- Methyl isobutyl ketone
-
Methyl isobutyl ketone  4-Methylpentan-2-oneOther namesIsopropylacetone, Hexone, Isobutyl methyl ketone, 4-Methylpentan-2-one, 4-methyl-2-pentanone, 4-methylpentan-2-one, 2-methyl-4-pentanone, 2-methylpropyl methyl ketone, 4-methyl-2-oxopentane, MIK, isobutylmethyl ketone, MIBK, isohexanone
4-Methylpentan-2-oneOther namesIsopropylacetone, Hexone, Isobutyl methyl ketone, 4-Methylpentan-2-one, 4-methyl-2-pentanone, 4-methylpentan-2-one, 2-methyl-4-pentanone, 2-methylpropyl methyl ketone, 4-methyl-2-oxopentane, MIK, isobutylmethyl ketone, MIBK, isohexanoneIdentifiers CAS number 108-10-1 
KEGG C19263 
RTECS number SA9275000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(C)CC(=O)C
Properties Molecular formula C6H12O Molar mass 100.16 g/mol Appearance colorless liquid Density 0.802 g/mL, liquid Melting point -84.7 °C, 188 K, -120 °F
Boiling point 117-118 °C, 390-391 K, 243-244 °F
Solubility in water 1.91 g/100 mL (20 °C) Refractive index (nD) 1.3958 Viscosity 0.58 cP at 20.0 °C Structure Dipole moment 4.2 D Hazards EU classification Flammable (F)
Harmful (Xn)R-phrases R11, R20, R36/37, R66 S-phrases (S2), S9, S16, S29 NFPA 704 Flash point 14 °C Autoignition
temperature449 °C Related compounds Related ketones Methyl isopropyl ketone
2-Pentanone
Diisobutyl ketoneRelated compounds 2-Methylpentan-4-ol  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK) is the organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCH2C(O)CH3. This colourless liquid, a ketone, is widely used as a solvent.
Contents
Production
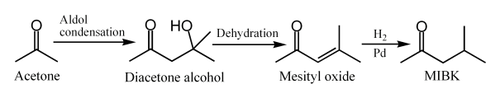
Methyl isobutyl ketone is manufactured from acetone via a three-step process. Firstly acetone undergoes an aldol condensation to give diacetone alcohol, which readily dehydrates to give mesityl oxide. Mesityl oxide can then be hydrogenated to give MIBK:
Modern processes combine these three steps into one.[1]
Several million kilograms are produced annually.[2]
Uses
MIBK is used as a solvent for nitrocellulose, lacquers, and certain polymers and resins.[2]
Precursor to 6PPD
Another major use is as a precursor to N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N'-phenyl-p-phenylene diamine (6PPD), an antiozonant used in tires. 6PPD is prepared by reductive coupling of MIBK with 4-aminodiphenylamine.[citation needed]
Solvent and niche applications
Unlike the other common ketone solvents, acetone and MEK, MIBK has quite low solubility in water, making it useful for liquid-liquid extraction. It has a similar polarity to ethyl acetate, but greater stability towards aqueous acid and base. It can be used to extract gold, silver and other precious metals from cyanide solutions, such as those found at gold mines, to determine the levels of those dissolved metals. Diisobutyl ketone (DIBK), a related lipophilic ketone, is also used for this purpose. Methyl isobutyl ketone is also used as a denaturing agent for denatured alcohol. When mixed with water or isopropyl alcohol MIBK serves as a developer for PMMA electron beam lithography resist. MIBK is used as a solvent for CS in the preparation of the CS spray used currently by British police forces.[3]
References
- ^ [1], Uhde Technology Profile: MIBK
- ^ a b Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, “Acetone” in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.
- ^ Peter J Gray; Stark, MM; Gray, P. J; Jones, G R. N (2000). "Is CS spray dangerous? : CS is a particulate spray, not a gas" (Response to editorial). BMJ 321 (7252): 26. doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7252.46. PMC 1127688. PMID 10939811. http://bmj.bmjjournals.com/cgi/eletters/320/7233/458.
External links
Categories:- Hazardous air pollutants
- Ketones
- Ketone solvents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.