesley M. Smith The General crisis of the seventeenth century Routledge, 1978 ISBN 0710088655
- María Antonia Garcés Cervantes in Algiers: A Captive's Tale Vanderbilt University Press, 2005 ISBN 0826514707
 Major Ottoman siegesPrusa (1326) • Nicaea (1331) • Nicomedia (1333) • Sofia (1385) • Tarnovo (1393) • Constantinople (1422) • Thessalonica (1422) • Svetigrad (1448) • Constantinople (1453) • Belgrade (1456) • Kruje (1478) • Rhodes (1480) • Otranto (1481) • Cairo (1517) • Rhodes (1522) • Algiers (1529) • Vienna (1529) • Güns (1532) • Tunis (1534) • Baghdat (1534) • Klis (1537) • Corfu (1537) • Diu (1538) • Aden (1538) • Castelnuovo (1539) • Buda (1541) • Nice (1543) • Esztergom (1543) • Van (1547) • Tripoli (1551) • Muscat (1552) • Hormuz (1552) • Eger (1552) • Oran (1556) • Oran (1563) • Malta (1565) • Szigetvar (1566) • Tunis (1574) • Gvozdansko (1578) • Sisak (1593) • Baghdad (1638) • Candia (1669) • Kamenets (1672) • Vienna (1683) • Belgrade (1739)Categories:
Major Ottoman siegesPrusa (1326) • Nicaea (1331) • Nicomedia (1333) • Sofia (1385) • Tarnovo (1393) • Constantinople (1422) • Thessalonica (1422) • Svetigrad (1448) • Constantinople (1453) • Belgrade (1456) • Kruje (1478) • Rhodes (1480) • Otranto (1481) • Cairo (1517) • Rhodes (1522) • Algiers (1529) • Vienna (1529) • Güns (1532) • Tunis (1534) • Baghdat (1534) • Klis (1537) • Corfu (1537) • Diu (1538) • Aden (1538) • Castelnuovo (1539) • Buda (1541) • Nice (1543) • Esztergom (1543) • Van (1547) • Tripoli (1551) • Muscat (1552) • Hormuz (1552) • Eger (1552) • Oran (1556) • Oran (1563) • Malta (1565) • Szigetvar (1566) • Tunis (1574) • Gvozdansko (1578) • Sisak (1593) • Baghdad (1638) • Candia (1669) • Kamenets (1672) • Vienna (1683) • Belgrade (1739)Categories:- Military history of Tunisia
- Tunis
- 16th century in Africa
- Conflicts in 1574
- Battles involving the Ottoman Empire
- Battles involving Spain
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


