- Raunkiær plant life-form
The Raunkiær system is a system for categorising plants using life-form categories, devised by
Christen C. Raunkiær . It was first proposed in a talk to the "Danish Botanical Society" in 1904 and briefly described in the society's journalBotanisk Tidsskrift [Raunkiær, C. (1904) Om biologiske Typer, med Hensyn til Planternes Tilpasninger til at overleve ugunstige Aarstider.Botanisk Tidsskrift 26, p. XIV.] Ch. 1 in Raunkiær (1934): Biological types with reference to the adaption of plants to survive the unfavourable season, p. 1.] . A fuller account appeared in French the following year [Raunkiær, C. (1905) Types biologiques pour la géographie botanique. Oversigt over DetKongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab s Forhandlinger, 1905, 347-438.] . Raunkiær elaborated further on the system and published this in Danish in 1907 [Raunkiær, C. (1907) Planterigets Livsformer og deres Betydning for Geografien. Gyldendalske Boghandel - Nordisk Forlag, København and Kristiania. 132 pp.] Ch. 2 in Raunkiær (1934): The life-forms of plants and their bearings on geography, p. 2-104.] . The original note and the 1907 paper were much later translated to English and published with Raunkiær's collected works [Raunkiær, C. (1934) The Life Forms of Plants and Statistical Plant Geography, being the collected papers of C. Raunkiær. Oxford University Press, Oxford. Reprinted 1978 (ed. by Frank N. Egerton), Ayer Co Pub., in the "History of Ecology Series". ISBN 0405104189] .Raunkiær's life-form scheme has subsequently been revised and modified by various authors [Müller-Dombois, D. & H. Ellenberg (1974) Aims and methods in vegetation ecology. John Wiley & Sons, New York. Reprint 2003, Blackburn Press, ISBN 1930665733] [Shimwell, D.W. (1971) The Description and Classification of Vegetation. Sidgwick & Jackson, London.] , but the main structure has survived.
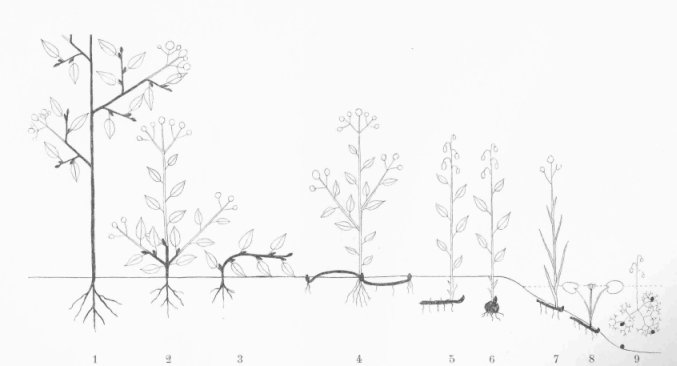
thumb|400px|right|Raunkiær's life forms:">
1. Phanerophyte.
2-3. Chamaephytes.
4. Hemicryptophyte.
5-6. Geophytes (cryptophytes).
7. Helophyte.
8-9. Hydrophytes.
Therophyte and epiphyte not shownThe subdivisions of the Raunkiær system are based on the location of the plant's growth-point (
bud ) during seasons with adverse conditions (cold seasons, dry seasons):;Phanerophyte s : Projecting into the air on stems – normally woody perennials - with resting buds more than 25 cms above soil level, e.g.tree s andshrub s, but alsoepiphytes , which Raunkiær separated out as a special group in later versions of the system. May be further subdivided according to plant height in "megaphanerophytes", "mesophanerophytes" and "nanophanerophytes" and other characterssuch as duration of leaves (evergreen or deciduous), presence of covering bracts on buds, succulence and epiphytism.;Chamaephyte s : Buds on persistent shoots near the ground – woody plants with perennating buds borne close to the ground, no more than 25 cms above soil surface, e.g.bilberry andperiwinkle .;Hemicryptophyte s : Buds at or near the soil surface , e.g.daisy ,dandelion .:; Protohemicryptophytes : only stem leaves:; Partial rosette plants : both stem and basal rosette leaves:; Rosette plants : only basal rosette leaves;Cryptophyte s : Below ground or under water - with resting buds lying either beneath the surface of the ground as a rhizome, bulb, corm, etc., or a resting bud submerged under water. Cryptophytes are divided into 3 groups::; Geophytes : Resting in dry ground, e.g.crocus ,tulip . May be further subdivided into rhizome, stem-tuber, root-tuber, bulb and root geophytes. :; Helophytes : Resting in marshy ground, e.g.reedmace ,marsh-marigold . :; Hydrophytes : Resting by being submerged under water, e.g.water-lily ,frogbit . ;Therophyte s : Annual plants which survive the unfavourable season in the form of seeds and completes its life-cycle during favourable seasons.Annual species are therophytes. Many desert plants are by necessity therophytes.;Aerophyte s : New addition to the Raunkiaer lifeform classification. Plant that obtains moisture (though not through haustorium), and nutrients from the air and rain; usually grows on other plants but not parasitic on it [ [http://www.jstor.org/pss/3237161 Galán de Mera, A., M. A. Hagen & J. A. Vicente Orellana (1999) Aerophyte, a New Life Form in Raunkiaer's Classification? Journal of Vegetation Science 10 (1): 65-68] ] .References
ee also
*
Plant life-form
*Christen C. Raunkiær
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.